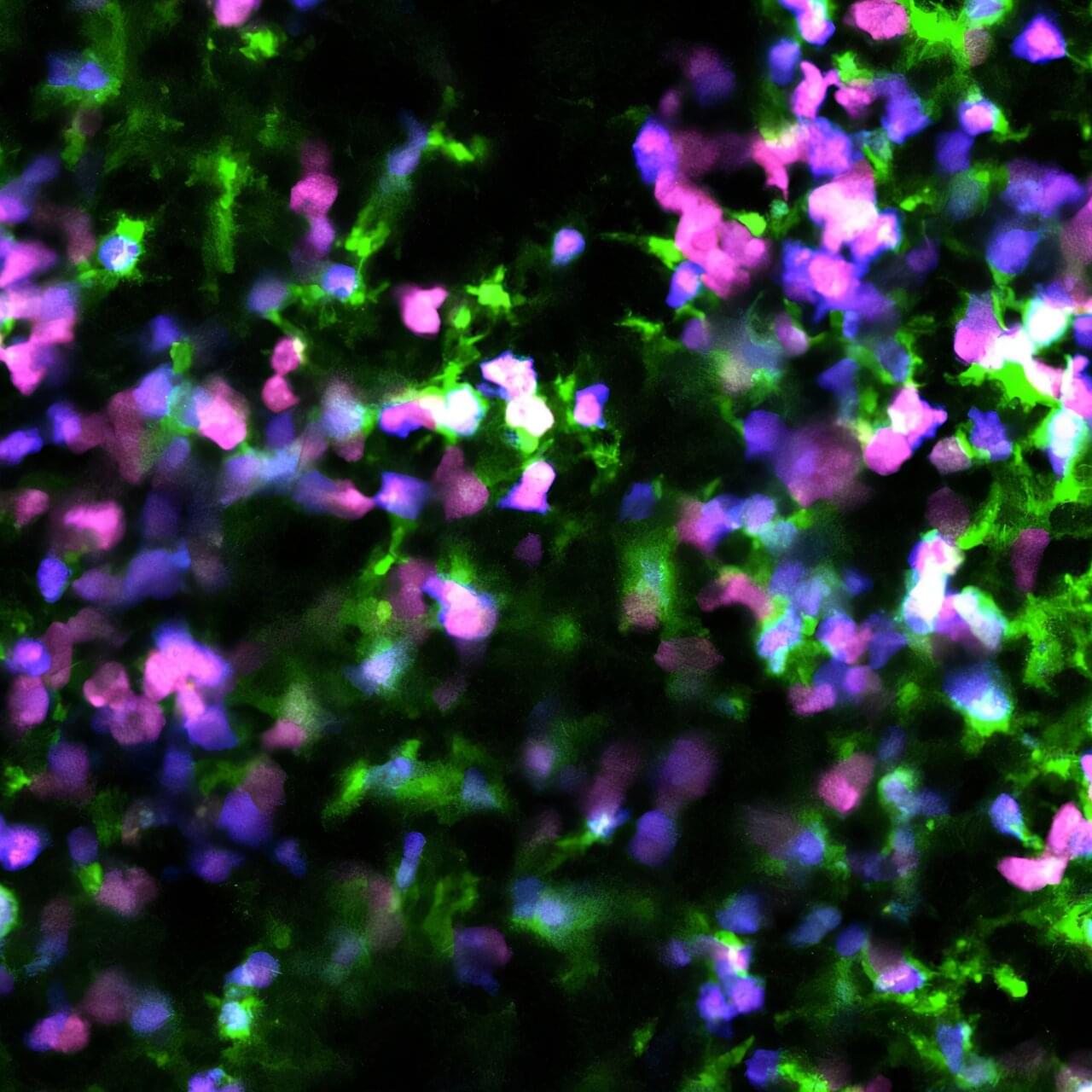
The aim of immunotherapy strategies is to leverage cells in the patient’s own immune system to destroy tumor cells. Using a preclinical model, scientists from the Institut Pasteur and Inserm successfully stimulated an effective anti-tumor immune response by reprogramming the death of malignant B cells. They demonstrated an effective triple-therapy approach for treating forms of blood cancer such as certain lymphomas and leukemias which affect B cells. The study was published on August 15 in the journal Science Advances.
Immunotherapy strategies represent a major breakthrough in cancer treatment. They aim to harness the patient’s immune system so that their own cells can recognize and specifically eliminate tumor cells. Immune cells can act like sentinels, scanning the body and identifying all residual tumor cells to reduce the risk of relapse. Various novel immunotherapy strategies are emerging, one of which makes use of a cell death mechanism known as necroptosis. Unlike apoptosis, which results in silent cell death, necroptosis releases warning signals that attract and stimulate immune cells so that they can kill any remaining tumor cells.
Scientists from the Dynamics of Immune Responses Unit (a joint Inserm/Institut Pasteur unit) set out to explore the effectiveness of this necroptosis-based immunotherapy strategy on hematological malignancies. They began by observing that necroptosis cannot be easily induced in malignant B cells because of the absence of the MLKL protein.