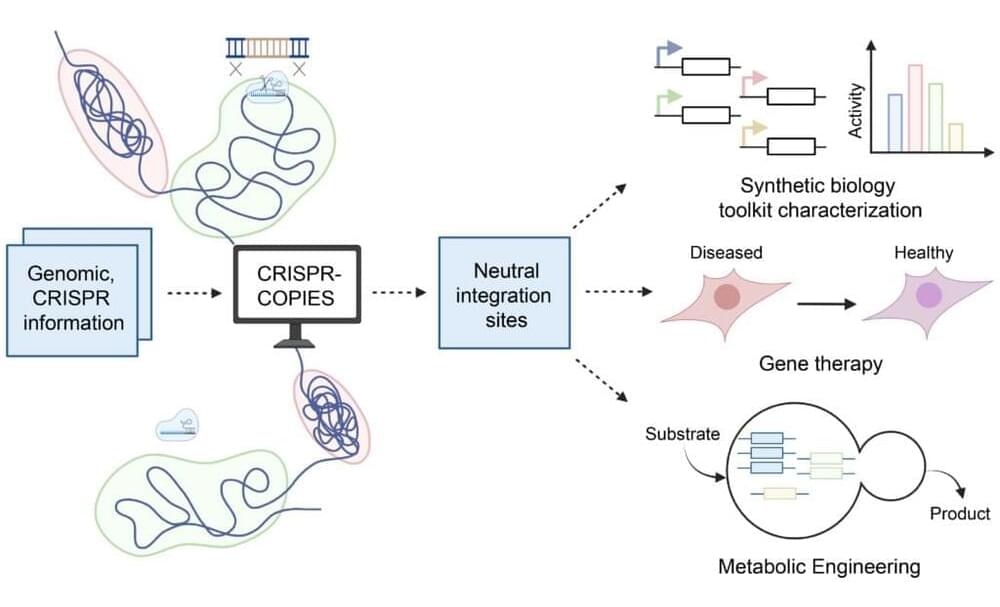
CRISPR/Cas systems have undergone tremendous advancement in the past decade. These precise genome editing tools have applications ranging from transgenic crop development to gene therapy and beyond. And with their recent development of CRISPR-COPIES, researchers at the Center for Advanced Bioenergy and Bioproducts Innovation (CABBI) are further improving CRISPR’s versatility and ease of use.
“CRISPR-COPIES is a tool that can quickly identify appropriate chromosomal integration sites for genetic engineering in any organism,” said Huimin Zhao, CABBI Conversion Theme Leader and Steven L. Miller Chair of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering (ChBE) at the University of Illinois. “It will accelerate our work in the metabolic engineering of non-model yeasts for cost-effective production of chemicals and biofuels.”
Gene editing has revolutionized scientists’ capabilities in understanding and manipulating genetic information. This form of genetic engineering allows researchers to introduce new traits into an organism, such as resistance to pests or the ability to produce a valuable biochemical.