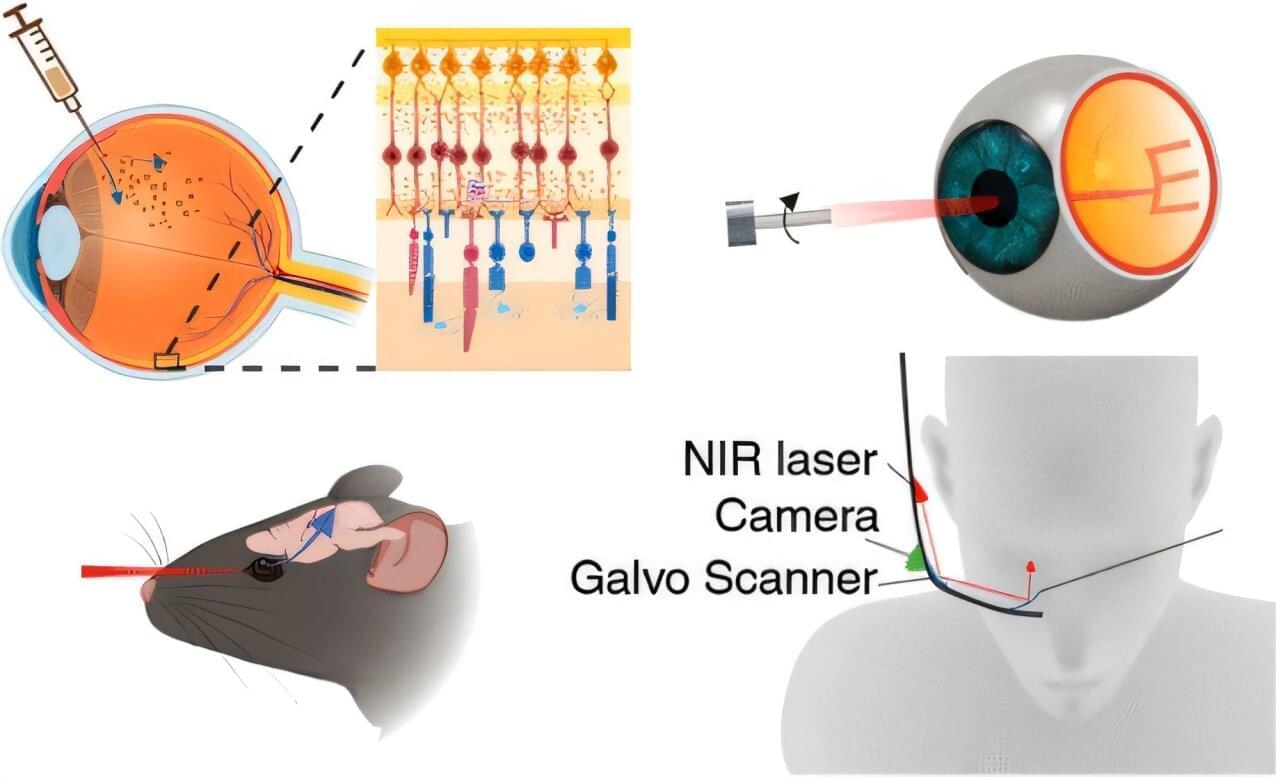
A new study by Brown University researchers suggests that gold nanoparticles—microscopic bits of gold thousands of times thinner than a human hair—might one day be used to help restore vision in people with macular degeneration and other retinal disorders.
In a study published in the journal ACS Nano, the research team showed that nanoparticles injected into the retina can successfully stimulate the visual system and restore vision in mice with retinal disorders. The findings suggest that a new type of visual prosthesis system in which nanoparticles, used in combination with a small laser device worn in a pair of glasses or goggles, might one day help people with retinal disorders to see again.
“This is a new type of retinal prosthesis that has the potential to restore vision lost to retinal degeneration without requiring any kind of complicated surgery or genetic modification,” said Jiarui Nie, a postdoctoral researcher at the National Institutes of Health who led the research while completing her Ph.D. at Brown. “We believe this technique could potentially transform treatment paradigms for retinal degenerative conditions.”