Despite millions of dollars in losses by the likes of Zillow, iBuying’s failure doesn’t signal the end of tech-led disruption, just a fumbled beginning.


Watch the full documentary on TUBI (free w/ads):
https://tubitv.com/movies/613341/consciousness-evolution-of-the-mind.
IMDb-accredited film, rated TV-PG
Director: Alex Vikoulov.
Narrator: Forrest Hansen.
Copyright © 2021 Ecstadelic Media Group, Burlingame, California, USA
*Based on The Cybernetic Theory of Mind eBook series (2022) by evolutionary cyberneticist Alex M. Vikoulov, available on Amazon:
as well as his magnum opus The Syntellect Hypothesis: Five Paradigms of the Mind’s Evolution (2020), available as eBook, paperback, hardcover, and audiobook on Amazon:
“You can’t explain consciousness in terms of classical physics or neuroscience alone. The best description of reality should be monistic. Quantum physics and consciousness are thus somehow linked by a certain mechanism… It is consciousness that assigns measurement values to entangled quantum states (qubits-to-digits of qualia, if you will). If we assume consciousness is fundamental, most phenomena become much easier to explain.
The Mind-Body dilemma has been known ever since René Descartes as Cartesian Dualism and later has been reformulated by the Australian philosopher David Chalmers as the ‘hard problem’ of consciousness. Western science and philosophy have been trying for centuries now, rather unsuccessfully, to explain how mind emerges from matter while Eastern philosophy dismisses the hard problem of consciousness altogether by teaching that matter emerges from mind. The premise of Experiential Realism is that the latter must be true: Despite our common human intuitions, Mind over Matter proves to be valid again and again in quantum physics experiments.
From the Digital Physics perspective, particles of matter are pixels, or voxels if you prefer, on the screen of our perception. Your Universe is in consciousness. And it’s a teleological process of unfolding patterns, evolution of your core self, ‘non-local’ consciousness instantiating into the phenomenal mind for the duration of a lifetime.

We are already living in the future. Our everyday lives are influenced by robots in many ways, whether we’re at home or at work. As artificial intelligence, open source algorithms, and cloud technology have been developed in recent years, they have contributed to creating favorable conditions for robot revolution, which is closer than you might expect.

View insights.
The growth potential of intelligent machines is attaining milestones almost every other day. Each day, new publications and media houses are reporting the new achievements of AI. But there were still questions about the creative potential of AI. Experts believe that artificial intelligence machines will never be able to achieve the creative consciousness that human intelligence possesses. Well, AI has again proved them wrong! The technology is now capable of creating its own art, out of its own imagination, and also poetry, that only the most deeply conscious human brains can do.
There have been several instances where programming and poetry have converged into generating some of the most outstanding pieces in the history of tech. Programming itself has its own set of minimalist aesthetics that does not take up much space and does not take too long to execute. Also, there have been many programmers who had links to poetry and art, which makes it easier for them to curate a mindblowing tech that can yield the same standard of results. Nowadays, companies like OpenAI create futuristic technology that is not only advanced but also boldly creative. In fact, its poetry-writing AI has made huge strides over the internet!
Verse by Verse, is a Google tool, that takes suggestions from classic American poets to compose poetry. The tool uses machine learning algorithms to identify the language pattern of a poet’s work and apply it to the poetry it generates. The tool allows users to choose from 22 different American classical poets and the type of poem they would like to write. The program offers poetic forms such as free verse, and quatrain, and also allows choosing the number of syllables to choose. What all it needs is, an opening line. Once given the first line, it generates the rest of the poem on its own, giving suggestions at every line, making it more interactive compared to other Open AI’s GPT-2 programs.
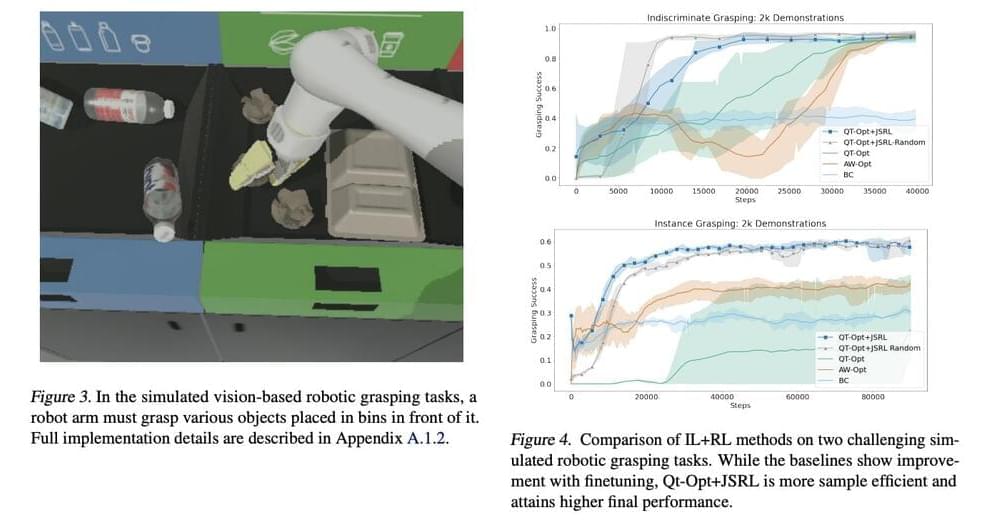
In the field of artificial intelligence, reinforcement learning is a type of machine-learning strategy that rewards desirable behaviors while penalizing those which aren’t. An agent can perceive its surroundings and act accordingly through trial and error in general with this form or presence – it’s kind of like getting feedback on what works for you. However, learning rules from scratch in contexts with complex exploration problems is a big challenge in RL. Because the agent does not receive any intermediate incentives, it cannot determine how close it is to complete the goal. As a result, exploring the space at random becomes necessary until the door opens. Given the length of the task and the level of precision required, this is highly unlikely.
Exploring the state space randomly with preliminary information should be avoided while performing this activity. This prior knowledge aids the agent in determining which states of the environment are desirable and should be investigated further. Offline data collected by human demonstrations, programmed policies, or other RL agents could be used to train a policy and then initiate a new RL policy. This would include copying the pre-trained policy’s neural network to the new RL policy in the scenario where we utilize neural networks to describe the procedures. This process transforms the new RL policy into a pre-trained one. However, as seen below, naively initializing a new RL policy like this frequently fails, especially for value-based RL approaches.
Google AI researchers have developed a meta-algorithm to leverage pre-existing policy to initialize any RL algorithm. The researchers utilize two procedures to learn tasks in Jump-Start Reinforcement Learning (JSRL): a guide policy and an exploration policy. The exploration policy is an RL policy trained online using the agent’s new experiences in the environment. In contrast, the guide policy is any pre-existing policy that is not modified during online training. JSRL produces a learning curriculum by incorporating the guide policy, followed by the self-improving exploration policy, yielding results comparable to or better than competitive IL+RL approaches.
If the W’s excess heft relative to the standard theoretical prediction can be independently confirmed, the finding would imply the existence of undiscovered particles or forces and would bring about the first major rewriting of the laws of quantum physics in half a century.
“This would be a complete change in how we see the world,” potentially even rivaling the 2012 discovery of the Higgs boson in significance, said Sven Heinemeyer, a physicist at the Institute for Theoretical Physics in Madrid who is not part of CDF. “The Higgs fit well into the previously known picture. This one would be a completely new area to be entered.”
The finding comes at a time when the physics community hungers for flaws in the Standard Model of particle physics, the long-reigning set of equations capturing all known particles and forces. The Standard Model is known to be incomplete, leaving various grand mysteries unsolved, such as the nature of dark matter. The CDF collaboration’s strong track record makes their new result a credible threat to the Standard Model.

Santiago Ramón y Cajal, a Spanish physician from the turn of the 19th century, is considered by most to be the father of modern neuroscience. He stared down a microscope day and night for years, fascinated by chemically stained neurons he found in slices of human brain tissue. By hand, he painstakingly drew virtually every new type of neuron he came across using nothing more than pen and paper. As the Charles Darwin for the brain, he mapped every detail of the forest of neurons that make up the brain, calling them the “butterflies of the brain”. Today, 200 years later, Blue Brain has found a way to dispense with the human eye, pen and paper, and use only mathematics to automatically draw neurons in 3D as digital twins. Math can now be used to capture all the “butterflies of the brain”, which allows us to use computers to build any and all the billons of neurons that make up the brain. And that means we are getting closer to being able to build digital twins of brains.
These billions of neurons form trillions of synapses – where neurons communicate with each other. Such complexity needs comprehensive neuron models and accurately reconstructed detailed brain networks in order to replicate the healthy and disease states of the brain. Efforts to build such models and networks have historically been hampered by the lack of experimental data available. But now, scientists at the EPFL Blue Brain Project using algebraic topology, a field of Math, have created an algorithm that requires only a few examples to generate large numbers of unique cells. Using this algorithm – the Topological Neuronal Synthesis (TNS), they can efficiently synthesize millions of unique neuronal morphologies.

In 1,832, Charles Darwin witnessed hundreds of ballooning spiders landing on the HMS Beagle while some 60 miles offshore. Ballooning is a phenomenon that’s been known since at least the days of Aristotle—and immortalized in E.B. White’s children’s classic Charlotte’s Web—but scientists have only recently made progress in gaining a better understanding of its underlying physics.
Now, physicists have developed a new mathematical model incorporating all the various forces at play as well as the effects of multiple threads, according to a recent paper published in the journal Physical Review E. Authors M. Khalid Jawed (UCLA) and Charbel Habchi (Notre Dame University-Louaize) based their new model on a computer graphics algorithm used to model fur and hair in such blockbuster films as The Hobbit and Planet of the Apes. The work could one day contribute to the design of new types of ballooning sensors for explorations of the atmosphere.
There are competing hypotheses for how ballooning spiders are able to float off into the air. For instance, one proposal posits that, as the air warms with the rising sun, the silk threads the spiders emit to spin their “parachutes” catch the rising convection currents (the updraft) that are caused by thermal gradients. A second hypothesis holds that the threads have a static electric charge that interacts with the weak vertical electric field in the atmosphere.
