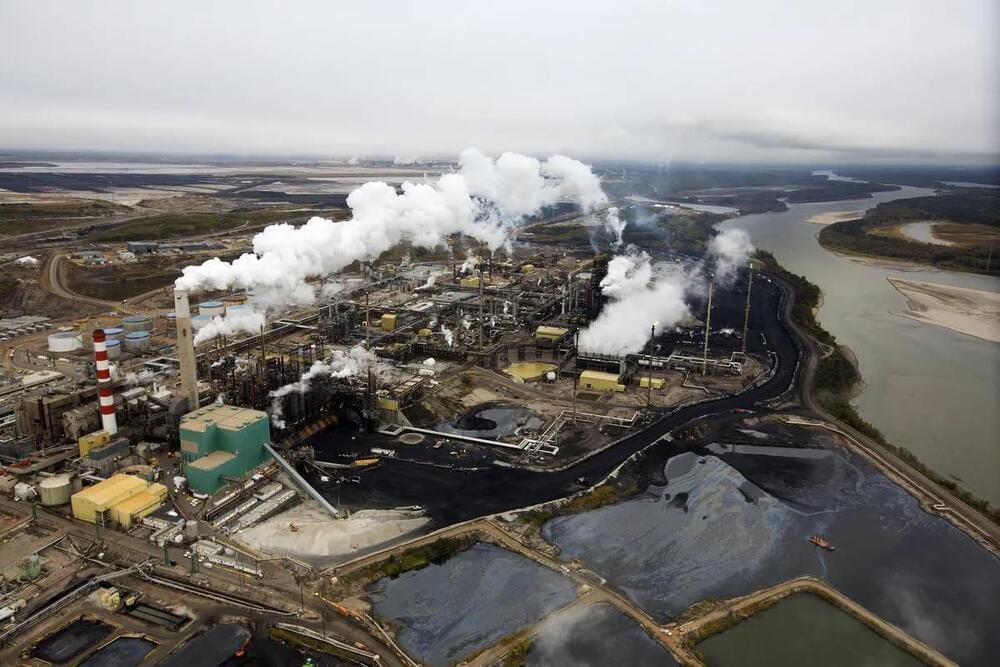
Canada’s largest oilsands companies under the umbrella of the Pathways Alliance are accused of greenwashing and making false environmental claims. via @torontostar
Greenpeace Canada alleges the consortium’s ad campaign, “Let’s clear the air,” is greenwashing — when a company makes false or misleading claims about the environmental attributes of their business.
“Our request to the Competition Bureau regarding the Pathways Alliance’s misleading ad campaign was accepted and has set off an official inquiry into the dubious advertising practices of the Pathways Alliance,” Greenpeace Canada’s senior researcher and writer, Nola Poirier, said in a statement. “We think the public deserves to be told the truth about the environmental harm caused by fossil fuel production, not fed misleading sound bites by industry.”
Mark Cameron, vice-president external relations at Pathways Alliance, said the campaign acknowledges the oilsands represents a significant share of Canada’s emissions and collaborative efforts must be made across the industry and with government to deliver “responsibly produced oil.”