Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is defined by synaptic and neuronal degeneration and loss accompanied by amyloid beta (Aβ) plaques and tau neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs)1,2,3. In vivo animal experiments indicate that both Aβ and tau pathologies synergistically interact to impair neuronal circuits4. For example, the hypersynchronous epileptiform activity observed in over 60% of AD cases5 may be generated by surrounding Aβ and/or tau deposition yielding neuronal network hyperactivity5,6. Cortical and hippocampal network hyperexcitability precedes memory impairment in AD models7,8. In an apparent feedback loop, endogenous neuronal activity, in turn, regulates Aβ aggregation, in both animal models and computational simulations9,10. Multiple other factors involved in AD pathogenesis-remarkably, neuroinflammatory dysregulations-also seemingly influence neuronal firing and act on hypo/hyperexcitation patterns11,12,13. Thus, mounting evidence suggest that neuronal excitability changes are a key mechanistic event appearing early in AD and a tentative therapeutic target to reverse disease symptoms3,4,7,14. However, the exact patterns of Aβ, tau and other disease factors’ neuronal activity alterations in AD’s neurodegenerative progression are unclear as in vivo and non-invasive measuring of neuronal excitability in human subjects remains impractical.
Brain imaging and electrophysiological monitoring constitute a reliable readout for brain network degeneration likely associating with AD’s neuro-functional alterations3,15,16,17,18. Patients present distinct resting-state blood-oxygen-level-dependent (BOLD) signal content in the low frequency fluctuations range (0.01–0.08 Hz)16,19. These differences increase with disease progression, from cognitively unimpaired (CU) controls to mild cognitive impairment (MCI) to AD, correlating with performance on cognitive tests16. Another characteristic functional change is the slowing of the electro-(magneto-) encephalogram (E/MEG), with the signal shifting towards low frequency bands15,18. Electrophysiological spectral changes associate with brain atrophy and with losing connections to hub regions including the hippocampus, occipital and posterior areas of the default mode network20. All these damages are known to occur in parallel with cognitive impairment20. Disease processes also manifest differently given subject-specific genetic and environmental conditions1,21. Models of multiple pathological markers and physiology represent a promising avenue for revealing the connection between individual AD fingerprints and cognitive deficits3,18,22.
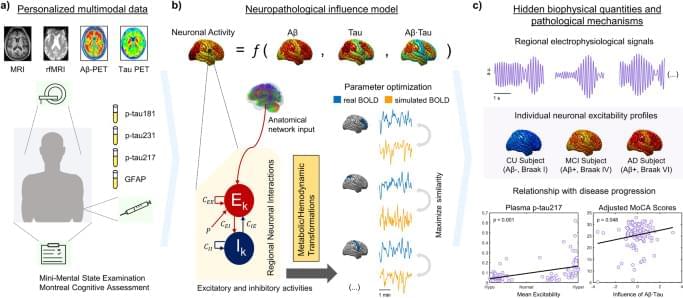
In effect, large-scale neuronal dynamical models of brain re-organization have been used to test disease-specific hypotheses by focusing on the corresponding causal mechanisms23,24,25. By considering brain topology (the structural connectome18) and regional profiles of a pathological agent24, it is possible to recreate how a disorder develops, providing supportive or conflicting evidence on the validity of a hypothesis23. Generative models follow average activity in relatively large groups of excitatory and inhibitory neurons (neural masses), with large-scale interactions generating E/MEG signals and/or functional MRI observations26. Through neural mass modeling, personalized virtual brains were built to describe Aβ pathology effects on AD-related EEG slowing25 and several hypotheses for neuronal hyperactivation have been tested27. Simulated resting-state functional MRI across the AD spectrum was used to estimate biophysical parameters associated with cognitive deterioration28. In addition, different intervention strategies to counter neuronal hyperactivity in AD have been tested10,22. Notably, comprehensive computational approaches combining pathophysiological patterns and functional network alterations allow the quantification of non-observable biological parameters29 like neuronal excitability values in a subject-specific basis1,3,18,21,23,24, facilitating the design of personalized treatments targeting the root cause(s) of functional alterations in AD.