We know that migraines, which are recurrent and sometimes debilitating headaches, have some genetic basis, but the link with our DNA isn’t entirely clear. Newly identified genetic variants could help in developing treatments.
By Chen Ly

We know that migraines, which are recurrent and sometimes debilitating headaches, have some genetic basis, but the link with our DNA isn’t entirely clear. Newly identified genetic variants could help in developing treatments.
By Chen Ly
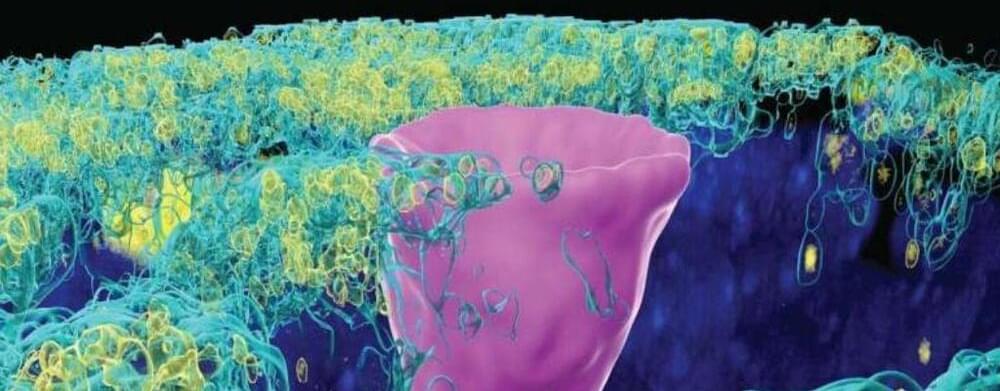
A type of cell once only thought to exist in the gills of freshwater fish and the skin of frogs, but recently found in humans lungs, has given scientists new insight into the underlying cause of cystic fibrosis (CF).
CF is a progressive, genetic disease that impacts the lungs and other organs, sometimes causing severe symptoms that can be life-threatening.
The disease is marked by the absence or mutation of a protein in the lungs called the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR).

The only cure for painful sickle cell disease today is a bone marrow transplant. But soon there may be a new cure that attacks the disorder at its genetic source.
On Tuesday, advisers to the Food and Drug Administration will review a gene therapy for the inherited blood disorder, which in the U.S. mostly affects Black people. Issues they will consider include whether more research is needed into possible unintended consequences of the treatment.
If approved by the FDA, it would be the first gene therapy on the U.S. market based on CRISPR, the gene editing tool that won its inventors the Nobel Prize in 2020.
A team of researchers has developed a software tool called DANGER (Deleterious and ANticipatable Guides Evaluated by RNA-sequencing) analysis that provides a way for the safer design of genome editing in all organisms with a transcriptome. For about a decade, researchers have used the CRISPR technology for genome editing. However, there are some challenges in the use of CRISPR. The DANGER analysis overcomes these challenges and allows researchers to perform safer on-and off-target assessments without a reference genome. It holds the potential for applications in medicine, agriculture, and biological research.
Their work is published in the journal Bioinformatics Advances on August 23, 2023.
Genome editing, or gene editing, refers to technologies that allow researchers to change the genomic DNA of an organism. With these technologies, researchers can add, remove or alter genetic material in the genome.
Get a Wonderful Person Tee: https://teespring.com/stores/whatdamath.
More cool designs are on Amazon: https://amzn.to/3wDGy2i.
Alternatively, PayPal donations can be sent here: http://paypal.me/whatdamath.
Hello and welcome! My name is Anton and in this video, we will talk about recent discoveries about human brain and various types of neuronal cells.
Links:
https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-023-03192-2
https://nemoarchive.org/
https://www.science.org/collections/brain-cell-census.
https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.adc8810
https://news.rub.de/english/press-releases/2022-06-0…ir-neurons.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41559-022-01933-6
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-06502-w.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41593-023-01284-w.
https://elifesciences.org/articles/76143
Previous video on major discoveries: https://youtu.be/iGdFh3ENjzc.
More about Neanderthals: https://youtu.be/BvrBl9-TbBs.
#brain #neuron #neuroscience.
0:00 Recent papers on the human brain.
1:00 Human brain atlas and 3,000 new types of cells.
2:00 What was this collaboration for?
2:40 Unexpected complexity of cells in certain brain parts.
4:00 Are there a lot of individual differences? Yes!
4:40 Physical structure appears same across species.
5:10 Genetic activity is very different though.
5:35 Human disorders are unique to humans.
6:30 Unusual layers protecting the brain — SLYM
7:38 Axons turned out to be more unusual, especially in other species.
9:35 Shape of the brain suggests apes and humans are similar only until adolescence.
12:15 Hippocampus in humans is unique focusing on vision…explaining art?
13:48 New memory cell discovered.
15:45 Limitations.
Support this channel on Patreon to help me make this a full time job:
https://www.patreon.com/whatdamath.
Bitcoin/Ethereum to spare? Donate them here to help this channel grow!
bc1qnkl3nk0zt7w0xzrgur9pnkcduj7a3xxllcn7d4
or ETH: 0x60f088B10b03115405d313f964BeA93eF0Bd3DbF
Space Engine is available for free here: http://spaceengine.org.
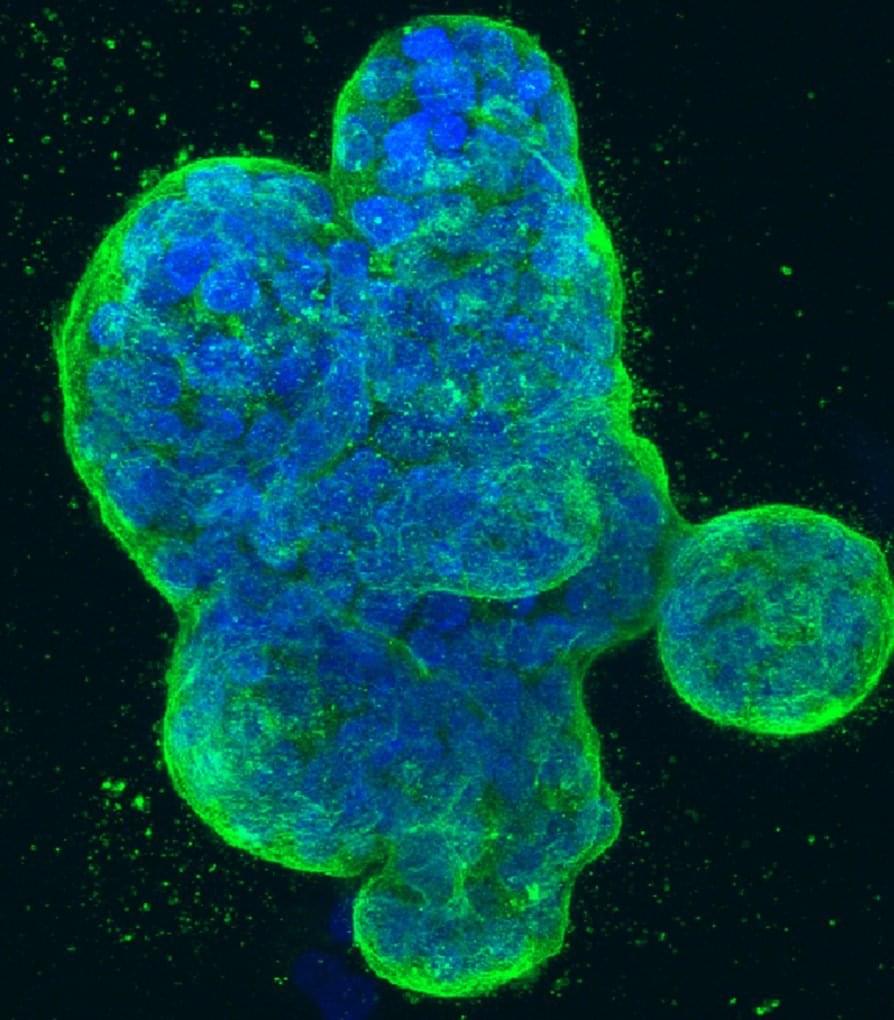
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine have identified a small molecule named 5D4 that can suppress the growth of breast and ovarian cancers in animal models. 5D4 works by binding to TopBP1 protein in cancer cells, disrupting its interactions with several pathways that promote cancer growth. Combining 5D4 with another cancer inhibitor, talazoparib, enhances the effectiveness of the anti-cancer activity.
The study, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, strongly supports continuing the investigation toward further developing this strategy for clinical use.
“Cancer development involves many steps of genetic alterations and signaling pathway deregulation. About 10 years ago, our team discovered that protein TopBP1 is at a convergent point of multiple cellular pathways involved in cancer growth and progression, making it a potential candidate for targeted cancer therapy,” said corresponding author Dr. Weei-Chin Lin, professor of medicine-hematology and oncology and of molecular and cellular biology at Baylor. He also is a member of Baylor’s Dan L Duncan Comprehensive Cancer Center. “Our idea was to identify molecules that would bind to TopBP1 and interfere with its interactions with molecular pathways that promote cancer growth.”


A threat actor who claimed responsibility for the compromise of the 23AndMe site earlier this month has released a new dataset, including the records of more than 4 million people’s genetic ancestry.
The cybercriminal, known by the handle Golem, alleges in a cybercrime Dark Web forum the stolen data includes information on, “the wealthiest people living in the US and Western Europe,” according to reports.
23andMe spokesperson Andy Kill said in a statement the organization is still trying to confirm whether the most recently leaked data is genuine.
Join us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhD
Discount Links:
NAD+ Quantification: https://www.jinfiniti.com/intracellular-nad-test/
Use Code: ConquerAging At Checkout.
Epigenetic Testing: https://trudiagnostic.com/?irclickid=U-s3Ii2r7xyIU-LSYLyQdQ6…M0&irgwc=1
Use Code: CONQUERAGING
At-Home Metabolomics: https://www.iollo.com?ref=michael-lustgarten.
Use Code: CONQUERAGING At Checkout.
At-Home Blood Testing: https://getquantify.io/mlustgarten.
Oral Microbiome: https://www.bristlehealth.com/?ref=michaellustgarten.

One of the most popular dog breeds is the Golden Retriever. Unfortunately, these dogs are also at high risk for developing cancer. New research has investigated genetic factors that may be able to extend the lives of these beloved dogs. This work focused on longevity genes instead of those that have been associated with cancer, and led to the identification of gene variants that could extend the dogs’ lifespan by as much as two years. The findings have been reported in GeroScience.
While most golden retrievers are predisposed to cancer, some of these dogs can live to be as old as 15 or 16 years. So the researchers thought that there might be genetic factors that were mitigating the effect of the cancer-related genes, noted co-corresponding study author Robert Rebhun, Maxine Adler Endowed Chair in oncology at the UC Davis School of Veterinary Medicine. The gene that had this effect was HER4.