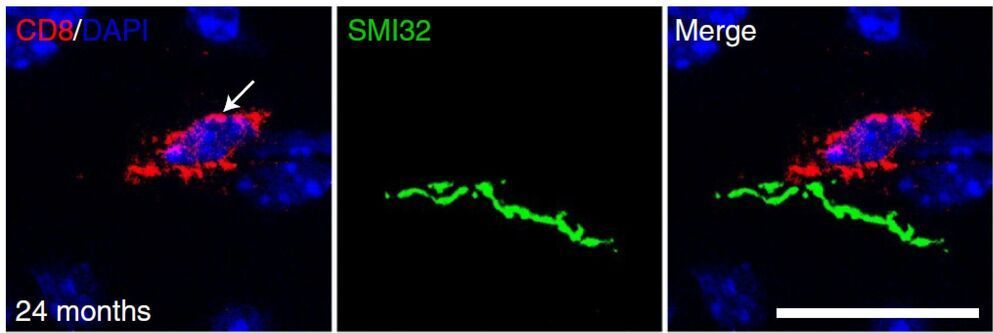
Aging is the biggest risk factor for perturbation of the nervous system, even in the absence of distinct disease or trauma. For yet unknown reasons, the impulse conducting, myelinated projections and synaptic connections between nerve cells are especially vulnerable to aging-related degeneration. These pathological alterations often manifest as cognitive, sensory, and motor decline in older adults and represent a serious socio-economic challenge.
Malactivation leads to damage
Scientists have long assumed that inflammation plays an important role in this process. Mal-or overactivation of distinct cells belonging to the innate immune system—the microglia—appears to promote damage of nerve fibers and synapses in the aging central nervous system (CNS). In a recent project, scientists of the University Hospital Würzburg have now discovered an important role of the adaptive immune system.