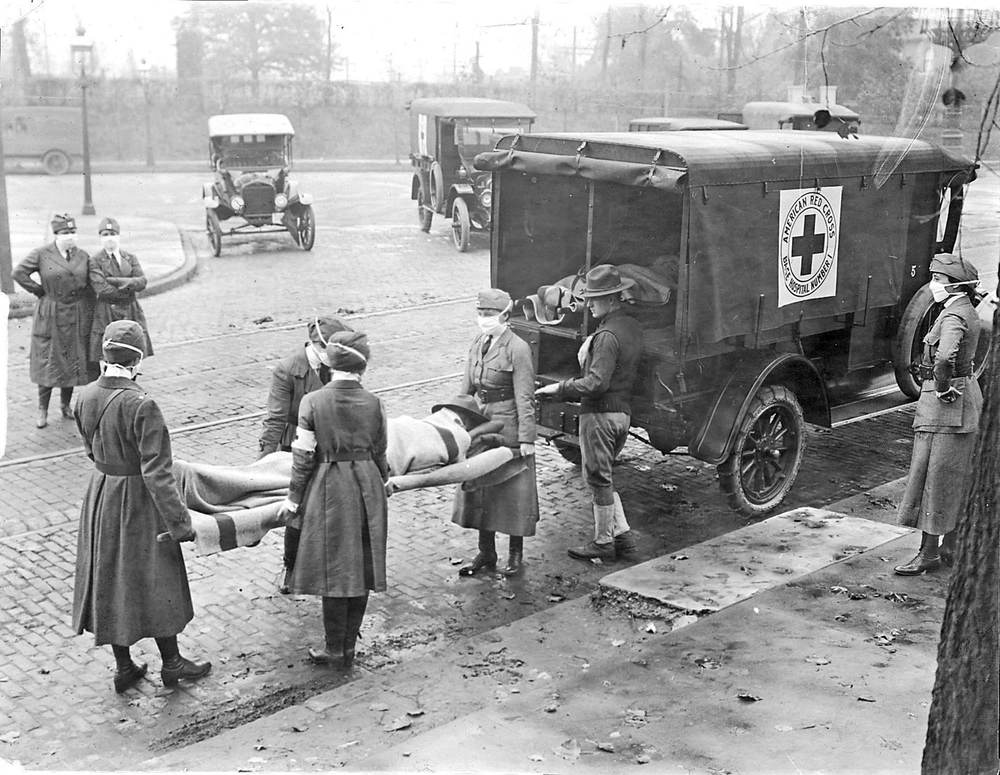
Additionally, some reports have suggested that then-President Woodrow Wilson downplayed the virus, but that is a “wrong and a false trope of popular history,” Markel said. Wilson, who would later contract the virus, was organizing and commanding the U.S. effort in World War I and once the war ended, he sailed for Paris, where he stayed until April of 1919 organizing a peace treaty and the League of Nations, Markel said.
“The federal government played a very small role in American public health during that era. It was primarily a city and state role and those agencies were hardly downplaying it,” he said.
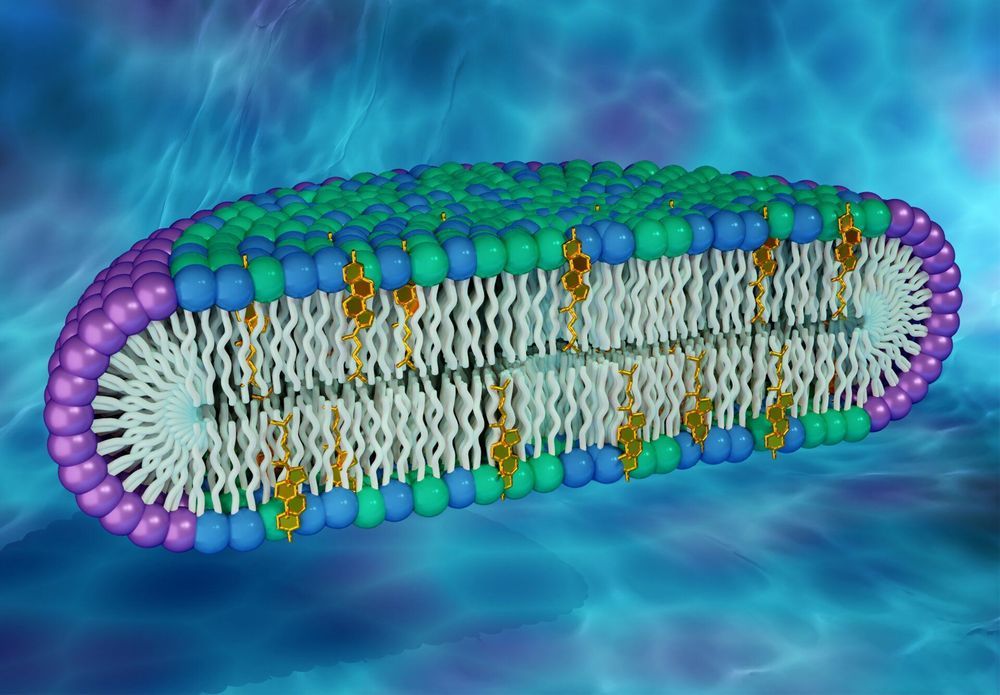
Unlike today, there was no CDC or national public health department. The Food and Drug Administration existed but consisted of a very small group of men. Additionally, there were no antibiotics, intensive care units, ventilators, IV fluids or vaccines. “You got a bed or maybe nursing care,” Markel said.