The future of medicine may very well lie in the personalization of health care—knowing exactly what an individual needs and then delivering just the right mix of nutrients, metabolites, and medications, if necessary, to stabilize and improve their condition. To make this possible, physicians first need a way to continuously measure and monitor certain biomarkers of health.
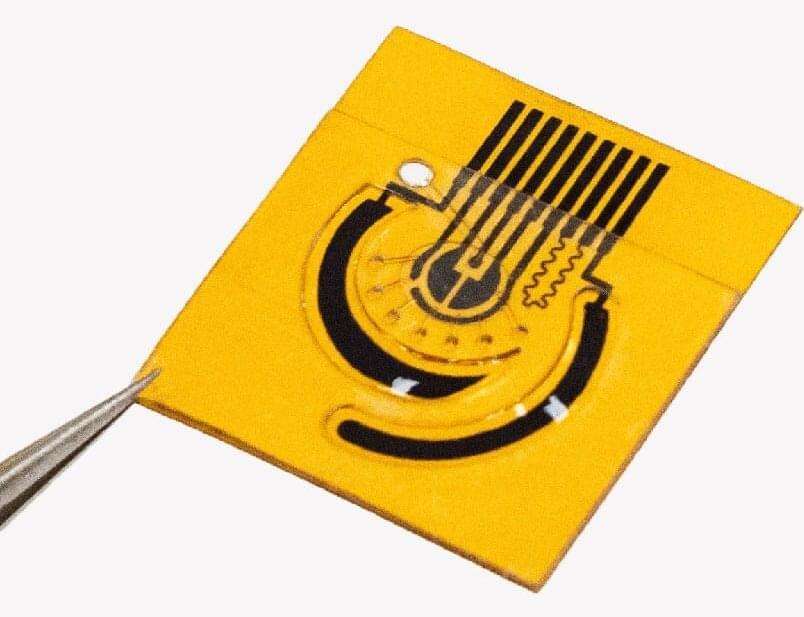
To that end, a team of Caltech engineers has developed a technique for inkjet printing arrays of special nanoparticles that enables the mass production of long-lasting wearable sweat sensors. These sensors could be used to monitor a variety of biomarkers, such as vitamins, hormones, metabolites, and medications, in real time, providing patients and their physicians with the ability to continually follow changes in the levels of those molecules.
Wearable biosensors that incorporate the new nanoparticles have been successfully used to monitor metabolites in patients suffering from long COVID and the levels of chemotherapy drugs in cancer patients at City of Hope in Duarte, California.