Just like how letters are strung together to form words, our DNA is also strung together by letters to encode proteins. The genetic alphabet contains only 4 natural letters — A, C, G and T, which hold the blueprint for the production of proteins that make our bodies work. Now, researchers from the Institute of Bioengineering and Nanotechnology (IBN) of the Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR) have created a DNA technology with two new genetic letters that could better detect infectious diseases, such as dengue and Zika.
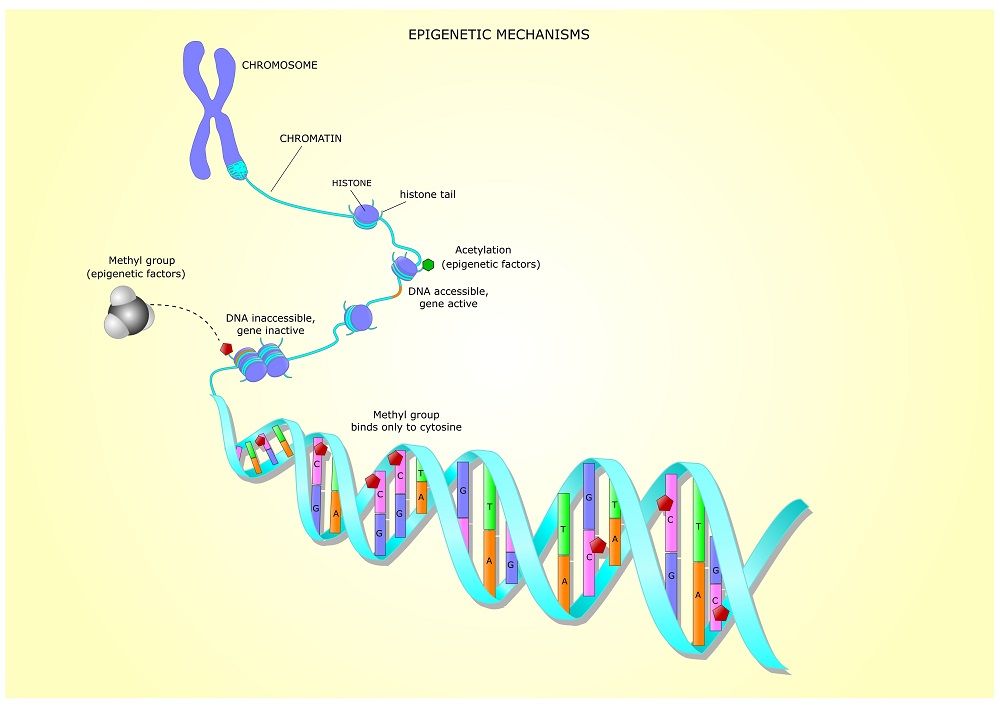
Genetic alphabet expansion technology is the introduction of artificial base pairs into DNA. The existing four genetic letters are naturally bound together in base pairs of A-T and G-C. These specific base pair formations are essential in DNA replication, which occurs in all living organisms. It is the process by which a DNA molecule is duplicated to produce two identical molecules.
“The expansion of the genetic alphabet is a significant scientific achievement. It sheds insights into DNA’s natural replication mechanism, which will help us to design unique DNA molecules and technologies. For example, our technology can be used to create novel diagnostics and therapeutic agents with superior efficacy,” said IBN Executive Director Professor Jackie Ying.