The purpose of this work is to investigate how several inflationary and bouncing scenarios can be realized by imperfect fluids. We shall use two different theoretical frameworks, namely classical cosmology and Loop Quantum Cosmology (LQC) (see where the derivation of the Hamiltonian in LQC was firstly derived to yield the modified Friedman equation, and also see for a recent derivation of the effective Hamiltonian in LQC, which was derived by demanding repulsive gravity, as in Loop Quantum Gravity). In both cases we shall investigate which imperfect fluid can realize various inflationary and bouncing cosmology scenarios. The inflationary cosmology and bouncing cosmology are two alternative scenarios for our Universe evolution. In the case of inflation, the Universe starts from an initial singularity and accelerates at early times, while in the case of the bouncing cosmology, the Universe initially contracts until it reaches a minimum radius, and then it expands again. With regards to inflation, we shall be interested in four different inflationary scenarios, namely the intermediate inflation, the Starobinsky inflation, and two constant-roll inflation scenarios. With regards to bouncing cosmologies, we shall be interested in realizing several well studied bouncing cosmologies, and particularly the matter bounce scenario, the superbounce scenario and the singular bounce.
As we already mentioned we shall use two theoretical frameworks, that of classical cosmology and that of LQC. After presenting the reconstruction methods for realizing the various cosmologies with imperfect fluids, we proceed to the realization of the cosmologies by using the reconstruction methods. In the case of classical cosmology, we will calculate the power spectrum of primordial curvature perturbations, the scalar-to-tensor ratio and the running of the spectral index for all the aforementioned cosmologies, and we compare the results to the recent Planck data. The main outcome of our work is that, although the cosmological scenarios we study in this paper are viable in other modified gravity frameworks, these are not necessarily viable in all the alternative modified gravity descriptions. As we will demonstrate, in some cases the resulting imperfect fluid cosmologies are not compatible at all with the observational data, and in some other cases, there is partial compatibility.
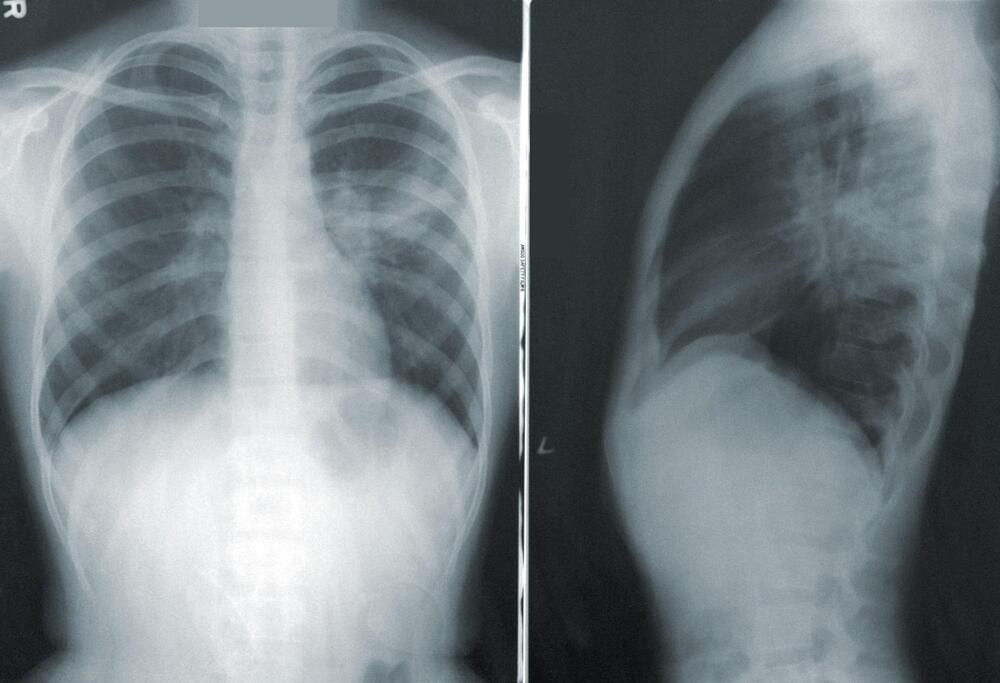
We need to note that the perturbation aspects in LQC are not transparent enough and assume that there are no non-trivial quantum gravitational modifications arising due to presence of inhomogeneities. As it was shown in, a consistent Hamiltonian framework does not allow this assumption to be true. The perturbations issues that may arise in the context of the present work, are possibly more related to some early works in LQC, so any calculation of the primordial power spectrum should be addressed as we commented above.