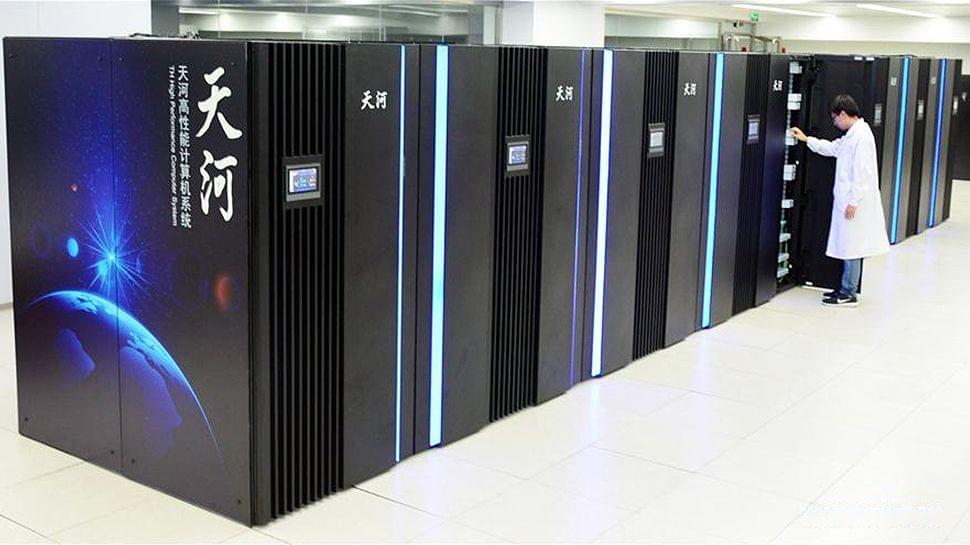
After the U.S. government imposed crippling sanctions against select Chinese high-tech and supercomputer companies through 2019 and 2020, firms like Huawei had to halt chip development; it is impossible to build competitive processors without access to leading-edge nodes. But Jiangnan Computing Lab, which develops Sunway processors, and National Supercomputing Center in Wuxi kept building new supercomputers and recently even submitted results of their latest machine for the Association for Computing Machinery’s Gordon Bell prize.
The new Sunway supercomputer built by the National Supercomputing Center in Wuxi (an entity blacklisted in the U.S.) employs around feature approximately 19.2 million cores across 49,230 nodes, reports Supercomputing.org. To put the number into context, Frontier, the world’s highest-performing supercomputer, uses 9,472 nodes and consumes 21 MW of power. Meanwhile, the National Supercomputing Center in Wuxi does not disclose power consumption of its latest system.