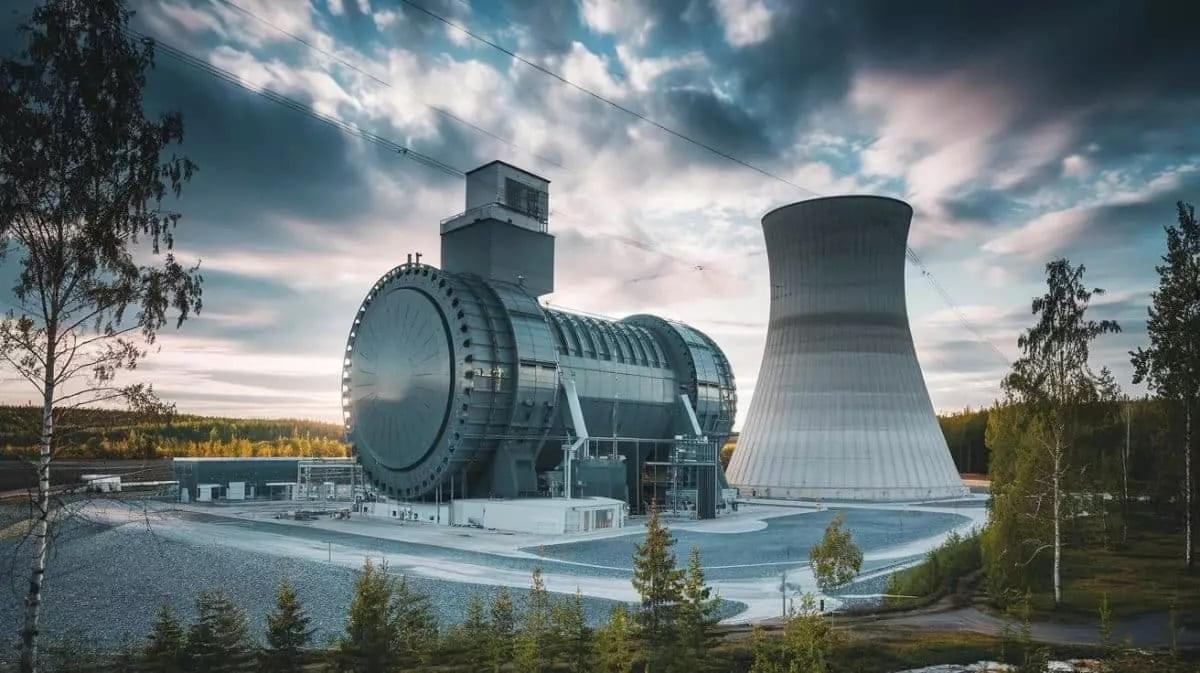
In a bold move towards a sustainable future, Helsinki, Finland’s capital, has installed the world’s largest heat pump, a groundbreaking piece of technology that has the capacity to power 30,000 homes. This ambitious project is a significant step in the fight against climate change, utilizing renewable energy sources to provide a reliable and efficient heating system even in the coldest of winters. In this article, we’ll explore how this technological marvel works, its environmental impact, and the potential it has to change energy production on a global scale.
Helsinki’s heat pump represents a major breakthrough in energy technology. The system works by transferring heat from a colder environment to a warmer one, ensuring maximum energy efficiency. One of the most impressive features of this heat pump is its use of carbon dioxide as a refrigerant, which allows the pump to generate heat at temperatures of up to 90°C.
A standout innovation is the oil-free compressor, a key component that ensures the system operates efficiently while minimizing its environmental footprint. This marks the first time such a system has been implemented on this scale, reinforcing Finland’s commitment to adopting sustainable solutions for energy production. By using renewable energy sources like wind and solar power, this heat pump reduces the need for fossil fuels and helps Finland move towards a more sustainable energy future.