Join the discussion on this paper page.


How can artificial intelligence help to improve the accuracy of lung cancer screening among people at high risk of developing the disease? Read to find out.
Lung cancers, the vast majority of which are caused by cigarette smoking, are the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the United States. Lung cancer kills more people than cancers of the breast, prostate, and colon combined. By the time lung cancer is diagnosed, the disease has often already spread outside the lung. Therefore, researchers have sought to develop methods to screen for lung cancer in high-risk populations before symptoms appear. They are evaluating whether the integration of artificial intelligence – the use of computer programs or algorithms that use data to make decisions or predictions – could improve the accuracy and speed of diagnosis, aid clinical decision-making, and lead to better health outcomes.

How the brain adjusts connections between #neurons during learning: this new insight may guide further research on learning in brain networks and may inspire faster and more robust learning #algorithms in #artificialintelligence.
Researchers from the MRC Brain Network Dynamics Unit and Oxford University’s Department of Computer Science have set out a new principle to explain how the brain adjusts connections between neurons during learning. This new insight may guide further research on learning in brain networks and may inspire faster and more robust learning algorithms in artificial intelligence.
The essence of learning is to pinpoint which components in the information-processing pipeline are responsible for an error in output. In artificial intelligence, this is achieved by backpropagation: adjusting a model’s parameters to reduce the error in the output. Many researchers believe that the brain employs a similar learning principle.
However, the biological brain is superior to current machine learning systems. For example, we can learn new information by just seeing it once, while artificial systems need to be trained hundreds of times with the same pieces of information to learn them. Furthermore, we can learn new information while maintaining the knowledge we already have, while learning new information in artificial neural networks often interferes with existing knowledge and degrades it rapidly.
In their public lecture at Perimeter on May 1, 2019, neuroscientist Anne M. Andrews and nanoscientist Paul S. Weiss outlined their scientific collaboration and explained the importance of communicating across disciplines to target significant problems. \
\
Perimeter Institute (charitable registration number 88,981 4323 RR0001) is the world’s largest independent research hub devoted to theoretical physics, created to foster breakthroughs in the fundamental understanding of our universe, from the smallest particles to the entire cosmos. The Perimeter Institute Public Lecture Series is made possible in part by the support of donors like you. Be part of the equation: https://perimeterinstitute.ca/inspiri…\
\
Subscribe for updates on future live webcasts, events, free posters, and more: https://insidetheperimeter.ca/newslet…\
\
facebook.com/pioutreach \
twitter.com/perimeter \
instagram.com/perimeterinstitute \
Donate: https://perimeterinstitute.ca/give-today
Alter 3 has just been unveiled by the University of Tokyo and its powered by GPT-4, capable of human-like activities and interpreting verbal instructions. Researchers at the Technical University of Munich developed a self-aware robot with proprioception, enhancing its movement and interaction capabilities. The University of Southern California introduced RoboCLIP, an algorithm that trains robots to perform tasks in new environments with minimal instruction. Intel Labs and partners created advanced motor control for robots using hierarchical generative models, significantly improving their ability to perform complex tasks.\
\
Deep Learning AI Specialization: https://imp.i384100.net/GET-STARTED\
AI Marketplace: https://taimine.com/\
\
AI news timestamps:\
0:00 Alter 3 GPT4 powered AI robot\
1:31 Robot self awareness\
3:30 RoboCLIP\
5:22 Motor control for autonomous robots\
\
#ai #robot #technology
Check Out Rogue History On PBS Origins: https://youtu.be/xuT35ud41QQPBS Member Stations rely on viewers like you. To support your local station, go to: http:/…
Did you know that Einstein’s most important equation isn’t E=mc^2? Find out all about his equation that expresses how spacetime curves, with Sean Carroll.
Buy Sean’s book here: https://geni.us/AIAOUHn.
YouTube channel members can watch the Q&A for this lecture here: • Q&A: The secrets of Einstein’s unknow…
Become one of our YouTube members for early, ad-free access to our videos, and other perks: / @theroyalinstitution.
This lecture was recorded at the Ri on Monday 14 August 2023.
00:00 Einstein’s most important equation.
3:37 Why Newton’s equations are so important.
9:30 The two kinds of relativity.
12:53 Why is it the geometry of spacetime that matters?
16:37 The principle of equivalence.
18:39 Types of non-Euclidean geometry.
26:26 The Metric Tensor and equations.
32:22 Interstellar and time and space twisting.
33:32 The Riemann tensor.
37:45 A physical theory of gravity.
43:28 How to solve Einstein’s equation.
47:50 Using the equation to make predictions.
51:05 How its been used to find black holes.
The real Einstein’s Equation is part of general relativity, which relates the curvature of spacetime to the mass and energy distributed within it.
An interview with J. Storrs Hall, author of the epic book “Where is My Flying Car — A Memoir of Future Past”: “The book starts as an examination of the technical limitations of building flying cars and evolves into an investigation of the scientific, technological, and social roots of the economic…
J. Storrs Hall or Josh is an independent researcher and author.
He was the founding Chief Scientist of Nanorex, which is developing a CAD system for nanomechanical engineering.
His research interests include molecular nanotechnology and the design of useful macroscopic machines using the capabilities of molecular manufacturing. His background is in computer science, particularly parallel processor architectures, artificial intelligence, particularly agoric and genetic algorithms.

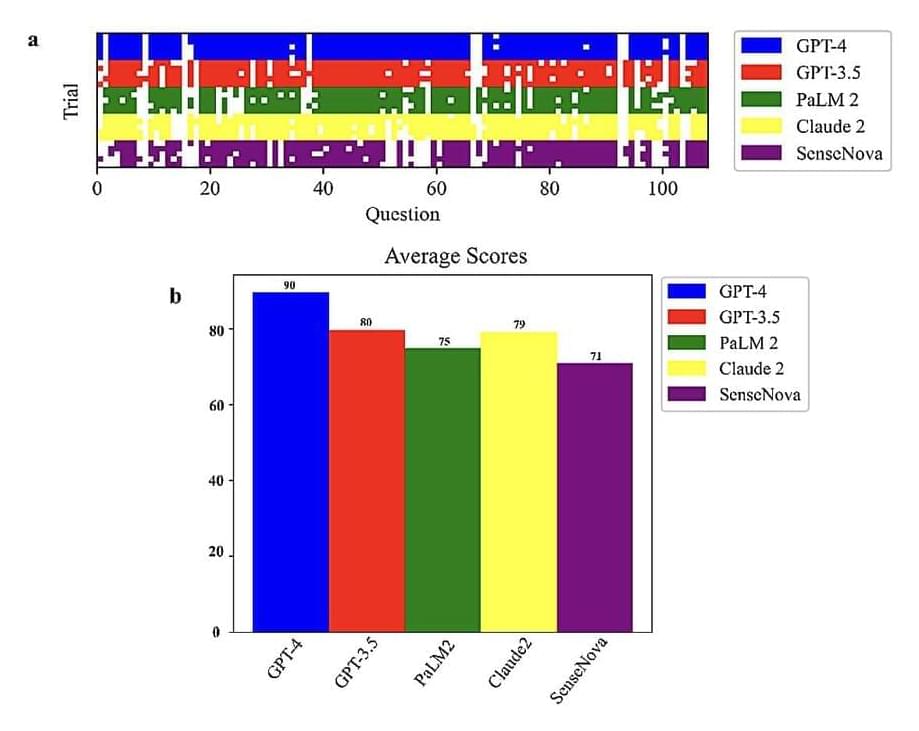
Large language models (LLMs) are advanced deep learning algorithms that can process written or spoken prompts and generate texts in response to these prompts. These models have recently become increasingly popular and are now helping many users to create summaries of long documents, gain inspiration for brand names, find quick answers to simple queries, and generate various other types of texts.
Researchers at the University of Georgia and Mayo Clinic recently set out to assess the biological knowledge and reasoning skills of different LLMs. Their paper, pre-published on the arXiv server, suggests that OpenAI’s model GPT-4 performs better than the other predominant LLMs on the market on reasoning biology problems.
“Our recent publication is a testament to the significant impact of AI on biological research,” Zhengliang Liu, co-author of the recent paper, told Tech Xplore. “This study was born out of the rapid adoption and evolution of LLMs, especially following the notable introduction of ChatGPT in November 2022. These advancements, perceived as critical steps towards Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), marked a shift from traditional biotechnological approaches to an AI-focused methodology in the realm of biology.”