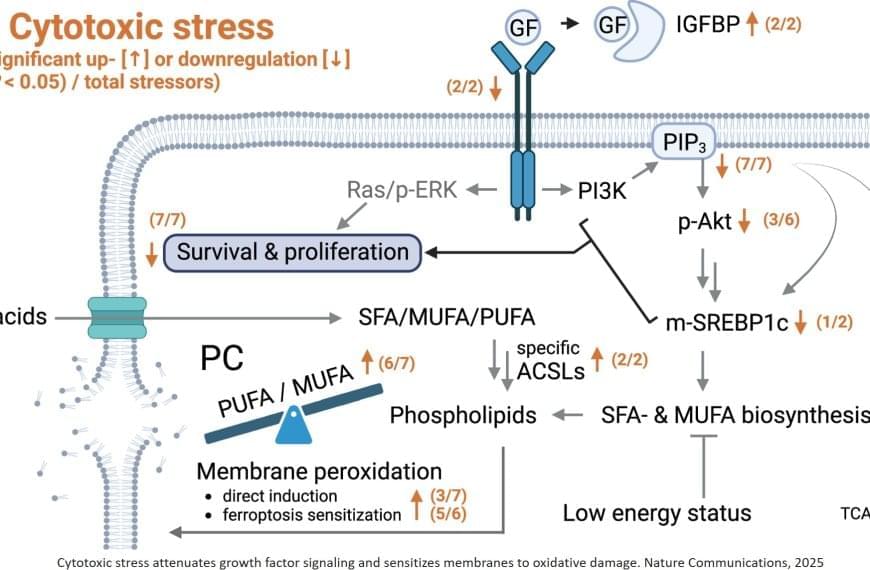
While studying the effect of various cytotoxic natural products on different cancer cells, the researchers have discovered a previously unknown mechanism that could point to new therapeutic options in the event of such resistance.
“When the cancer cells come into contact with the active substance, they show a stress reaction. Even at this very early stage, long before they might possibly die, reduced growth signals cause increased levels of polyunsaturated fatty acids to be incorporated into the membrane. This makes them more susceptible to a particular cell death pathway, ferroptosis,” explains the researcher, adding: “The mechanism appears to be universal. This means that it can be observed in all the cancer cells examined and in most cytotoxic agents.” During ferroptosis, polyunsaturated fatty acids in cell membranes are damaged by oxygen radicals. The membranes become porous and the cell dies.
These findings create a basis for the systematic research of innovative treatment strategies for therapy-resistant tumors. Even if conventional chemotherapeutic agents do not kill the cells, they at least trigger a membrane change that can be utilized. “By adding substances that induce ferroptosis, cancer cells could ultimately be eliminated completely,” the author suspects.
One particular challenge in the treatment of cancer is therapy resistance. An international research team has now discovered a mechanism that opens up new treatment strategies for tumors in which conventional chemotherapeutic agents have reached their limits.
“Cytotoxic agents from nature lead to an increased incorporation of polyunsaturated fatty acids into the membrane of cancer cells. This makes them more susceptible to ferroptosis, a type of cell death, at a very early stage,” reports the lead author of the study, which has just been published in the scientific journal Nature Communications.
In the treatment of cancer with chemotherapy, natural substances, such as those from the Chinese “happy tree”, play an important role. They interfere with vital cell processes and thereby damage them. However, a few cancer cells are often able to adapt to these challenges and survive. This is called resistance.