It’s complicated. So we reached out to legal experts for some definitive answers.



On June 17, United States district court Judge Amy Berman Jackson approved an agreement between Binance. US, Binance, and the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), dismissing a previous temporary restraining order (TRO) that would freeze all Binance. US assets.
On June 14, Jackson said she would prefer the parties reach an agreement independently rather than have her rule. The sides reportedly reached an agreement on June 16.
“We are pleased to inform you that the Court did not grant the SEC’s request for a TRO and freeze of assets on our platform which was clearly unjustified by both the facts and the law,” Binance. US said on Twitter.
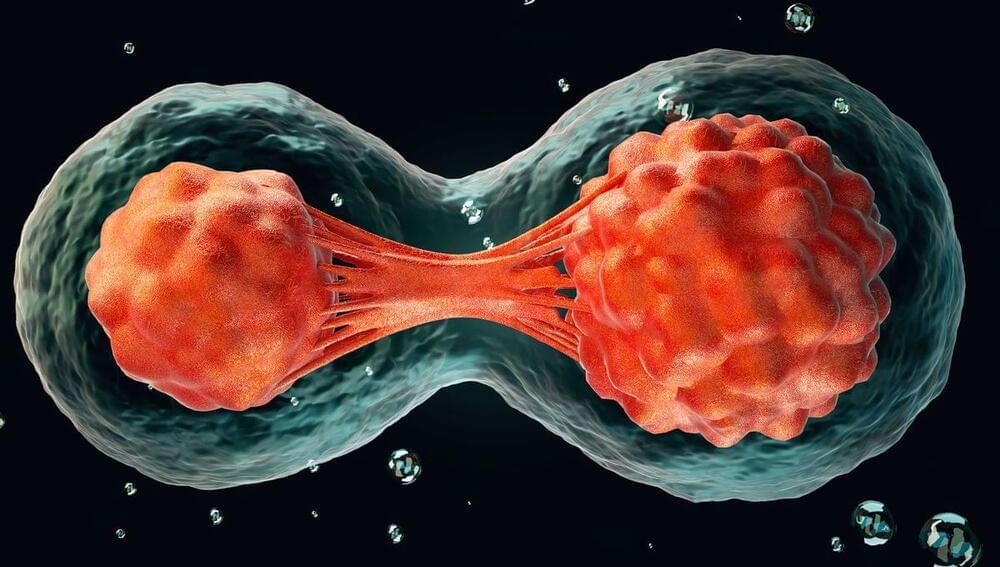
Synthetic human embryos – derived from stem cells without the need for eggs or sperm – have been created for the first time, scientists say. The structures represent the very earliest stages of human development, which could allow for vital studies into disorders like recurrent miscarriage and genetic diseases. But questions have been posed about the legal and ethical implications, as the pace of scientific discovery outstrips the legislation.
The breakthrough was reported by the Guardian newspaper following an announcement by Professor Magdalena Żernicka-Goetz, a developmental biologist at the University of Cambridge and Caltech, at the 2023 annual meeting of the International Society for Stem Cell Research. The findings have not yet been published in a peer-reviewed paper.
It’s understood that the synthetic structures model the very beginnings of human development. They do not yet contain a brain or heart, for example, but comprise the cells that would be needed to form a placenta, yolk sac, and embryo. Żernicka-Goetz told the conference that the structures have been grown to just beyond the equivalent of 14 days of natural gestation for a human embryo in the womb. It’s not clear whether it would be possible to allow them to mature any further.


A team of researchers in the United States and United Kingdom say they have created the world’s first synthetic human embryo-like structures from stem cells, bypassing the need for eggs and sperm.
These embryo-like structures are at the very earliest stages of human development: They don’t have a beating heart or a brain, for example. But scientists say they could one day help advance the understanding of genetic diseases or the causes of miscarriages.
The research raises critical legal and ethical questions, and many countries, including the US, don’t have laws governing the creation or treatment of synthetic embryos.
The experiments are the first of their kind and could lead to new advances in computing.
A team at the University of Chicago.
Founded in 1,890, the University of Chicago (UChicago, U of C, or Chicago) is a private research university in Chicago, Illinois. Located on a 217-acre campus in Chicago’s Hyde Park neighborhood, near Lake Michigan, the school holds top-ten positions in various national and international rankings. UChicago is also well known for its professional schools: Pritzker School of Medicine, Booth School of Business, Law School, School of Social Service Administration, Harris School of Public Policy Studies, Divinity School and the Graham School of Continuing Liberal and Professional Studies, and Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering.
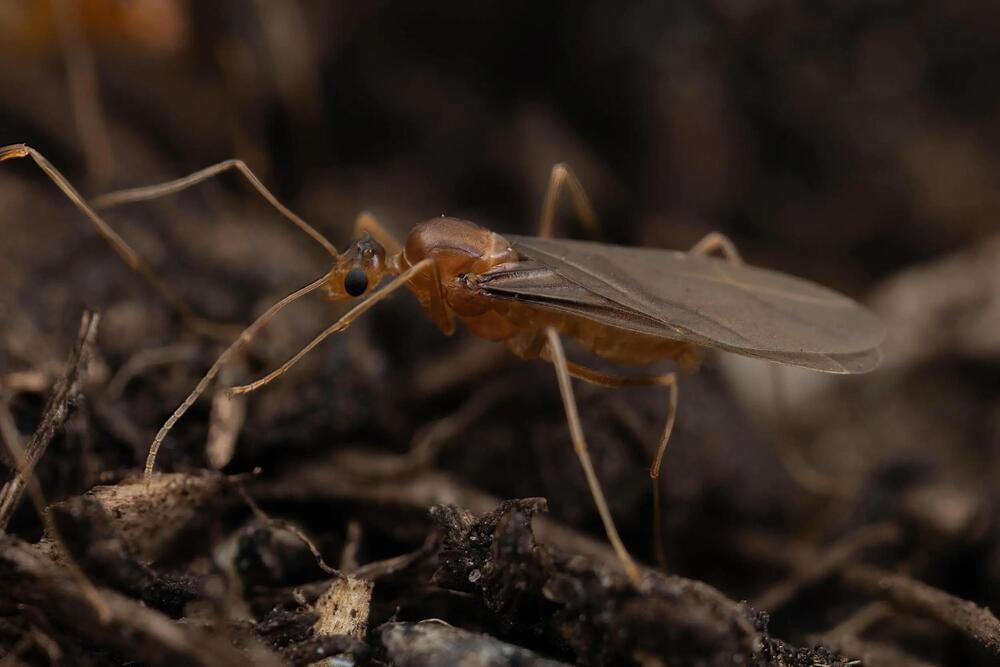

International researchers studying the yellow crazy ant, or Anoplolepis gracilipes, found that male ants of this species are chimeras, containing two genomes from different parent cells within their bodies. This unique reproductive process, originating from a single fertilized egg that undergoes separate maternal and paternal nuclear division, is unprecedented and challenges the fundamental biological inheritance law stating that all cells of an individual should contain the same genome. Credit: Hugo Darras.
The yellow crazy ant, known scientifically as Anoplolepis gracilipes, is notorious for being one of the most devastating invasive species.
A species is a group of living organisms that share a set of common characteristics and are able to breed and produce fertile offspring. The concept of a species is important in biology as it is used to classify and organize the diversity of life. There are different ways to define a species, but the most widely accepted one is the biological species concept, which defines a species as a group of organisms that can interbreed and produce viable offspring in nature. This definition is widely used in evolutionary biology and ecology to identify and classify living organisms.
One month into living under Russian occupation in northern Ukraine, Marina cycled cautiously through her village. She was five doors from her elderly parents’ blue garden gate when three soldiers ordered her to stop. Grabbing her hair, they dragged Marina into a neighbour’s empty house.
“They forced me to strip naked,” the 47-year-old said, picking at the skin around her fingernails. “I asked them not to touch me, but they said: ‘Your Ukrainian soldiers are killing us’.”
Marina paused, wiped her tears and tried to steady her shaking hands. “They were shooting their guns inches away from my head so I couldn’t move or run,” she said. “Then they started raping me.”
Weeks after a Ukrainian town is liberated, its civilians are visited by sexual violence prosecutors and asked an indirect question: “Did the Russians behave?”
The answers have been harrowing; men’s genitals have been electrocuted, women forced to parade naked, and children as young as four orally raped.
The use of rape in war has existed for as long as there has been conflict. It’s used to terrorise and degrade a community, and has been committed in 17 ongoing conflicts around the world. Yet although it is deemed a war crime under international law, it mostly remains undisclosed and hidden under layers of stigma and fear.

A group of scientists has discovered new laws governing the flow of fluids by conducting experiments on an ancient technology: the drinking straw. This newfound understanding has the potential to enhance fluid management in medical and engineering contexts.
“We found that sipping through a straw defies all the previously known laws for the resistance or friction of flow through a pipe or tube,” explains Leif Ristroph, an associate professor at New York University’s Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences and an author of the study, which appears in the Journal of Fluid Mechanics. “This motivated us to search for a new law that could work for any type of fluid moving at any rate through a pipe of any size.”
The movement of liquids and gases through conduits such as pipes, tubes, and ducts is a common phenomenon in both natural and industrial contexts, including in scenarios like the circulation of blood or the transportation of oil through pipelines.
As my friends Tristan Harris and Aza Raskin of the Center for Humane Technology (CHT) explain in their April 9th YouTube presentation, the AI revolution is moving much too fast for, and proving much too slippery for, conventional legal and regulatory responses by humans and their state power.
Crucially, these two idealistic Silicon Valley renegades point out, in an accessible manner, exactly what has made the recent jump in AI capacity possible: