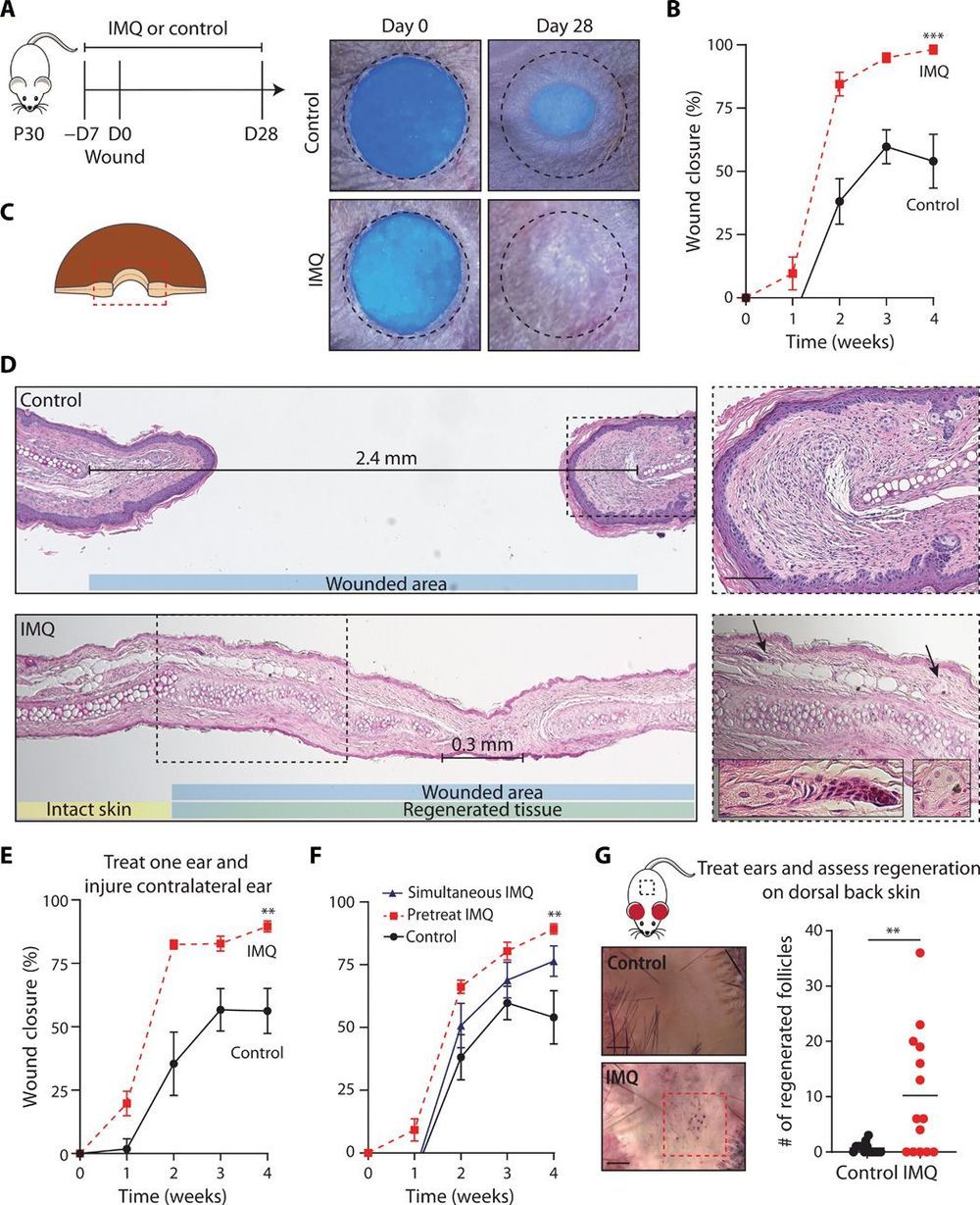
Excerpts of talks and interviews on biological radical life extension given by some of the world top longevity scientists.
The compendium includes thoughts, predictions and claims made by the following longevity leaders (listed in alphabetical order):
Aubrey de Grey, PhD: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aubrey_de_Grey
David Sinclair, PhD: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/David_Andrew_Sinclair
George Church, PhD: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/George_Church_(geneticist)
Juan Carlos Izpisúa Belmonte, PhD: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Juan_Carlos_Izpisua_Belmonte
María Blasco Marhuenda, PhD: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mar%C3%ADa_Blasco_Marhuenda
I added embedded subtitles in English when scientists speak in Spanish.
For subtitles in Spanish when scientists speak in English, just choose the option in Youtube to add the subtitles in Spanish I created.
These are some of my social media channels, you’re invited to keep in touch through any of them:
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/andresgrases/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/andres.grases
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/andgrabri/
Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/andresgrases
This is my own website which includes a digital library with more than 26.000 links and growing, organized in 19 main categories and many other sub-categories: https://transhumanplus.com/
Ahhh, and if you haven’t done so, please consider subscribing to my YouTube channel smile