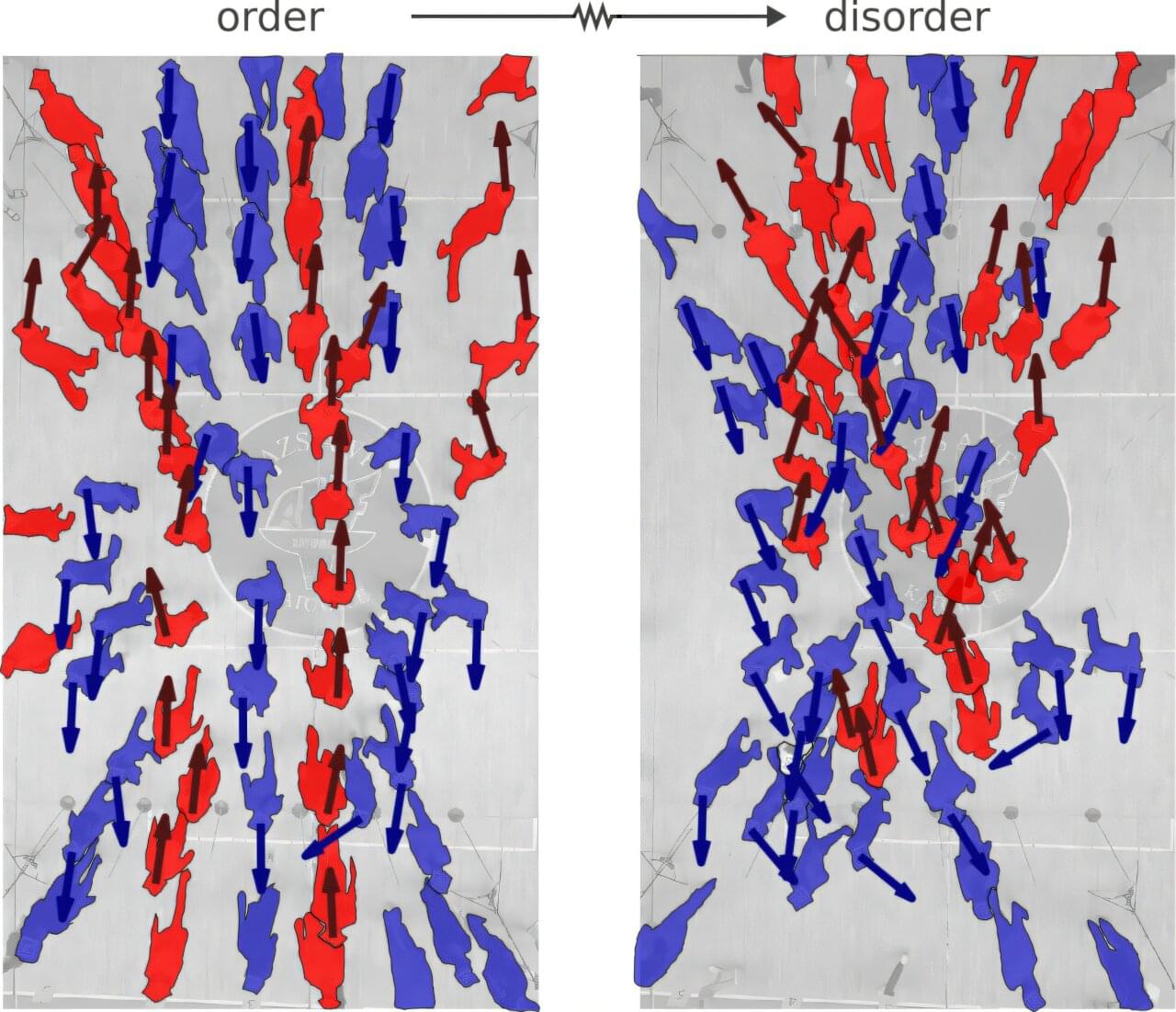
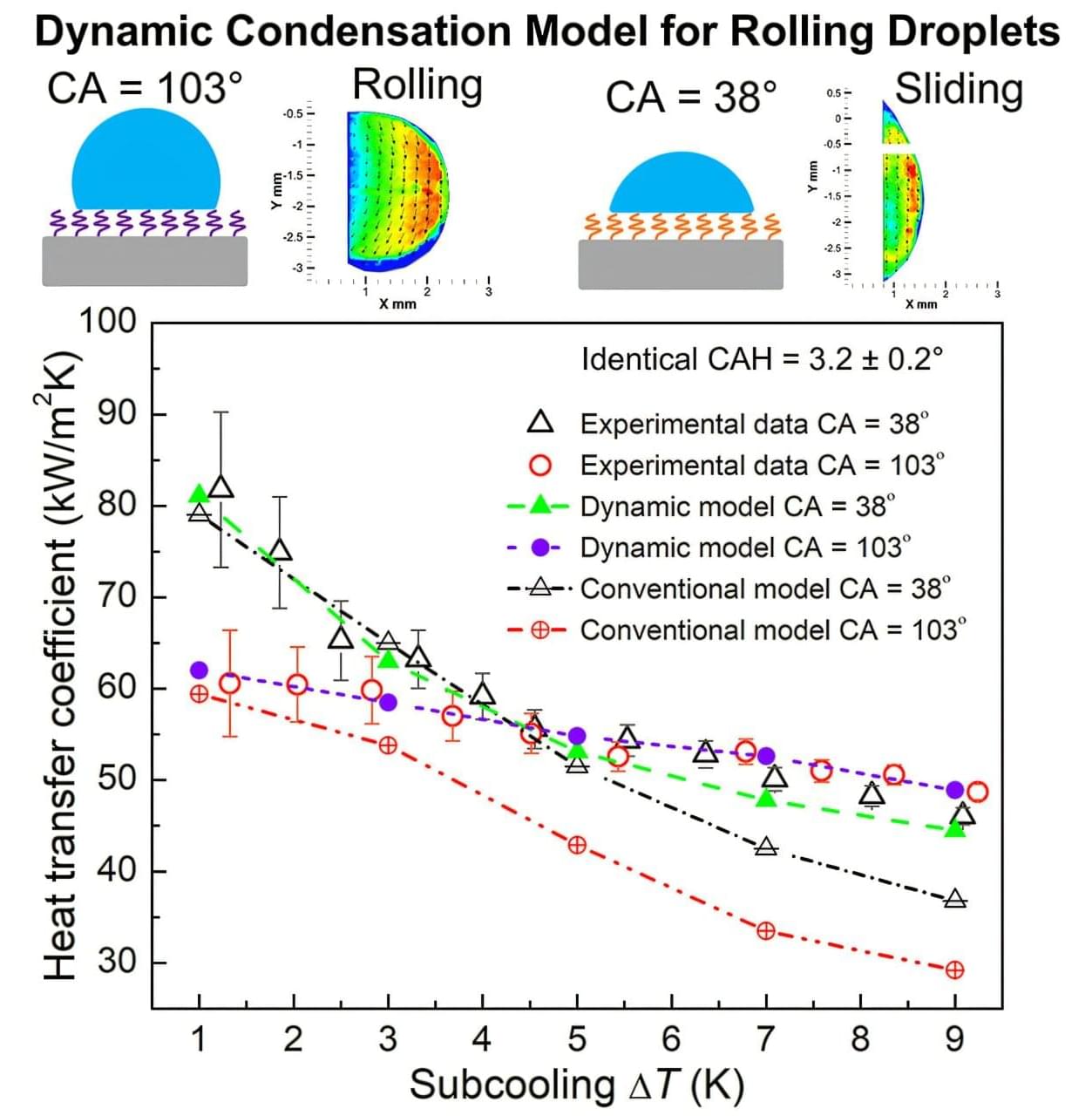
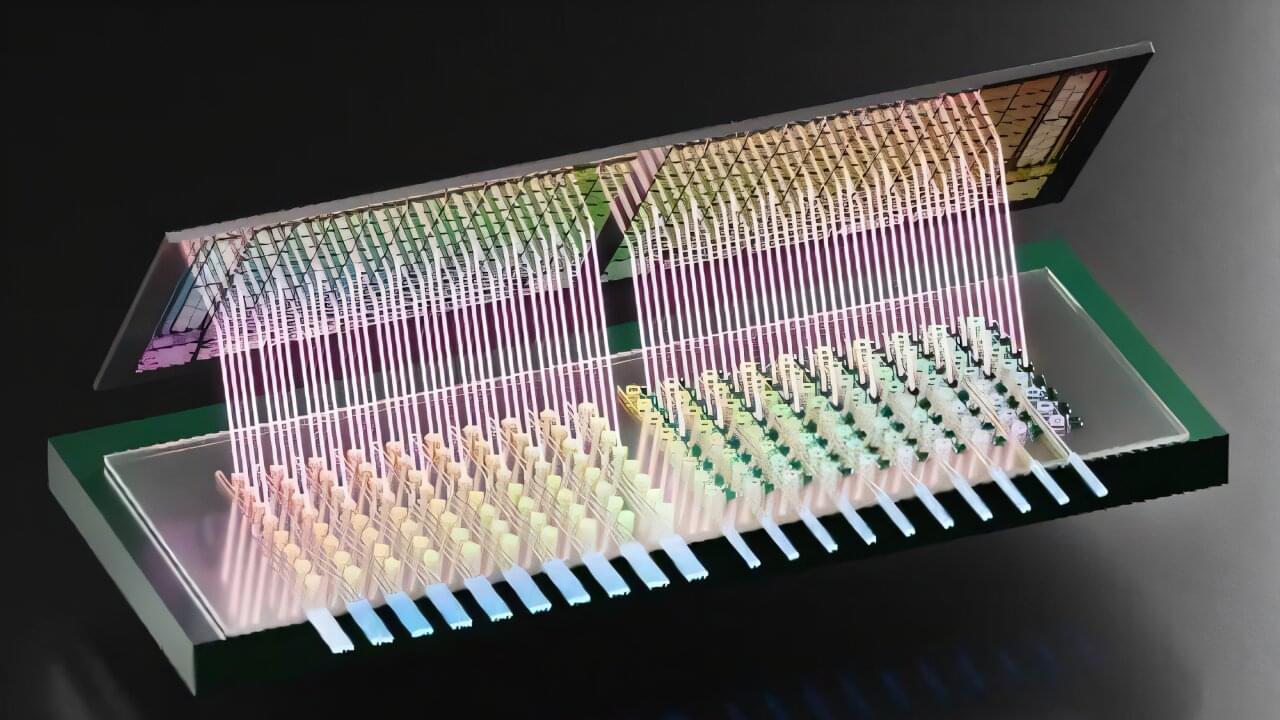
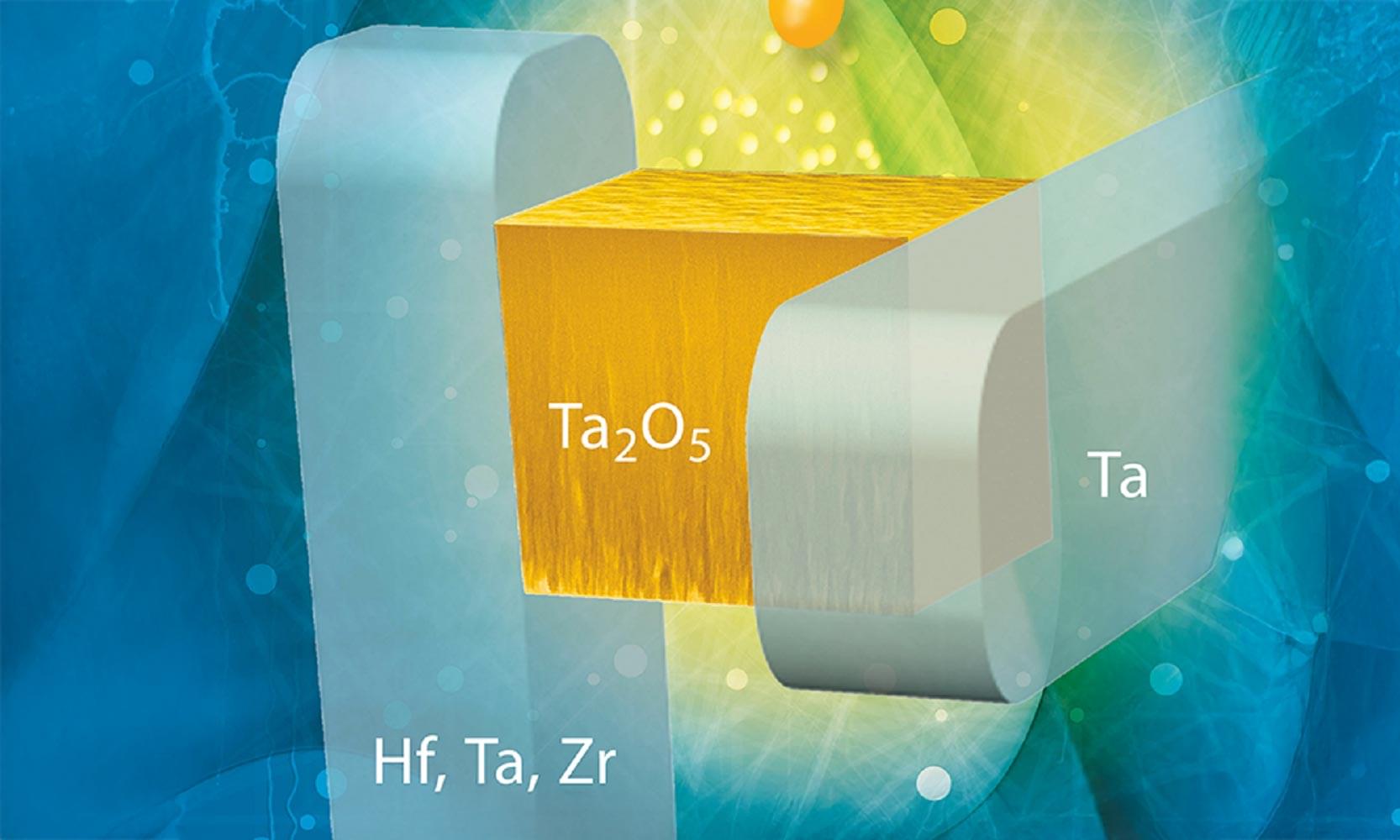
Thanks to breakthroughs in hydrogel material science, we now have material that functions similar to Star Wars Bacta.
2nd Channel: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCICVgpk90CmHmQoX-vSSuZA
Follow Generation Tech on Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/generationtechofficial.
Follow Generation Tech on Facebook: http://bit.ly/GenerationTechFB
Latest Videos: http://bit.ly/LatestGT
Popular Videos: http://bit.ly/GTPopular.
Please help our channel by becoming a Patron: http://bit.ly/GTPatreon.
Follow our Host.
ALLEN XIE
YOUTUBE https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCrc275yYmYcj9x275_OtSIg.
INSTAGRAM AXIEFILMS
TIKTOK AXIEFILMS
FACEBOOK https://www.facebook.com/AxieFilms/