A mathematician in England just solved a decades-old Diophantine equation for the number 33. Now, only 42 remains.


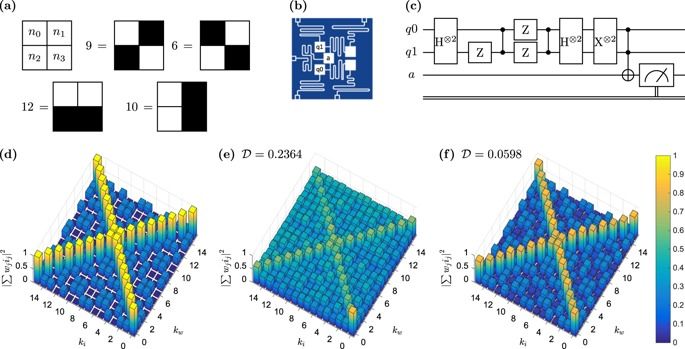
Artificial neural networks are the heart of machine learning algorithms and artificial intelligence. Historically, the simplest implementation of an artificial neuron traces back to the classical Rosenblatt’s “perceptron”, but its long term practical applications may be hindered by the fast scaling up of computational complexity, especially relevant for the training of multilayered perceptron networks. Here we introduce a quantum information-based algorithm implementing the quantum computer version of a binary-valued perceptron, which shows exponential advantage in storage resources over alternative realizations. We experimentally test a few qubits version of this model on an actual small-scale quantum processor, which gives answers consistent with the expected results. We show that this quantum model of a perceptron can be trained in a hybrid quantum-classical scheme employing a modified version of the perceptron update rule and used as an elementary nonlinear classifier of simple patterns, as a first step towards practical quantum neural networks efficiently implemented on near-term quantum processing hardware.


Hot off the press…
Barnes & Noble Press releases a new non-fiction book The Syntellect Hypothesis: Five Paradigms of the Mind’s Evolution by Alex M. Vikoulov as Hardcover (Press Release, San Francisco, CA, USA, March 22, 2019 11.00 AM PST)
Named “The Book of the Year” by futurists and academics alike, “# 1 Hot New Release” in Amazon charts in Physics of Time, Phenomenology, and Phenomenological Philosophy, the book has now been released by Barnes & Noble Press as hardcover in addition to ebook and paperback released earlier this year. In one volume, the author covers it all: from quantum physics to your experiential reality, from the Big Bang to the Omega Point, from the ‘flow state’ to psychedelics, from ‘Lucy’ to the looming AI Singularity, from natural algorithms to the operating system of your mind, from geo-engineering to nanotechnology, from anti-aging to immortality technologies, from oligopoly capitalism to Star-Trekonomics, from the Matrix to Universal Mind, from Homo sapiens to Holo syntellectus.
https://paper.li/e-1437691924#/
Geoffrey Rockwell and Bettina Berendt’s (2017) article calls for ethical consideration around big data and digital archive, asking us to re-consider whether. In outlining how digital archives and algorithms structure potential relationships with whose testimony has been digitized, Rockwell and Berendt highlight how data practices change the relationship between research and researched. They make a provocative and important argument: datafication and open access should, in certain cases, be resisted. They champion the careful curation of data rather than large-scale collection of, pointing to the ways in which these data are used to construct knowledge about and fundamentally limit the agency of the research subject by controlling the narratives told about them. Rockwell and Berendt, drawing on Aboriginal Knowledge (AK) frameworks, amongst others, argue that some knowledge is just not meant to be openly shared: information is not an inherent good, and access to information must be earned instead. This approach was prompted, in part, by their own work scraping #gamergate Twitter feeds and the ways in which these data could be used to speak for others, in, without their consent.
From our vantage point, Rockwell and Berendt’s renewed call for an ethics of datafication is a timely one, as we are mired in media reports related to social media surveillance, electoral tampering, and on one side. Thanks, Facebook. On the other side, academics fight for the right to collect and access big data in order to reveal how gender and racial discrimination are embedded in the algorithms that structure everything from online real estate listings, to loan interest rates, to job postings (American Civil Liberties Union 2018). As surveillance studies scholars, we deeply appreciate how Rockwell and Berendt take a novel approach: they turn to a discussion of Freedom of Information (FOI), Freedom of Expression (FOE), Free and Open Source software, and Access to Information. In doing so, they unpack the assumptions commonly held by librarians, digital humanists and academics in general, to show that accumulation and datafication is not an inherent good.
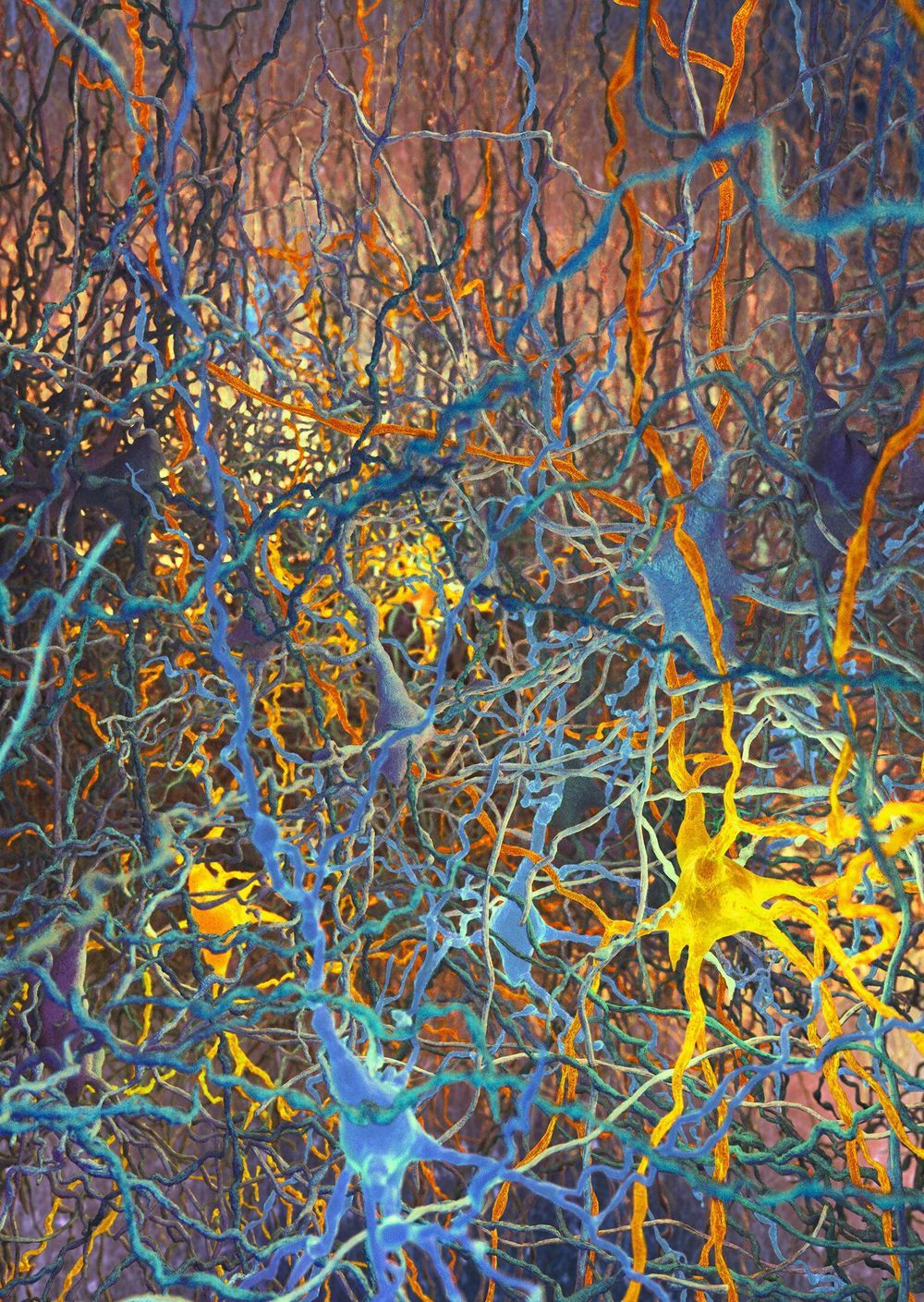
A team led by Lida Kanari now reports a new system for distinguishing cell types in the brain, an algorithmic classification method that the researchers say will benefit the entire field of neuroscience. Blue Brain founder Professor Henry Markram says, “For nearly 100 years, scientists have been trying to name cells. They have been describing them in the same way that Darwin described animals and trees. Now, the Blue Brain Project has developed a mathematical algorithm to objectively classify the shapes of the neurons in the brain. This will allow the development of a standardized taxonomy [classification of cells into distinct groups] of all cells in the brain, which will help researchers compare their data in a more reliable manner.”
The team developed an algorithm to distinguish the shapes of the most common type of neuron in the neocortex, the pyramidal cells. Pyramidal cells are distinctively tree-like cells that make up 80 percent of the neurons in the neocortex, and like antennas, collect information from other neurons in the brain. Basically, they are the redwoods of the brain forest. They are excitatory, sending waves of electrical activity through the network, as people perceive, act, and feel.
The father of modern neuroscience, Ramón y Cajal, first drew pyramidal cells over 100 years ago, observing them under a microscope. Yet up until now, scientists have not reached a consensus on the types of pyramidal neurons. Anatomists have been assigning names and debating the different types for the past century, while neuroscience has been unable to tell for sure which types of neurons are subjectively characterized. Even for visibly distinguishable neurons, there is no common ground to consistently define morphological types.
When Genevieve posted about optical tweezers, I noticed the similarity with acoustic tweezers, so I needed to post this article as well, so as to add to hers.
A new algorithm recently helped scientists levitate multiple objects using sound waves in very strategic positions. It marked the first time that sound helped capture numerous objects in various positions. The findings were recently published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Science. It was funded by the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) in the United Kingdom.
For the first time ever, an international team of researchers successfully used sound waves to make a series of objects float in strategic locations.
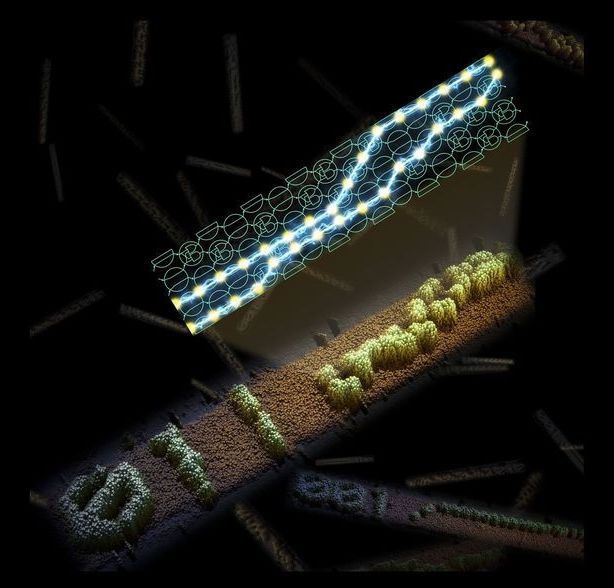
Computer scientists at the University of California, Davis, and the California Institute of Technology have created DNA molecules that can self-assemble into patterns essentially by running their own program. The work is published March 21 in the journal Nature.
“The ultimate goal is to use computation to grow structures and enable more sophisticated molecular engineering,” said David Doty, assistant professor of computer science at UC Davis and co-first author on the paper.
The system is analogous to a computer, but instead of using transistors and diodes, it uses molecules to represent a six-bit binary number (for example, 011001). The team developed a variety of algorithms that can be computed by the molecules.

A team of researchers at the Rochester Institute of Technology invented a “toilet seat-based cardiovascular monitoring system” that could help hospitals monitor patients for risk of congestive heart failure — a toilet, in other words, that detects whether your heart is about to give out.
“This system will be uniquely positioned to capture trend data in the home that has been previously unattainable,” reads the paper, published in the journal JMIR Mhealth Uhealth.
Integrated into the seat is a device that measures heart rate, blood pressure, and blood oxygenation levels. Algorithms will take in all that data and notify health practitioners if the patient’s condition deteriorates.