A longevity expert said he added years to his life with healthy morning habits like strength workouts, meditation, and drinking an anti-aging smoothie.




“The inevitability of death is what makes life worth living.” — Henry.
“Would we need to extend the years everyone should continue to be in the workforce, in order to pay for those not contributing?” — Marianne.
“Imagine you have people with all the prejudices they grew up with and they never die. Or you have someone who is a dictator and they get to live forever and be dictator forever. Or you have Congress where you have 80 and 90 year olds holding office forever but now they never die so nobody new can take over.” — Avram.
A couple minutes of your time for a little optimism.
Dr David Sinclair talks about no matter all the push backs and criticizes, he believes reverse aging therapy for human will be succeeded in this short clip.
David Sinclair is a professor in the Department of Genetics and co-director of the Paul F. Glenn Center for the Biology of Aging at Harvard Medical School, where he and his colleagues study sirtuins—protein-modifying enzymes that respond to changing NAD+ levels and to caloric restriction—as well as chromatin, energy metabolism, mitochondria, learning and memory, neurodegeneration, cancer, and cellular reprogramming.
Dr David Sinclair has suggested that aging is a disease—and that we may soon have the tools to put it into remission—and he has called for greater international attention to the social, economic and political and benefits of a world in which billions of people can live much longer and much healthier lives.
Dr David Sinclair is the co-founder of several biotechnology companies (Life Biosciences, Sirtris, Genocea, Cohbar, MetroBiotech, ArcBio, Liberty Biosecurity) and is on the boards of several others.

I wanted to test how well endowed is ChatGPT in the field of Longevity. For that matter I asked the following two questions: Which are the most promising therapies which are being developed to significantly extend healthy lifespan in humans using 4,000 characters (about maximum lenght to be readable in one page).
Which are the most promising therapies to achieve epigenetic cellular rejuvenation.
I created a two-page document in PDF with a screenshot of the responses for the two questions, so to show them exactly as they appeared in my laptop (no editing by me whatsoever).
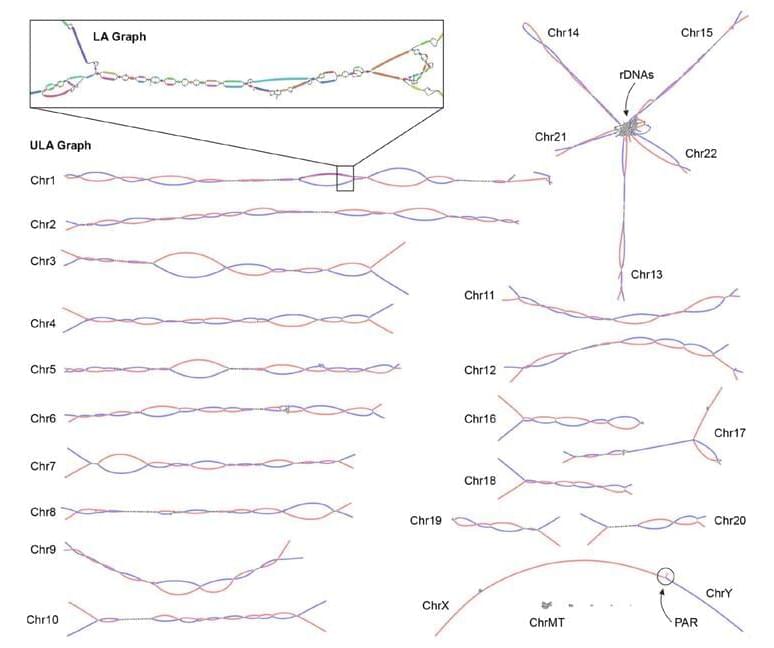
National Institutes of Health researchers have developed and released an innovative software tool to assemble truly complete (i.e., gapless) genome sequences from a variety of species.
This software, called Verkko, which means “network” in Finnish, makes the process of assembling complete genome sequences more affordable and accessible. A description of the new software was published today in Nature Biotechnology.
Verkko grew from assembling the first gapless human genome sequence, which was finished last year by the Telomere-to-Telomere (T2T) consortium, a collaborative project funded by the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI), part of NIH.
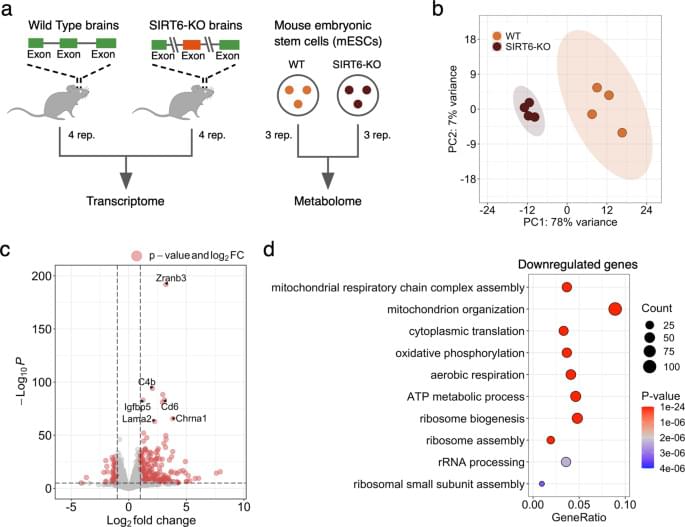
Though mitochondrial dysfunction is a known marker of aging and neurodegenerative diseases, the exact mechanism behind it remains unknown. Our study suggests that the decay of SIRT6 levels during aging [18] and in Alzheimer’s disease [18, 23, 46] could be a key mechanism causing the deterioration of mitochondrial functions. The changes induced by the SIRT6 knockout that we observe at the metabolite level support this claim: metabolites related to mitochondrial energy system pathways (in particular, OXPHOS and TCA cycle) are significantly overrepresented among differentially abundant metabolites. In line with the discussed mitochondrial dysfunction in aging, all these metabolites are downregulated in the SIRT6-KO samples. Importantly, the dramatic decline of one of them, NAD+, was also associated with pro-senescence mechanisms in various species [47, 48], as well as with limited neuroprotective activity of sirtuins [49].
Accordingly, the vast majority of differentially expressed mitochondria-related genes were downregulated in our gene expression analysis. As they were strongly enriched with mitochondrial respiratory chain complexes, we measured the mitochondrial membrane potential and mitochondrial content in SIRT6-KO cells because reduced gene expression might indicate the loss of mitochondria. Both measured characteristics were significantly decreased, validating the suggested impairment of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation and mitochondrial biogenesis in SIRT6-deficient brains. Interestingly, the average decrease of mtDNA gene expression (~19.7%) in SIRT6-KO was in good agreement with the corresponding reduction of mitochondrial content (21.8%), suggesting impaired mitochondrial biogenesis as a primary cause of the observed transcriptional dysregulation in mitochondria upon SIRT6 knockout.
Concordantly, the impaired membrane potential upon SIRT6-KO can be partially rescued by restoring SIRT3 and SIRT4 levels, which were significantly downregulated in SIRT6-deficient brains. Both of them are localized in mitochondria and impact mitochondrial pathways related to redox homeostasis and cellular metabolism [38] and have important roles in mitochondria metabolism ROS balance and lifespan [50,51,52]. The analysis of our and publicly available gene expression data [39] confirms that SIRT6 transcriptionally regulates SIRT3 and SIRT4. Our analysis further indicates that SIRT6 regulates mitochondrial gene expression through the transcription factor YY1. We have previously shown that SIRT6 and YY1 form a complex that regulates many shared target genes [24]. Our analysis of YY1 ChIP-seq data [53] suggests that SIRT6 and YY1 regulate mitochondrial processes coordinately.

Potentially huge. Effecting blood plasma via a pill. This is of course a mice experiment and they are working to see if the process happens in humans too.
Some wealthy elites prefer young blood plasma transfusions for anti-aging purposes. There are suggestions that the body’s organs are rejuvenated by young blood. However, a recent study from Columbia University in New York suggests that anti-inflammatory drugs can rejuvenate the body and possibly extend the human lifespan by decades, negating the need for blood transfusions to turn back the body’s clock.
According to Emmanuelle Passegué, Ph.D., director of the Columbia Stem Cell Initiative, who has been researching how blood changes with age, “an aging blood system, because it’s a vector for a lot of proteins, cytokines, and cells, has a lot of bad consequences for the organism,”

The Methuselah Foundation is a non-profit medical charity focused on extending the healthy human lifespan by making 90 the new 50 by 2030. Our goal is to accelerate results in the longevity field, as well as the biotechnology, regenerative medicine, life sciences sectors. We incubate and sponsor mission-relevant ventures, fund research, and support projects and prizes.
