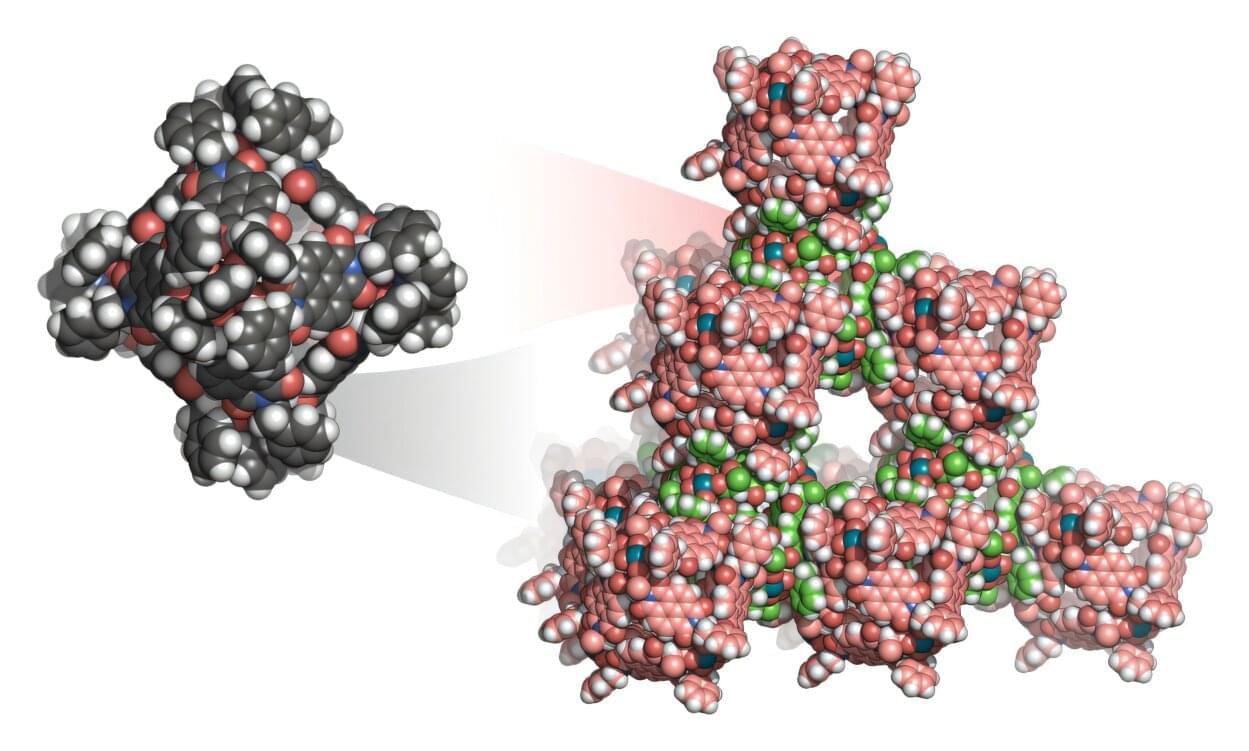
Researchers from Kyoto University have achieved a significant advancement in materials science by developing the world’s first three-dimensional van der Waals open frameworks (WaaFs). This innovation challenges the conventional belief that van der Waals interactions are too weak for open framework materials, demonstrating their potential for stable and highly porous materials.
Published in Nature Chemistry, the study presents a strategy using octahedral metal-organic polyhedra (MOPs) as building blocks to construct WaaFs. These frameworks exhibit high thermal stability, exceptional porosity, and reversible assembly, opening new avenues for applications in gas storage, separation, and catalysis.
WaaFs utilize van der Waals interactions, which were previously considered too weak, to form robust three-dimensional frameworks. These structures maintain their integrity at temperatures up to 593 K and achieve surface areas exceeding 2,000 m2/g, making them highly stable and efficient for various industrial applications.