Like it or not, humans are becoming as gods. Where will this trend lead?How about the ability to bring back to life people who died years, decades, or centur…
Category: futurism – Page 418
Hamza Ahmed ‐ T-duality and flavor symmetries of Heterotic Little String Theories (LSTs)
6D Heterotic Little String Theories(LSTs) are a subsector of every 6D SUGRA (with at least one tensor multiplet), after decoupling gravity. As such, while possessing usual QFT-like properties such as global symmetries, they also possess gravity-like properties such as T-duality, which makes them an interesting intermediate. Recently, a fruitful line of research has been to chart the landscape of T-dual LSTs, and establish certain invariants across this T-duality, which includes the 5D Coulomb branch dimension, and the 2-Group structure constants (mixed anomalies). In this talk, we will argue that the rank of the flavor algebra is another invariant across this duality. This involves using 6D anomaly cancellation conditions and carefully taking into account potential ABJ anomalies. We will then discuss some interesting novel LSTs with non-trivial flavor holonomies, focusing on their T-duality structure. Based on arXiv:2311.02168.
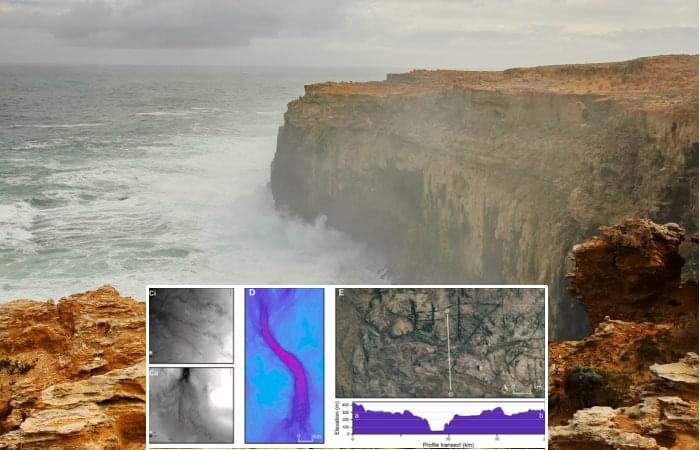

Large Underwater Site That Was Home To 500,000 People About 14,000 Years Ago Identified Northwest Of Australia
Jan Bartek — AncientPages.com — Some already call it Australia’s lost Atlantis, but it is not quite the mythical underwater city Plato mentions. A large underwater site that was home to hundreds of thousands of people has been identified and mapped by scientists. Rising seas submerged the land northwest of Australia at the end of the last glacial period.
Rough sea along the coast in Australia. Credit: Adobe Stock — totajla
Using newly available high-resolution sonar data, the research team reconstructed the topography of the 400,000 square kilometers of land that is now covered by the Indian Ocean, known as the Northwest Shelf.

Indian Tectonic Plate Is Splitting in Two Beneath Tibet, Latest Analysis Finds
The engines driving the growth of the world’s highest mountains into the sky run deep beneath the planet’s skin. Geologists have some idea of the mechanisms at work, but evidence has so far left plenty of room for debate over the details.
Combined with a fresh look at previous research, a recent analysis of new seismic data collected from across southern Tibet has delivered a surprising depiction of the titanic forces operating below the Himalayas.
Presenting at the American Geophysical Union conference in San Francisco last December, researchers from institutions in the US and China described a disintegration of the Indian continental plate as it grinds along the basement of the Eurasian tectonic plate that sits atop it.


New graphene semiconductor could revolutionize electronics
The first working graphene semiconductor outperformed silicon, suggesting that the supermaterial could be the future of electronics.

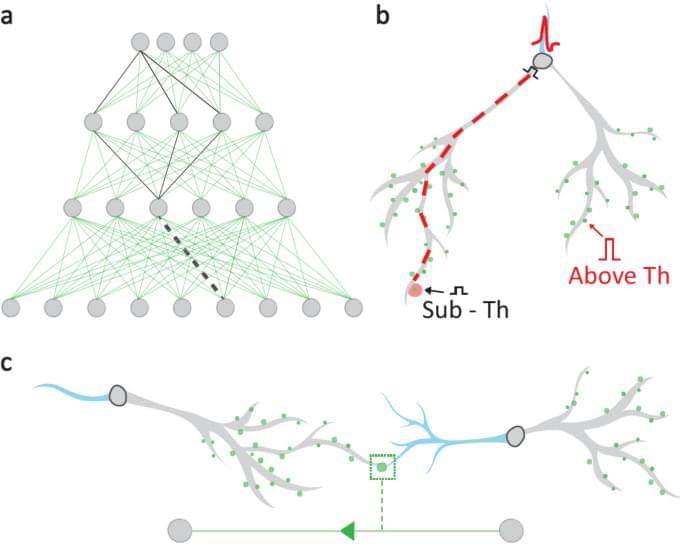
Efficient dendritic learning as an alternative to synaptic plasticity hypothesis
Hodassman, S., Vardi, R., Tugendhaft, Y. et al. Efficient dendritic learning as an alternative to synaptic plasticity hypothesis. Sci Rep 12, 6,571 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-10466-8
Seismic Shifts: USGS Unveils Groundbreaking Earthquake Hazard Map
The research-based map is the first to display an updated, comprehensive National Seismic Hazard Model for all 50 states.
Nearly 75 percent of the U.S. could experience damaging earthquake shaking, according to a recent U.S. Geological Survey-led team of 50+ scientists and engineers.
This was one of several key findings from the latest USGS National Seismic Hazard Model (NSHM). The model was used to create a color-coded map that pinpoints where damaging earthquakes are most likely to occur based on insights from seismic studies, historical geologic data, and the latest data-collection technologies.