Category: internet – Page 194

Laser-Driven Semiconductor Switch for Next-Generation Communications
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory engineers have designed a new kind of laser-driven semiconductor switch that can theoretically achieve higher speeds at higher voltages than existing photoconductive devices. If the device could be realized, it could be miniaturized and incorporated into satellites to enable communication systems beyond 5G, potentially transferring more data at a faster rate and over longer distances, according to researchers. Credit: LLNL
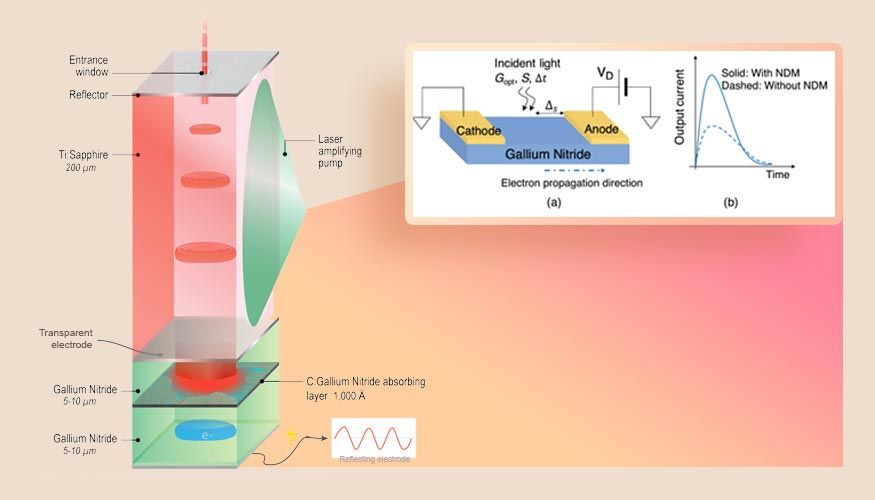
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) engineers have designed a new kind of laser-driven semiconductor switch that can theoretically achieve higher speeds at higher voltages than existing photoconductive devices. The development of such a device could enable next-generation satellite communication systems capable of transferring more data at a faster rate, and over longer distances, according to the research team.
Scientists at LLNL and the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign (UIUC) reported on the design and simulation of the novel photoconductive device in a paper published in the IEEE Journal of the Electron Devices Society. The device utilizes a high-powered laser to generate an electron charge cloud in the base material gallium nitride while under extreme electric fields.

Big Tech Is Going Public in India
That could reshape the Indian market, which has very few internet companies. While big tech firms are among the largest listed companies in China and the U.S., energy, financials and IT outsourcers currently dominate the Indian market. Reliance Industries —India’s biggest listed company, controlled by the country’s richest man—is pivoting away from oil and gas and last year secured investments from Facebook and Google for its tech unit, Jio Platforms.
Companies such as Zomato, Flipkart and fintech giant Paytm are considering initial public offerings in what could be a transformative moment for India’s stock market.
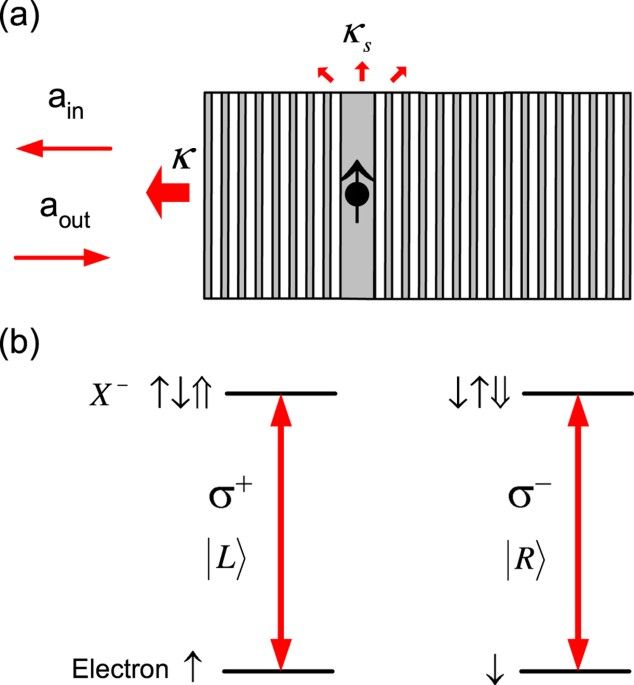
Photonic transistor and router using a single quantum-dot-confined spin in a single-sided optical microcavity
Circa 2017
The future Internet is very likely the mixture of all-optical Internet with low power consumption and quantum Internet with absolute security. The optical regular Internet would be used by default, but switched over to quantum Internet when sensitive data need to be transmitted. PT and and its counterpart in the quantum limit SPT would be the core components for both OIP and QIP in future Internet. Compared with electronic transistors, PTs/SPTs potentially have higher speed, lower power consumption and compatibility with fibre-optic communication systems.
Several schemes for PT6,7,8,9,10 and SPT11,12,13,14,15,16,17 have been proposed or even proof-of-principle demonstrated. All these prototypes exploit optical nonlinearities, i.e., photon-photon interactions18. However, photons do not interact with each other intrinsically, so indirect photon-photon interactions via electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT)19, photon blockade20 and Rydberg blockade21 were intensively investigated in this context over last two decades in either natural atoms22,23 or artificial atoms including superconducting boxes24,25 and semiconductor quantum dots (QDs)12,13. PT can seldom work in the quantum limit as SPT with the gain greater than 1 because of two big challenges, i.e., the difficulty to achieve the optical nonlinearities at single-photon levels and the distortion of single-photon pulse shape and inevitable noise produced by these nonlinearities26. The QD-cavity QED system is a promising solid-state platform for information and communication technology (ICT) due to their inherent scalability and matured semiconductor technology. But the photon blockade resulting from the anharmonicity of Jaynes-Cummings energy ladder27 is hard to achieve due to the small ratio of the QD-cavity coupling strength to the system dissipation rates12,13,28,29,30,31,32 and the strong QD saturation33. Moreover, the gain of this type of SPT based on the photon blockade is quite limited and only 2.2 is expected for In(Ga)As QDs12,13.
In this work, a different PT and SPT scheme exploiting photon-spin interactions rather than photon-photon interactions is proposed based on a linear quantum-optical effect — giant optical Faraday rotation (GFR) induced by a single QD-confined spin in a single-sided optical microcavity34. This spin-cavity transistor is genuinely a quantum transistor in three aspects: it is based on a quantum effect, i.e., the linear GFR; it has the duality as a quantum gate for QIP and a classical transistor for OIP; it can work in the quantum limit as a SPT to amplify a single-photon state to Schrödinger cat state. Therefore this new-concept transistor can be more powerful than the traditional electronic transistors. Theoretically the maximum gain can reach ~105 in the state-of-the-art pillar microcavity, several orders of magnitude greater than previous PT/SPT schemes6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17. The large gain is attributed to the linear GFR that is robust against classical and quantum fluctuations and the long spin coherence time compared with the cavity lifetime. The maximal speed which is determined by the cavity lifetime has the potential to break the terahertz (THz) barrier for electronic transistors35,36. Based on this versatile spin-cavity transistor, optical Internet1, quantum computers (QCs)37,38 (either spin-cavity hybrid QCs or all-optical QCs), and quantum Internet4 could become reality even with current semiconductor technology.
Threat Actors Use Google Docs to Host Phishing Attacks
Exploit in the widely used document service leveraged to send malicious links that appear legitimate but actually steal victims credentials.
Threat actors are exploiting Google Docs by hosting their attacks within the web-based document service in a new phishing campaign that delivers malicious links aimed at stealing victims’ credentials.
Researchers at email and collaboration security firm Avanan discovered the campaign, which is the first time they said they’ve seen attackers use this type of exploit in Google’s hosted document service, according to a report published Thursday by Jeremy Fuchs, marketing content manager for Avanan.



New record distance for quantum communications
Toshiba’s Cambridge Research Laboratory has achieved quantum communications over optical fibres exceeding 600 km in length, three times further than the previous world record distance.
The breakthrough will enable long distance, quantum-secured information transfer between metropolitan areas and is a major advance towards building a future Quantum Internet.
The term “Quantum Internet” describes a global network of quantum computers, connected by long distance quantum communication links. This technology will improve the current Internet by offering several major benefits – such as the ultra-fast solving of complex optimisation problems in the cloud, a more accurate global timing system, and ultra-secure communications. Personal data, medical records, bank details, and other information will be physically impossible to intercept by hackers. Several large government initiatives to build a Quantum Internet have been announced in China, the EU and the USA.

Amazon Sidewalk could raise your Wifi bill cybersecurity, expert says
LYNCHBURG, Va (WSET) — Strangers may soon be able to use your Wi-Fi — It’s all through Amazon Sidewalk.
It’s an internet-sharing network for Amazon Echo, Ring and Tile devices. Officials say it’s a way to use WiFi from neighboring homes that also have Amazon products.
Randy Marchany a cybersecurity expert with Virginia Tech feels this is another way to collect information. He says it’s specifically picking up on user habits and whereabouts.