Neurotech will bring many amazing positive changes to the world, such as treating ailments like blindness, depression, and epilepsy, giving us superhuman sensory capabilities that allow us to understand the world in new ways, accelerating our ability to cognitively process information, and more. But in an increasingly connected society, neuroprivacy will represent a crucial concern of the future. We must carefully devise legal protections against misuse of “mind reading” technology as well as heavily invest in “neurocybersecurity” R&D to prevent violation of people’s inner thoughts and feelings by authorities and malignant hackers. We can capitalize on the advantages, but we must do establish safety mechanisms as these technologies mature. #neurotechnology #neuroscience #neurotech #computationalbiology #future #brain
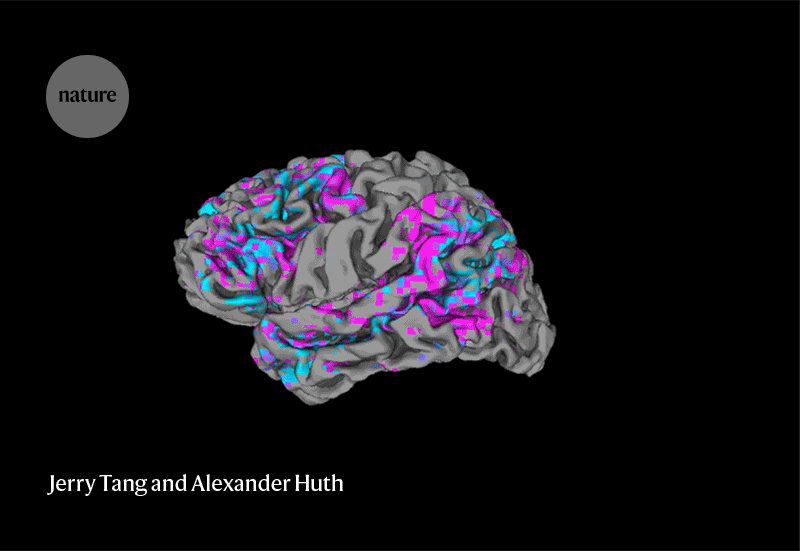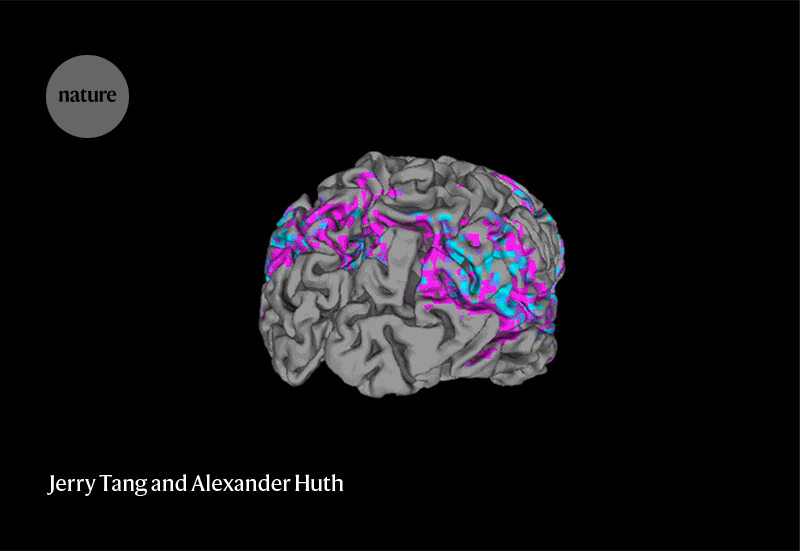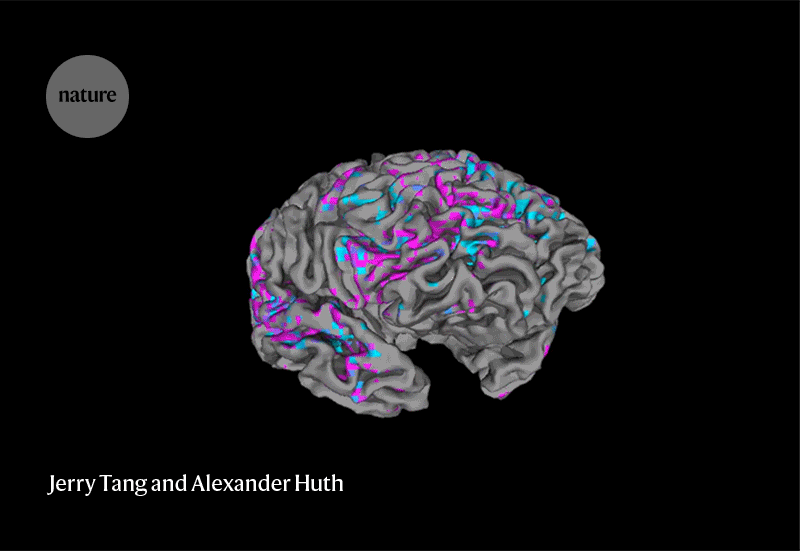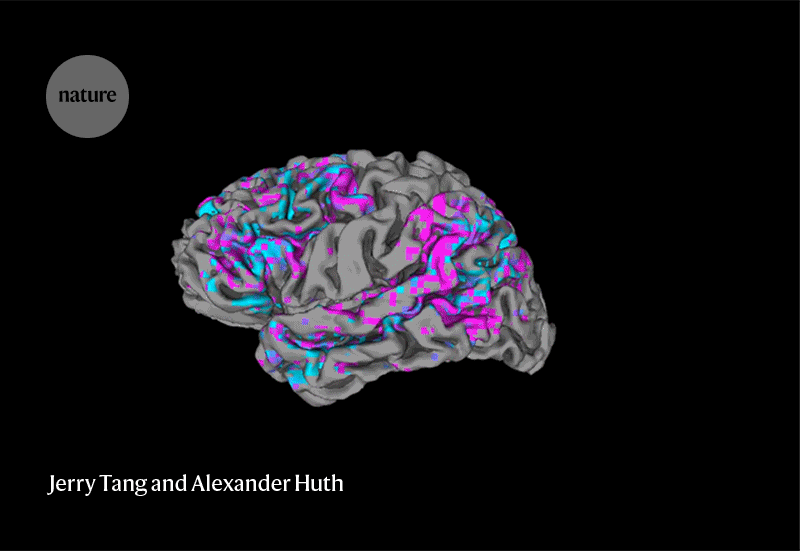
Determining how the brain creates meaning from language is enormously difficult, says Francisco Pereira, a neuroscientist at the US National Institute of Mental Health in Bethesda, Maryland. “It’s impressive to see someone pull it off.”‘
‘Wake-up call’
Neuroethicists are split on whether the latest advance represents a threat to mental privacy. “I’m not calling for panic, but the development of sophisticated, non-invasive technologies like this one seems to be closer on the horizon than we expected,” says bioethicist Gabriel Lázaro-Muñoz at Harvard Medical School in Boston. “I think it’s a big wake-up call for policymakers and the public.”