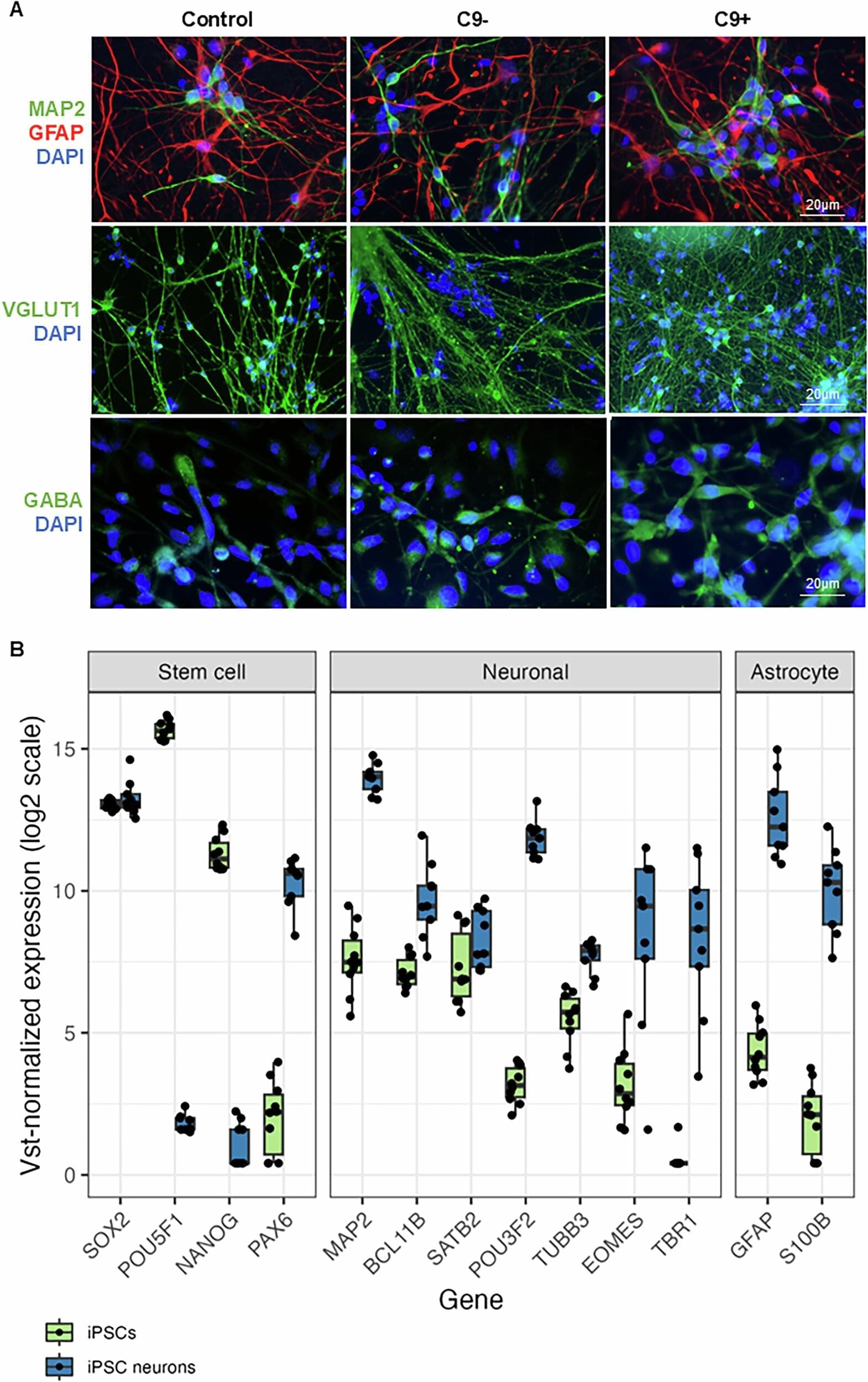
Neurons produced from frontotemporal dementia patients’ skin biopsies using modern stem cell technology recapitulate the synaptic loss and dysfunction detected in the patients’ brains, a new study from the University of Eastern Finland shows.
Frontotemporal dementia is a progressive neurodegenerative disease affecting the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain. The most common symptoms are behavioral changes, difficulties in understanding or producing speech, problems in movement, and psychiatric symptoms.
Often, frontotemporal dementia has no identified genetic cause, but especially in Finnish patients, hexanucleotide repeat expansion in the C9orf72 gene is a common genetic cause, present in about half of the familial cases and in 20% of the sporadic cases where there is no family history of the disease.