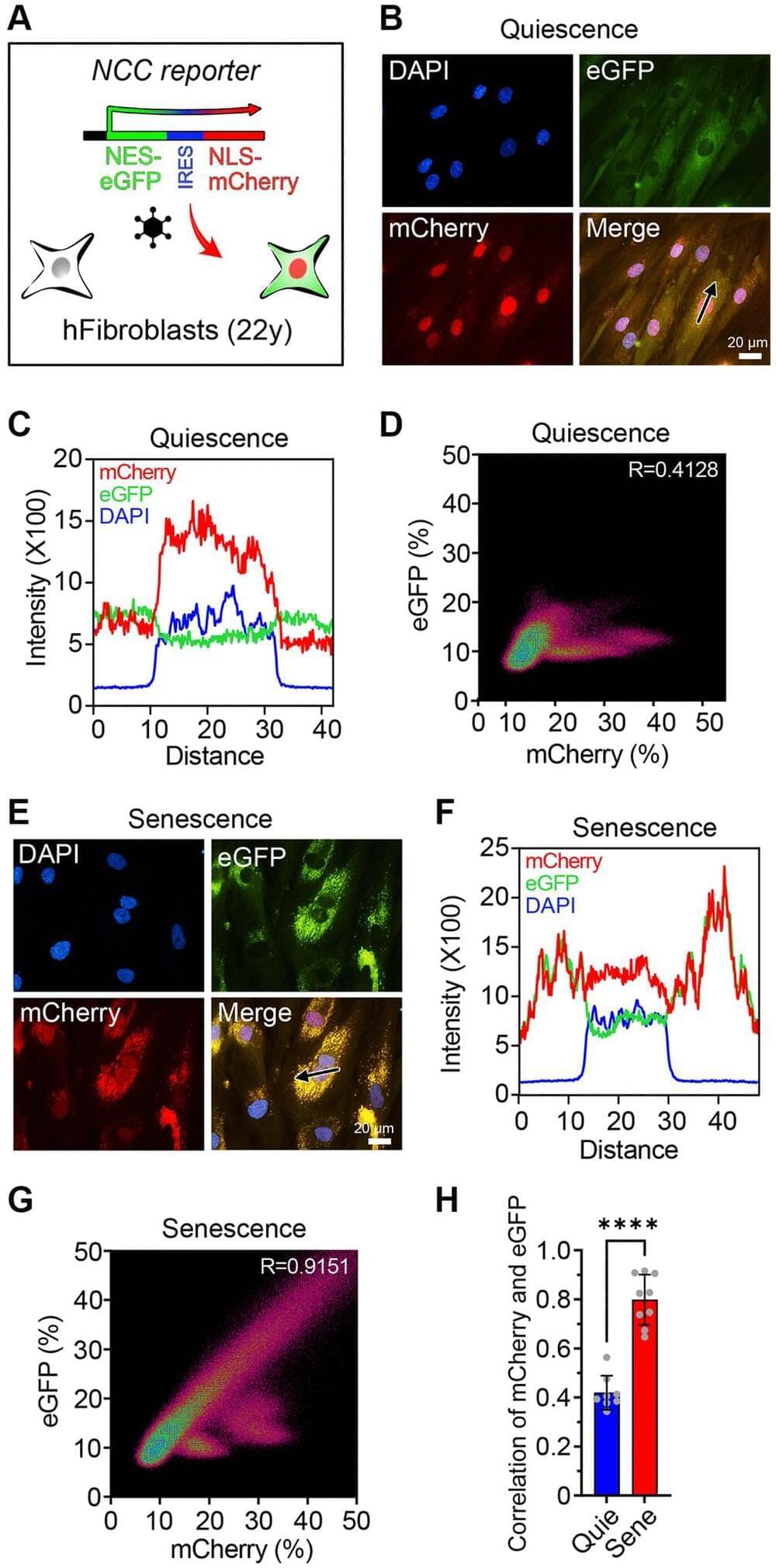
Cats already have 9 lives, but what if we could give them 18? Longevity research isn’t just benefiting humans: I looked into some supplements and products that may help you extend your cat’s lifespan, or at least their healthspan.
If you proudly share a house or apartment with one or more cats, chances are you want your precious pet to live a long and healthy life. In addition to getting the basics of diet, exercise, and safety right (basically, do the opposite of the cartoon Garfield), there are many cat longevity products out there that aim to increase your cat’s lifespan.
We’ve taken the time to explore some of them, and this comprehensive list of the top nine cat longevity products is a resource you can use to discover options that may keep that furry feline of yours not only healthy but also happy, energetic, and curious for many years to come.
Our list features cat nutrition products, including longevity cat food and joint care for cats products, as well as cat supplements, and some more unconventional cat health products like pet insurance. As always, we are highlighting high-quality, science-backed products that generally have research showing at least healthspan-, if not lifespan-, extending effects.