Year 2019 😗
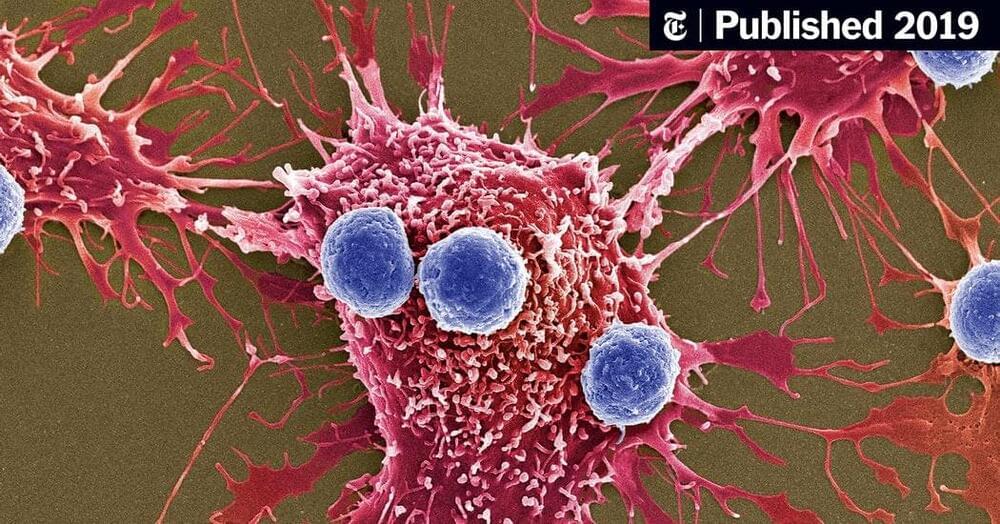
Genetically modified microbes release “nanobodies” that alert the immune system to cancer in mice, scientists report.
What led to the emergence of complex organisms on Earth? It’s a significant unanswered question in biology. Researchers from Christa Schleper’s team at the University of Vienna and Martin Pilhofer’s team at ETH Zurich have taken a step towards resolving it. The scientists succeeded in cultivating a special archaeon and characterizing it more precisely using microscopic methods.
This member of the Asgard archaea exhibits unique cellular characteristics and may represent an evolutionary “missing link” to more complex life forms such as animals and plants. The study was recently published in the journal Nature.
All life forms on earth are divided into three major domains: eukaryotes, bacteria and archaea. Eukaryotes include the groups of animals, plants and fungi. Their cells are usually much larger and, at first glance, more complex than the cells of bacteria and archaea. The genetic material of eukaryotes, for example, is packaged in a cell nucleus and the cells also have a large number of other compartments. Cell shape and transport within the eukaryotic cell are also based on an extensive cytoskeleton. But how did the evolutionary leap to such complex eukaryotic cells come about?

Join us on Patreon!
https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhD
Green Tea Discount Link (Ocha & Co)
https://www.ochaandco.com/?ref=conqueraging.
Bristle Discount Link (Oral Microbiome Quantification):
ConquerAging15
https://www.bmq30trk.com/4FL3LK/GTSC3/
TruDiagnostic Discount Link (Epigenetic Testing)
CONQUERAGING!
https://bit.ly/3Rken0n.
Quantify Discount Link (At-Home Blood Testing):
https://getquantify.io/mlustgarten.
Cronometer Discount Link (Daily Diet Tracking):


Epigenetic Leaderboard The Rejuvenation Olympics – where you win by never crossing the finish line See How You Rank Top 15 largest age reversals validated by phenotypically trained epigenetic methylation algorithms Rank Name % Improved From Baseline Chronological Age Baseline PACE PACE Of Aging Now (Mean Of 3 Tests) Managing Doctor 1 Bryan […].
I never thought I’d order live human kidney cells to my address, but that all changed when I found out about biohacker Jo Zayner’s at-home genetic engineering class.
You may know Jo Zayner, a “biohacker” who has been in the vanguard of scientific self-experimentation for years, from their role in Netflix’s 2019 docuseries Unnatural Selection. The series shows Zayner attempting to edit their DNA by injecting themselves with CRISPR, a gene-editing technology. The action inspired a firestorm of criticism.
Zayner is also known for a variety of other bold moves, such as claiming to create a DIY at-home COVID vaccine in 2020 and executing their own fecal microbiome transplant.
CRISPR may be in for a fight thanks to this new, faster, safer, AI-powered zinc-finger gene-editing technique.
A new study has developed what the researchers call the “world’s first” simple, modifiable proteins. Called “zinc fingers,” these special proteins were developed partially through artificial intelligence.
Scientists from the University of Toronto and the NYU Grossman School of Medicine came up with the method, which is expected to speed up the development of gene therapies. This could be a game-changer for how doctors treat DNA mistakes that happen over time. This is partly because our genes change naturally as we age, which makes it inevitable that mistakes will happen. Or, of course, from genetic disorders inherited at birth.

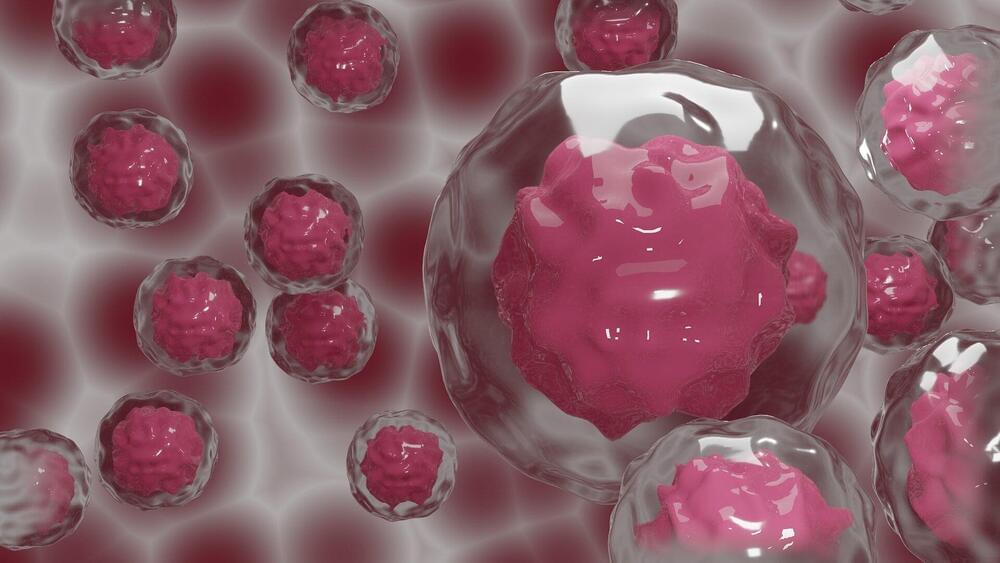
Cancer cells can shrink or super-size themselves to survive drug treatment or other challenges within their environment, researchers have discovered.
Scientists at The Institute of Cancer Research, London, combined biochemical profiling technologies with mathematical analyses to reveal how genetic changes lead to differences in the size of cancer cells—and how these changes could be exploited by new treatments.
The researchers believe smaller cells could be more vulnerable to DNA-damaging agents like chemotherapy combined with targeted drugs, while larger cancer cells might respond better to immunotherapy.