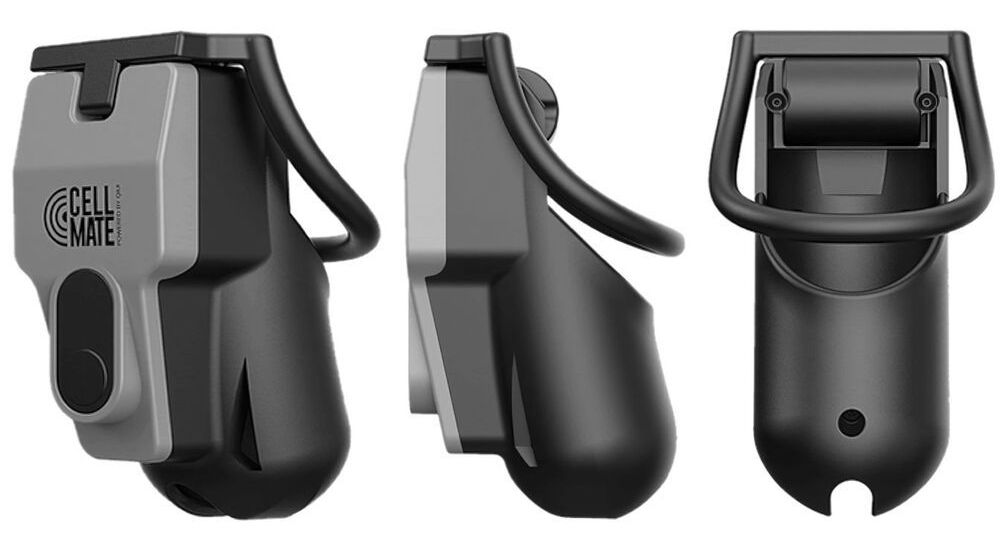
There’s an internet sex toy that could leave you wearing it a good deal longer than intended.


When SpaceX deploy batches of Starlink satellites they drop them off in lower orbits and expect the satellites themselves to navigate towards their final operational orbits. This is quite a complex process and one that’s worth discussing, the satellites need to be able to reach the target orbital plane, raise the orbit to operational altitude, and then finally maneuver to a specific slot within that plane before they become operational.
Satellite Orbital Maps by Celestrak.
https://celestrak.com/
Starlink Map by Mike Puchol.
https://starlink.sx/
Deployment plots by Elias Eccli.
https://www.youtube.com/c/EliasEccli
60 Minutes+ correspondent Laurie Segall reports on the big money being spent in a world somewhere between digital and reality. See the story, streaming now only on Paramount+.
“60 Minutes” is the most successful television broadcast in history. Offering hard-hitting investigative reports, interviews, feature segments and profiles of people in the news, the broadcast began in 1,968 and is still a hit, over 50 seasons later, regularly making Nielsen’s Top 10.
Watch full episodes: http://cbsn.ws/1Qkjo1F
Get more “60 Minutes” from “60 Minutes: Overtime”: http://cbsn.ws/1KG3sdr.
Follow “60 Minutes” on Instagram: http://bit.ly/23Xv8Ry.
Like “60 Minutes” on Facebook: http://on.fb.me/1Xb1Dao.
Follow “60 Minutes” on Twitter: http://bit.ly/1KxUsqX
Download the CBS News app: http://cbsn.ws/1Xb1WC8
Try Paramount+ free: https://bit.ly/2OiW1kZ
For video licensing inquiries, contact: [email protected]

Learn More
University of Advancing Technology’s Artificial Intelligence (AI) degree explores the theory and practice of engineering tools that simulate thinking, patterning, and advanced decision behaviors by software systems. With inspiration derived from biology to design, UAT’s Artificial Intelligence program teaches students to build software systems that solve complex problems. Students will work with technologies including voice recognition, simulation agents, machine learning (ML), and the internet of things (IoT).
Students pursuing this specialized computer programming degree develop applications using evolutionary and genetic algorithms, cellular automata, artificial neural networks, agent-based models, and other artificial intelligence methodologies. UAT’s degree in AI covers the fundamentals of general and applied artificial intelligence including core programming languages and platforms used in computer science.

Doubtful. But, i hope so, it will convince them to spend more money here to move AI research faster.
TOKYO — China is overtaking the U.S. in artificial intelligence research, setting off alarm bells on the other side of the Pacific as the world’s two largest economies jockey for AI supremacy.
In 2,020 China topped the U.S. for the first time in terms of the number of times an academic article on AI is cited by others, a measure of the quality of a study. Until recently, the U.S. had been far ahead of other countries in AI research.
One reason China is coming on strong in AI is the ample data it generates. By 2,030 an estimated 8 billion devices in China will be connected via the Internet of Things — a vast network of physical objects linked via the internet. These devices, mounted on cars, infrastructure, robots and other instruments, generate a huge amount of data.


The download speed is 100 Mbps and the upload speed is 13.89 Mbps.
“Starlink” is a satellite internet project of SpaceX. From 2,019 to 2,024 SpaceX plans to use five years to send thousands of satellites needed for networking into low-Earth orbit to form a “Starlink” network to provide internet services. Currently, there are 1,650 satellites on the “Starlink” network.
The Speedtest report shows that in the second quarter of this year, the average download speed of Starlink satellite internet services in the US market was 97.23 Mbps. This is not far from the average download speed of fixed broadband in the US, which is 115.22 Mbps.

No, it’s not forbidden to innovate, quite the opposite, but it’s always risky to do something different from what people are used to. Risk is the middle name of the bold, the builders of the future. Those who constantly face resistance from skeptics. Those who fail eight times and get up nine.
(Credit: Adobe Stock)
Fernando Pessoa’s “First you find it strange. Then you can’t get enough of it.” contained intolerable toxicity levels for Salazar’s Estado Novo (Portugal). When the level of difference increases, censorship follows. You can’t censor censorship (or can you?) when, deep down, it’s a matter of fear of difference. Yes, it’s fear! Fear of accepting/facing the unknown. Fear of change.
What do I mean by this? Well, I may seem weird or strange with the ideas and actions I take in life, but within my weirdness, there is a kind of “Eye of Agamotto” (sometimes being a curse for me)… What I see is authentic and vivid. Sooner or later, that future I glimpse passes into this reality.
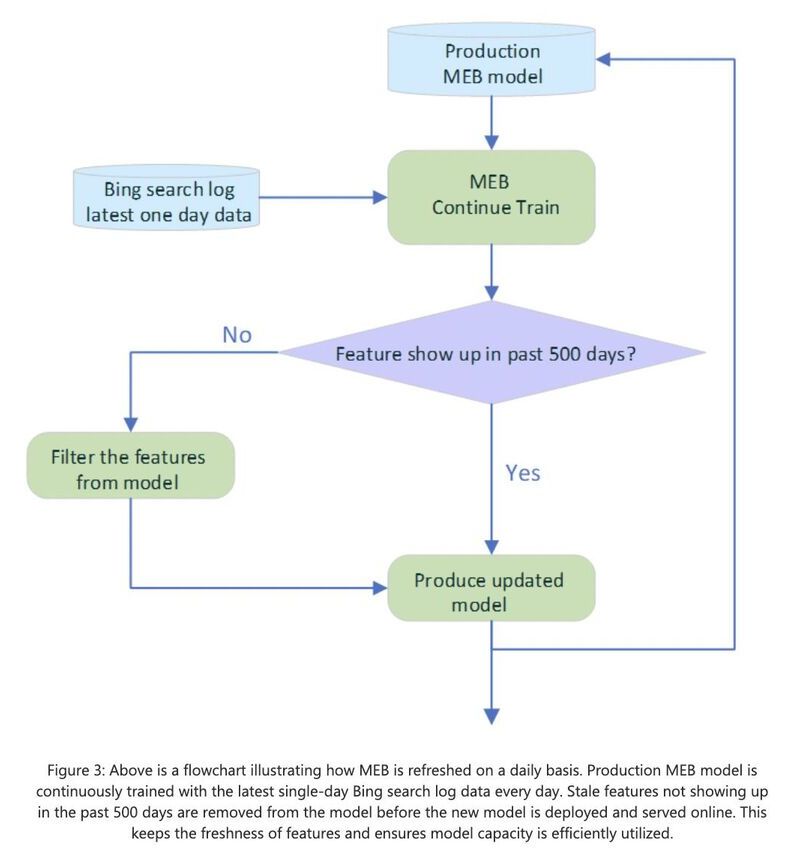
Transformer-based deep learning models like GPT-3 have been getting much attention in the machine learning world. These models excel at understanding semantic relationships, and they have contributed to large improvements in Microsoft Bing’s search experience. However, these models can fail to capture more nuanced relationships between query and document terms beyond pure semantics.
The Microsoft team of researchers developed a neural network with 135 billion parameters, which is the largest “universal” artificial intelligence that they have running in production. The large number of parameters makes this one of the most sophisticated AI models ever detailed publicly to date. OpenAI’s GPT-3 natural language processing model has 175 billion parameters and remains as the world’s largest neural network built to date.
Microsoft researchers are calling their latest AI project MEB (Make Every Feature Binary). The 135-billion parameter machine is built to analyze queries that Bing users enter. It then helps identify the most relevant pages from around the web with a set of other machine learning algorithms included in its functionality, and without performing tasks entirely on its own.
The space-faring firm’s satellite internet service promises connections with high speed and low latency — and data suggests the rollout pace is now increasing.