Among survivors of non-small cell lung cancer, nearly 8% developed non-lung secondary cancers over about 6 years, and this risk may be driven by genetic factors.


Humans have it. So does Drosophila. But not yeast. That “it” is a small pause at the start of gene activity—a brief molecular halt that may have helped life evolve from simple cells to complex animals.
A new study by Charles Danko, associate professor in life science and technology at Cornell’s Baker Institute for Animal Health and in the Department of Biomedical Sciences in the College of Veterinary Medicine, and colleagues explores how this key step in gene regulation—promoter-proximal pausing—evolved across species.
Promoter-proximal pausing occurs just after a cell’s molecular “copy machine”– RNA polymerase II—is activated. The polymerase temporarily stops, usually after about 20 to 60 nucleotides or “letters” of the gene, waiting for further signals.

A new study from the MRC Laboratory of Medical Sciences (LMS) in London, UK reveals how ancient viral DNA once written off as “junk” plays a crucial role in the earliest moments of life. The research, published in Science Advances, begins to untangle the role of an ancient viral DNA element called MERVL in mouse embryonic development and provides new insights into a human muscle wasting disease.
Transposable elements are stretches of DNA that can move around the genome. Many of these DNA sequences originate from long ago, when viruses inserted their genetic material into our ancestors’ genomes during infection. Today, these viral transposable elements make up around 8–10% of the mammalian genome.
Once disregarded as “junk” DNA, we now know that many transposable elements play an important role in influencing how genes are turned on and off, especially during early development. They have a variety of beneficial and harmful roles in the body, for example, some help regulate normal immune responses, while others can disrupt genes and contribute to diseases like cancer.
Epigenetic clocks, based on DNA methylation profiles at CpG sites, are widely recognized as reliable biomarkers of biological aging. However, common single-nucleotide polymorphisms (cSNPs), genomic variants that can overlap CpG sites, may affect DNA methylation profiles in ways that potentially interfere with the accuracy of epigenetic clocks. Moreover, because the prevalence of cSNPs varies across populations, such cSNP-CpG overlaps may differentially affect the age predictions of epigenetic clocks in diverse cohorts. Here, we present the first systematic cross-ancestry evaluation of cSNP robustness in the epigenetic clock, examining how cSNP-CpG overlaps affect the performance of epigenetic clocks across nine major genomic ancestry groups. We employed three complementary strategies: (a) testing whether cSNP-CpG overlaps are overrepresented in established epigenetic clocks or particular populations, (b) evaluating whether overlapping CpG sites correspond to the most influential aging predictors within clock models, and © simulating the effects of cSNP-associated methylation changes on predicted biological age. Our findings indicate that cSNP-CpG overlaps are not enriched among the CpG sites used in current epigenetic clocks, nor do they tend to involve the most influential sites. Furthermore, our simulation analysis revealed that current epigenetic clocks appear robust to cSNP-related methylation variations. Our findings underscore the overall stability of current epigenetic clocks, even in the presence of population-specific cSNP-CpG overlaps that are known to affect DNA methylation levels.
The authors have declared no competing interest.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by the disruption of nerve signals and various associated neurological symptoms, ranging from vision problems to numbness, weakness, fatigue and cognitive impairments. These symptoms emerge when the immune system starts to attack mature oligodendrocytes (MOLs), specialized cells that produce the protective sheath surrounding nerve fibers (i.e., myelin).
There are several subtypes of MOLs, which might exhibit different immune cell-like genetic responses in patients diagnosed with MS. While various studies have investigated the neural and molecular underpinnings of MS, how these different cell subtypes respond as the disease progresses has not yet been elucidated.
Researchers at Karolinska Institute in Sweden recently carried out a mouse study aimed at mapping how different MOL subtypes might differ in their sensitivity to neuroinflammation across different stages of MS.
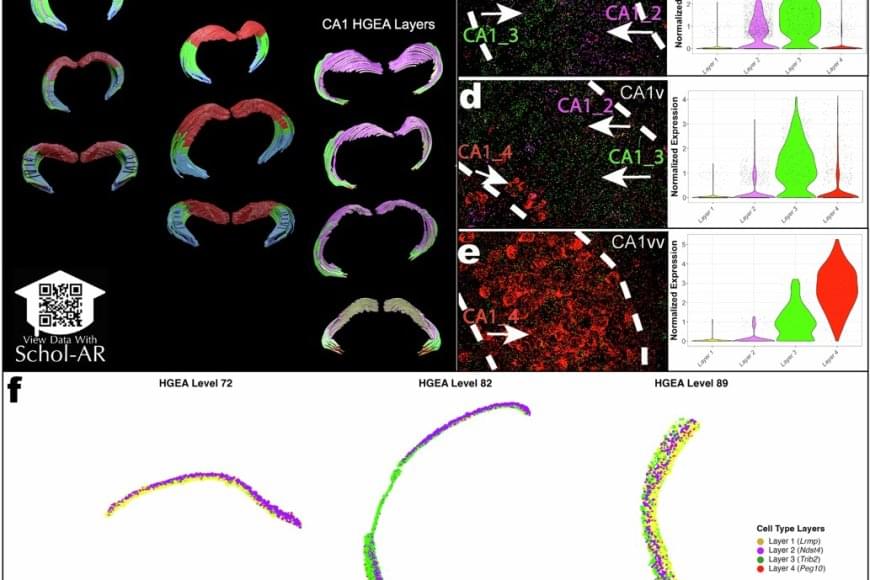
Using a powerful RNA labeling method called RNAscope with high-resolution microscopy imaging, the team captured clear snapshots of single-molecule gene expression to identify CA1 cell types inside mouse brain tissue. Within 58.065 CA1 pyramidal cells, they visualized more than 330,000 RNA molecules—the genetic messages that show when and where genes are turned on. By tracing these activity patterns, the researchers created a detailed map showing the borders between different types of nerve cells across the CA1 region of the hippocampus.
The results showed that the CA1 region consists of four continuous layers of nerve cells, each marked by a distinct set of active genes. In 3D, these layers form sheets that vary slightly in thickness and structure along the length of the hippocampus. This clear, layered pattern helps make sense of earlier studies that saw the region as a more gradual mix or mosaic of cell types.
“When we visualized gene RNA patterns at single-cell resolution, we could see clear stripes, like geological layers in rock, each representing a distinct neuron type,” said a co–first author of the paper. “It’s like lifting a veil on the brain’s internal architecture. These hidden layers may explain differences in how hippocampal circuits support learning and memory.”
The hippocampus is among the first regions affected in Alzheimer’s disease and is also implicated in epilepsy, depression, and other neurological conditions. By revealing the CA1’s layered structure, the study provides a roadmap to investigate which specific neuron types are most vulnerable in these disorders.
The new CA1 cell-type atlas, built using data from the Hippocampus Gene Expression Atlas (HGEA), is freely available to the global research community. The dataset includes interactive 3D visualizations accessible through the Schol-AR augmented-reality app, which allows scientists to explore hippocampal layers in unprecedented detail.
Researchers have identified a previously unknown pattern of organization in one of the brain’s most important areas for learning and memory. The study, published in Nature Communications, reveals that the CA1 region of a mouse’s hippocampus, a structure vital for memory formation, spatial navigation, and emotions, has four distinct layers of specialized cell types. This discovery changes our understanding of how information is processed in the brain and could explain why certain cells are more vulnerable in diseases like Alzheimer’s and epilepsy.
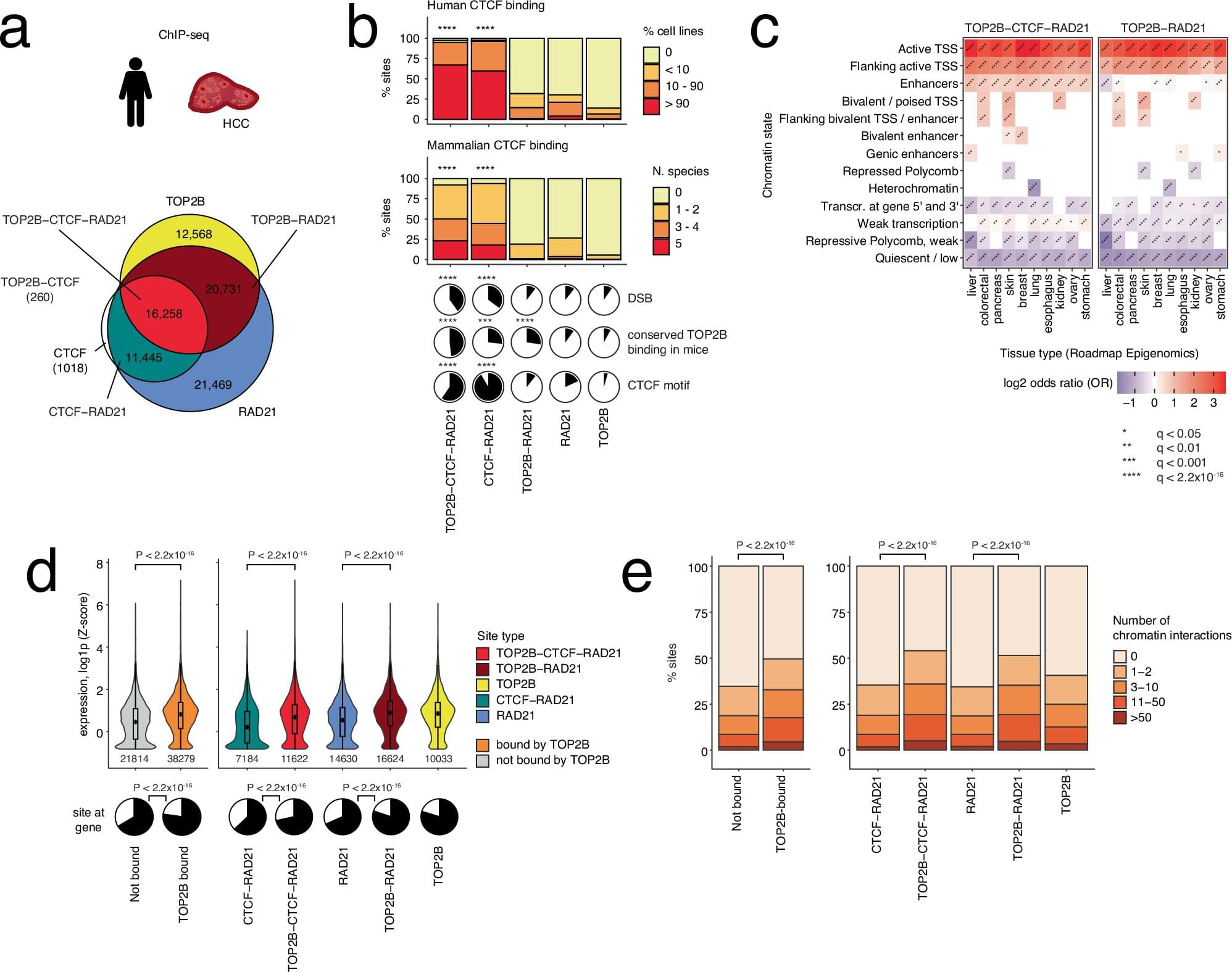
New research published in Nature Communications has linked a normal cellular process to an accumulation of DNA mutations in cancer and identified cancer-driving mutations in an underexplored part of the genome.
Led by Dr. Jüri Reimand of the Ontario Institute for Cancer Research (OICR), the study centers around a protein called TOP2B, part of a family of enzymes that serve an important function in cells and are targets of common cancer chemotherapies.
Strands of DNA are long and complex, and they often get looped and tangled. When that happens, TOP2B and other topoisomerase proteins make cuts to DNA strands to help untangle and repair them. But Reimand and colleagues found many genetic mutations present at the sites of these cuts.
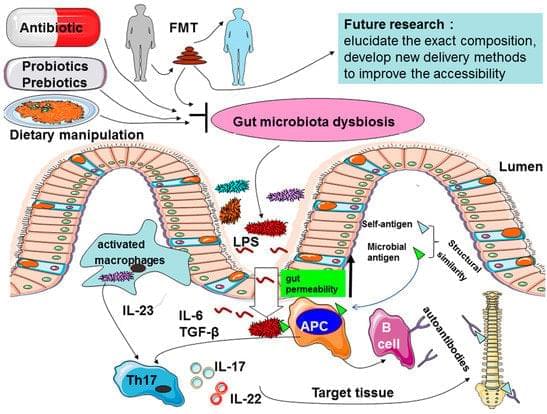
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory disease primarily affecting the sacroiliac joints and the spine, for which the pathogenesis is thought to be a result of the combination of host genetic factors and environmental triggers. However, the precise factors that determine one’s susceptibility to AS remain to be unraveled. With 100 trillion bacteria residing in the mammalian gut having established a symbiotic relation with their host influencing many aspects of host metabolism, physiology, and immunity, a growing body of evidence suggests that intestinal microbiota may play an important role in AS. Several mechanisms have been suggested to explain the potential role of the microbiome in the etiology of AS, such as alterations of intestinal permeability, stimulation of immune responses, and molecular mimicry.