Researchers have discovered that T cells, which are white blood cells inside our bodies, can be reprogrammed to fight aging.


The fountain of youth has eluded explorers for ages.
Summary: Researchers found that T cells can be genetically reprogrammed to target and eliminate senescent cells, which contribute to aging-related diseases. By using CAR (chimeric antigen receptor) T cells in mice, they achieved significant health improvements including lower body weight, enhanced metabolism, and increased physical activity.
This groundbreaking approach, offering long-term effects from a single treatment, could revolutionize treatments for age-related conditions like obesity and diabetes, transcending the potential of CAR T cells beyond their current use in cancer therapy.
Join us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhDDiscount Links: Telomere, Epigenetic Testing: https://trudiagnostic.com/?irclickid=U-s3Ii2r7x…

I hope more research is fruitful because I got the doctor’s results from my recent colonoscopy. The polyps are benign but pre cancerous. I go back in 5 years and I’ll be eating healthier and exercising. I gotta admit I don’t feel great but it could be something I ate.
Scientists in China have demonstrated a new kind of antidepressant could also have the potential to restore the body’s ability to fight some types of cancer.
In strategic combination with anti-tumor drugs, the oral antidepressant ansofaxine hydrochloride appears to inhibit colon cancer cell growth in cell cultures and in mice, strengthening the immune system and inducing a form of programmed cell death.
Yet to be tested on humans, it’s unclear how the results will translate as an actual cancer treatment.

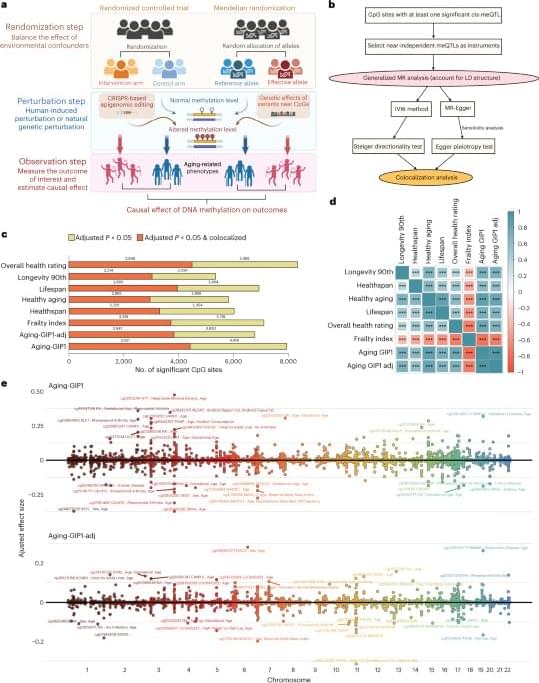
Aging is a common phenomenon among organisms, however, lifespan tends to vary across different species to a significant extent among vertebrates themselves. Aging occurs due to the gradual increase in DNA damage, disruption of cellular organelles, deregulation of protein function, disrupted metabolism and oxidative stress [1].
Longevity. Technology: The differences in lifespan are driven by trade-offs and evolutionary trajectories in the genomes of organisms. Age-specific selection also impacts allele (variations of a gene) frequencies in a population. This in turn impacts environment-specific mortality risk and disease susceptibility. Moreover, mutational processes are influenced by life history and age in both somatic and germline cells.
Now, a new review published in Trends in Genetics discusses recent advances in the evolution of aging at population, organismal and cellular scales.
Here we have a deathist vid. This fellow does run a good channel, cool bloke. But he seems to think longer life means you’ll just never be motivated and only the knowledge of death with get you moving in life. I did leave a comment.

This story is part of a series on the current progression in Regenerative Medicine. This piece discusses advances in Alzheimer’s therapy.
In 1999, I defined regenerative medicine as the collection of interventions that restore normal function to tissues and organs damaged by disease, injured by trauma, or worn by time. I include a full spectrum of chemical, gene, and protein-based medicines, cell-based therapies, and biomechanical interventions that achieve that goal.
An emerging combination of focused ultrasound therapy with a recently approved medication could be our best treatment for Alzheimer’s disease to date. In the New England Journal of Medicine, Dr. Ali Rezai and colleagues from West Virginia University describe an approach to reduce cerebral amyloid-beta load, a biomarker for neurodegeneration, in patients with Alzheimer’s. While in its preliminary stages, the combination treatment can potentially help thousands, if not millions, suffering from the disease in the near future.