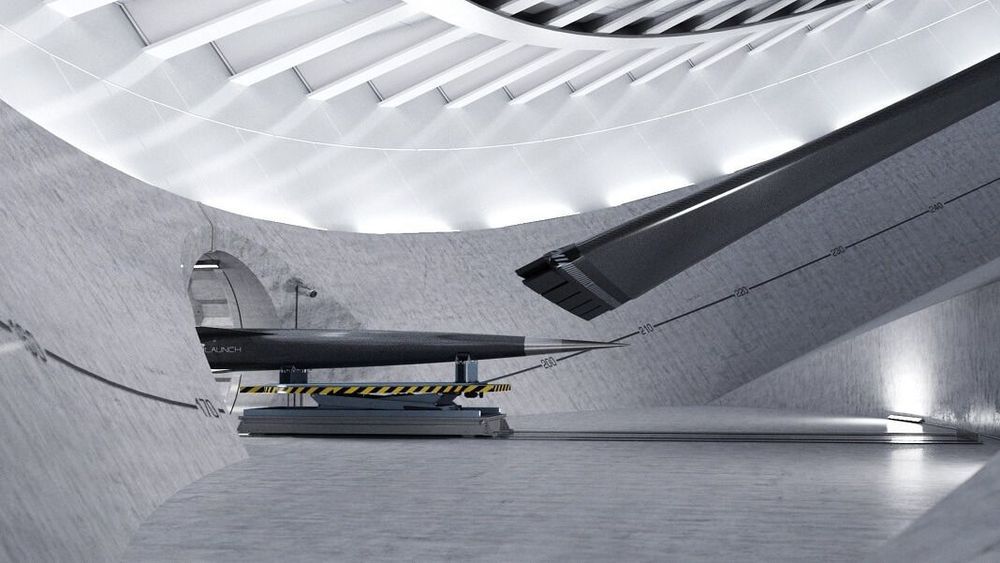
The rapidly falling cost of getting into orbit has spurred a boom in the space industry as a host of new applications become economical. Now a secretive startup plans to slash the cost to just $250,000 by flinging rockets into space rather than firing them.
Over the last decade, the pioneering work done by SpaceX has shown that getting stuff into orbit doesn’t need to be so expensive and that there are viable business opportunities to be had in the private space industry. Combined with advances in satellite technology, there’s now a thriving market for small, inexpensive spacecraft in low- E arth orbit doing everything from remote sensing to delivering broadband internet access.
But while costs have fallen dramatically, the cheapest option for reaching low-Earth orbit —a rideshare on SpaceX’s Falcon 9—still starts at $1 million, and launches only happen twice a month at best. California-based startup SpinLaunch says its technology will allow up to five launches a day for as little as $250,000.