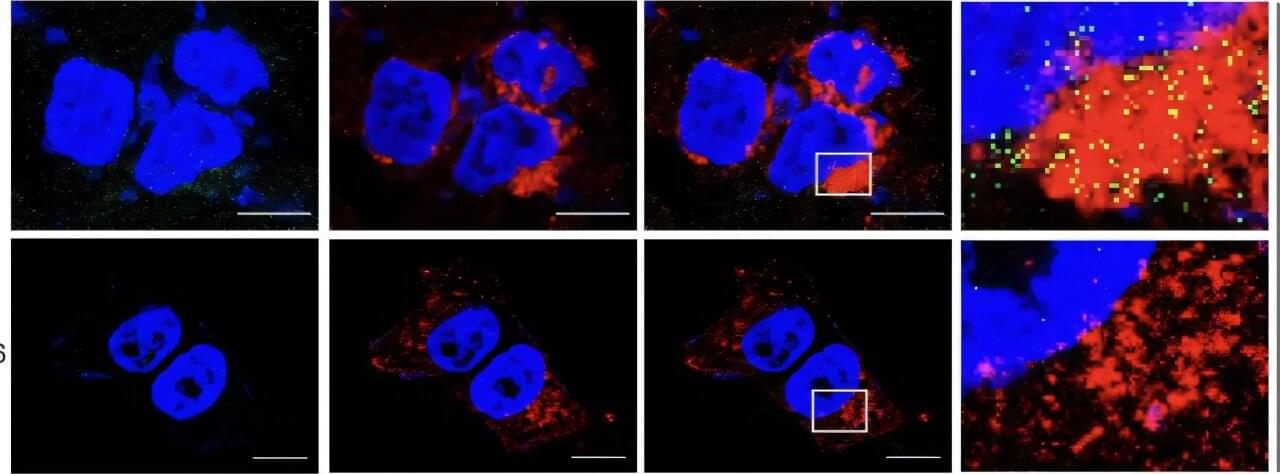
A new USC study suggests that gut imbalances in children with autism may create an imbalance of metabolites in the digestive system—ultimately disrupting neurotransmitter production and influencing behavioral symptoms.
The research, published in Nature Communications, adds to a growing body of science implicating the “gut-brain” axis in autism. The discovery raises the possibility of new treatment avenues. It’s an example of how research at USC, and other universities, drives innovation and leads to discoveries that improve lives.
“We demonstrated that gut metabolites impact the brain, and the brain, in turn, affects behavior. Essentially, the brain acts as the intermediary between gut health and autism-related behaviors,” said first author Lisa Aziz-Zadeh, a professor at the Brain and Creativity Institute at the USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences.