Physicists find hints that entanglement explains Einstein’s equations for gravity.

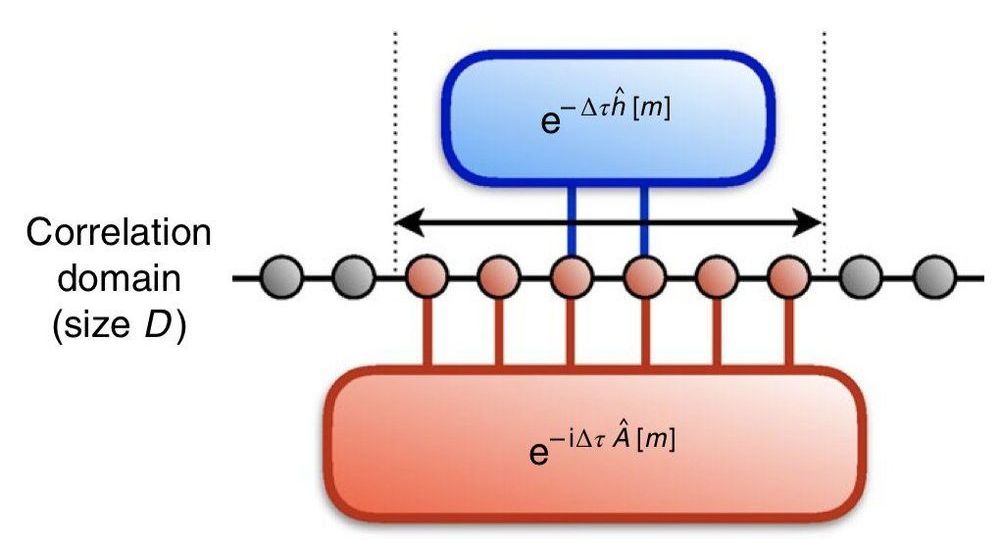
Determining the quantum mechanical behavior of many interacting particles is essential to solving important problems in a variety of scientific fields, including physics, chemistry and mathematics. For instance, in order to describe the electronic structure of materials and molecules, researchers first need to find the ground, excited and thermal states of the Born-Oppenheimer Hamiltonian approximation. In quantum chemistry, the Born-Oppenheimer approximation is the assumption that electronic and nuclear motions in molecules can be separated.
A variety of other scientific problems also require the accurate computation of Hamiltonian ground, excited and thermal states on a quantum computer. An important example are combinatorial optimization problems, which can be reduced to finding the ground state of suitable spin systems.
So far, techniques for computing Hamiltonian eigenstates on quantum computers have been primarily based on phase estimation or variational algorithms, which are designed to approximate the lowest energy eigenstate (i.e., ground state) and a number of excited states. Unfortunately, these techniques can have significant disadvantages, which make them impracticable for solving many scientific problems.
Ira Pastor, ideaXme exponential health ambassador, interviews Dr. Ronald Mallett, Professor Emeritus, Theoretical Physics, Department of Physics at the University of Connecticut.
Ira Pastor Comments:
Time travel is the concept of movement between certain points in time, analogous to movement between different points in space, by an object or a person, typically with the use of a hypothetical device known as a time machine.
Time travel is a widely recognized concept in philosophy and fiction and the idea of a time machine was originally popularized by H. G. Wells’ 1895 novel The Time Machine.
Forward time travel, outside the usual sense of the perception of time, is an extensively observed phenomenon and well-understood within the framework of special relativity and general relativity and making one body advance a few milliseconds compared to another body has been demonstrated in experiments comparing atomic clocks on jets and satelites versus the earth.
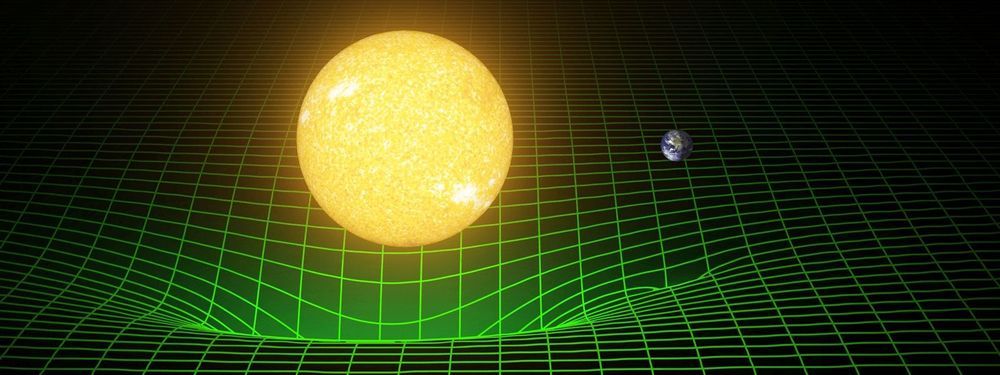
As for backward time travel, it is possible to find solutions in general relativity that allow for it, in a theoretical system known as a “closed timelike curve” (sometimes abbreviated CTC), which is where the world line of an object (the path that an object traces in 4-dimensional space-time) follows a curious path where it eventually returns to the exact same coordinates in space and time that it was at previously. In other words, a closed timelike curve is the mathematical result of physics equations that allows for time travel to the past.

“We want a new space race—space races are exciting,” declared SpaceX founder Elon Musk after the successful inaugural flight last year of the Falcon Heavy, the most powerful rocket since the Space Shuttle.
Hawks and headline writers think space races are exciting too, especially the “new space race” between China and the United States. That’s why they keep referring to it—even though it doesn’t exist.
Historic changes are indeed afoot in the space sector. Private crewed spaceflight is about to come of age. Mobile robotic spacecraft are being built to rendezvous with satellites to service them. Vast swarms of broadband satellites are set to make the Internet truly global for the first time, and increase the number of spacecraft in orbit tenfold. Back on Earth, satellite imagery fed through artificial intelligence algorithms promises powerful insights into all manner of human activity. Dozens of countries are active in space and the number is growing all the time. The tired trope of the superpower space race does little to make sense of all this.
Uncovering trolls and malicious or spammy accounts on social media is increasingly difficult as the miscreants find more and more ways to camouflage themselves as seemingly legitimate. Writing in the International Journal of Intelligent Engineering Informatics, researchers in India have developed an algorithm based on ant-colony optimization that can effectively detect accounts that represent a threat to normal users.
Asha Kumari and Balkishan Department of Computer Science and Applications at Maharshi Dayanand University, in Rohtak, India, explain that the connections between twitter users are analogous to the pheromone chemical communication between ants and this can be modeled in an algorithm based on how ant colonies behave to reveal the strongest connections in the twitter network and so uncover the accounts that one might deem as threatening to legitimate users.
The team’s tests on their system were successful in terms of precision, recall, f-measure, true-positive rate, and false-positive rate based on 26 features examined by the system played against almost 41,500 user accounts attracted to honeypots. Moreover, they report that the approach is superior to existing techniques. The team adds that they hope to be able to improve the system still further by adding so-called machine learning into the algorithm so that it can be trained to better identify threatening accounts based on data from known threats and legitimate accounts.
Over the last few years, rapid progress in AI has enabled our smartphones, social networks, and search engines to understand our voice, recognize our faces, and identify objects in our photos with very good accuracy. These dramatic improvements are due in large part to the emergence of a new class of machine learning methods known as Deep Learning.
Animals and humans can learn to see, perceive, act, and communicate with an efficiency that no Machine Learning method can approach. The brains of humans and animals are “deep”, in the sense that each action is the result of a long chain of synaptic communications (many layers of processing). We are currently researching efficient learning algorithms for such “deep architectures”. We are currently concentrating on unsupervised learning algorithms that can be used to produce deep hierarchies of features for visual recognition. We surmise that understanding deep learning will not only enable us to build more intelligent machines but will also help us understand human intelligence and the mechanisms of human learning. http://www.cs.nyu.edu/~yann/research/deep/
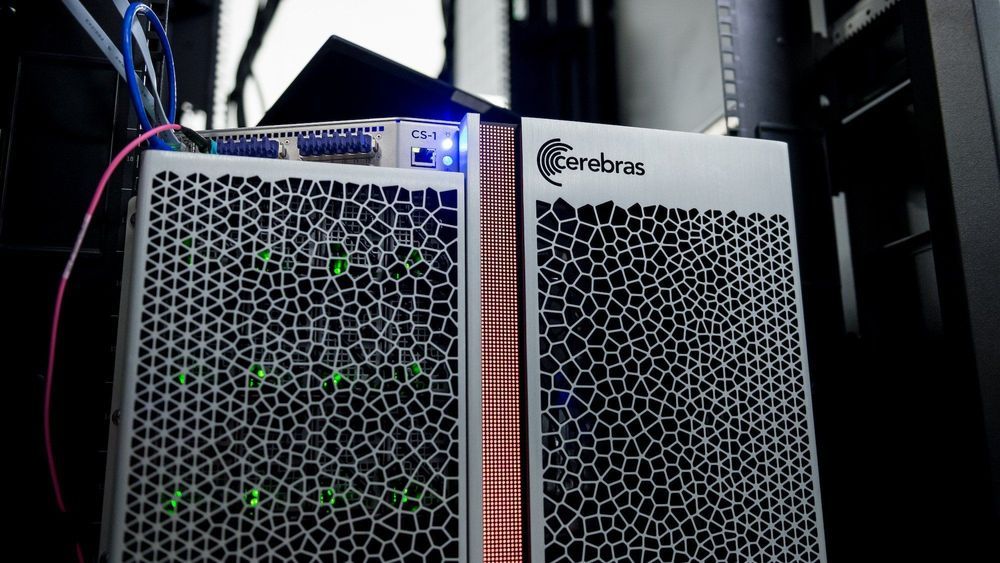

But in the last few years, AI has changed the game. Deep-learning algorithms excel at quickly finding patterns in reams of data, which has sped up key processes in scientific discovery. Now, along with these software improvements, a hardware revolution is also on the horizon.
Yesterday Argonne announced that it has begun to test a new computer from the startup Cerebras that promises to accelerate the training of deep-learning algorithms by orders of magnitude. The computer, which houses the world’s largest chip, is part of a new generation of specialized AI hardware that is only now being put to use.
“We’re interested in accelerating the AI applications that we have for scientific problems,” says Rick Stevens, Argonne’s associate lab director for computing, environment, and life sciences. “We have huge amounts of data and big models, and we’re interested in pushing their performance.”

Maybe interesting for this group too.
Visit http://TED.com to get our entire library of TED Talks, transcripts, translations, personalized Talk recommendations and more.
The danger of artificial intelligence isn’t that it’s going to rebel against us, but that it’s going to do exactly what we ask it to do, says AI researcher Janelle Shane. Sharing the weird, sometimes alarming antics of AI algorithms as they try to solve human problems — like creating new ice cream flavors or recognizing cars on the road — Shane shows why AI doesn’t yet measure up to real brains.
The TED Talks channel features the best talks and performances from the TED Conference, where the world’s leading thinkers and doers give the talk of their lives in 18 minutes (or less). Look for talks on Technology, Entertainment and Design — plus science, business, global issues, the arts and more. You’re welcome to link to or embed these videos, forward them to others and share these ideas with people you know. For more information on using TED for commercial purposes (e.g. employee learning, in a film or online course), submit a Media Request here: http://media-requests.TED.com
Follow TED on Twitter: http://twitter.com/TEDTalks
Like TED on Facebook: http://facebook.com/TED
Most humans can learn how to complete a given task by observing another person perform it just once. Robots that are programmed to learn by imitating humans, however, typically need to be trained on a series of human demonstrations before they can effectively reproduce the desired behavior.
Researchers were recently able to teach robots to execute new tasks by having them observe a single human demonstration, using meta-learning approaches. However, these learning techniques typically require real-world data that can be expensive and difficult to collect.
To overcome this challenge, a team of researchers at Imperial College London has developed a new approach that enables one-shot imitation learning in robots without the need for real-world human demonstrations. Their approach, presented in a paper pre-published on arXiv, uses algorithms known as task-embedded control networks (TecNets), which allow artificial agents to learn how to complete tasks from a single or multiple demonstrations, as well as artificially generated training data.