SonicWall released fixes for an actively exploited SMA 100 vulnerability enabling privilege escalation and chained root access attacks.



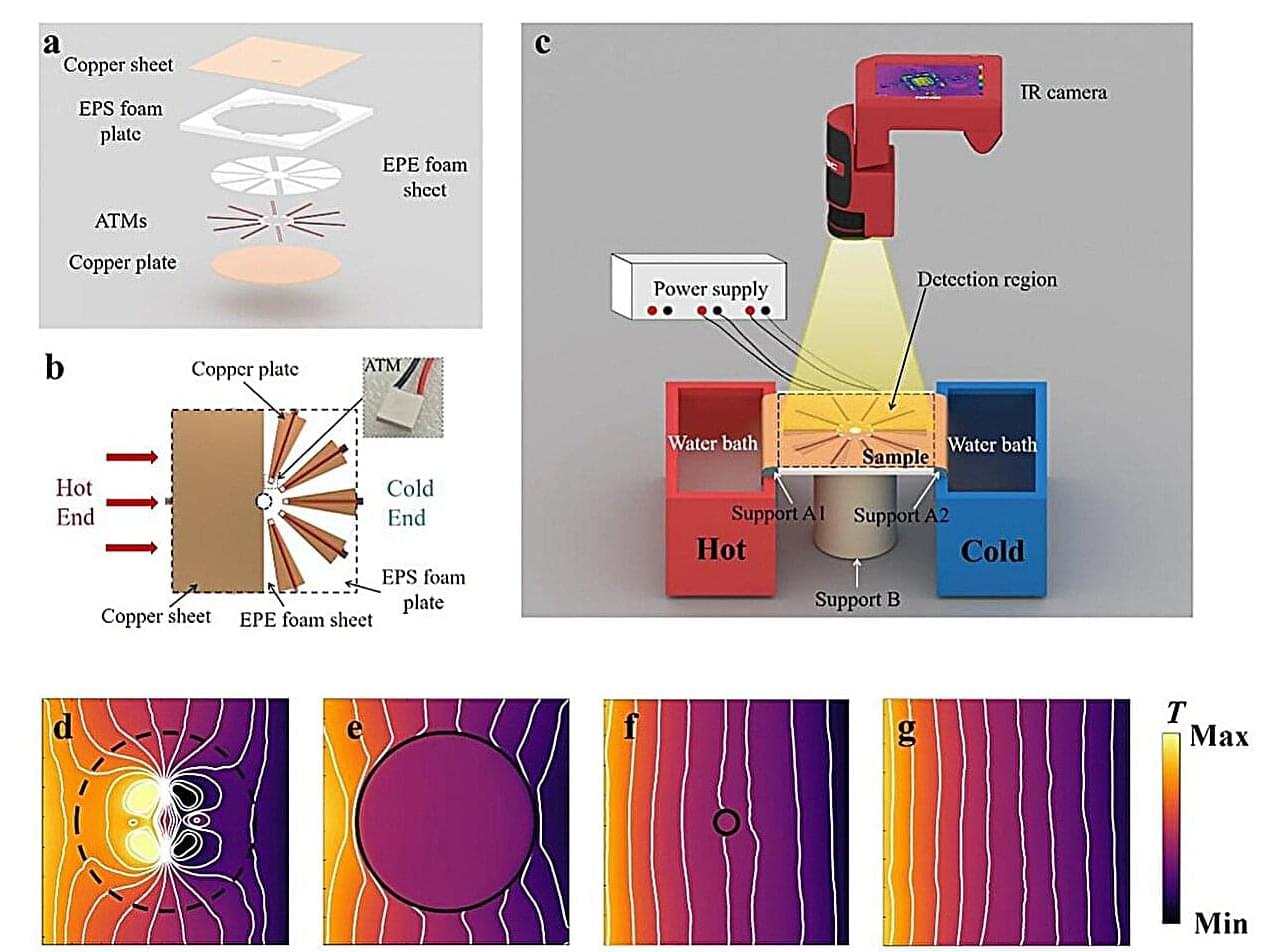
Light undergoes a unique phenomenon called superscattering, an optical illusion where a very small object scatters far more light than expected. This happens when multiple scattering modes overlap and interact, allowing tiny objects to scatter far more light than their size should allow.
Scientists have now found a way to expand the scope of superscattering beyond optics into the thermal world.
A team of researchers from Taiyuan University of Technology, China, has experimentally demonstrated thermal superscattering by surrounding an object with an active shell comprising arrays of controllable heating and cooling elements along its boundary. This shell allowed the tiny object to fake the thermal signatures of an object nine times larger than itself.
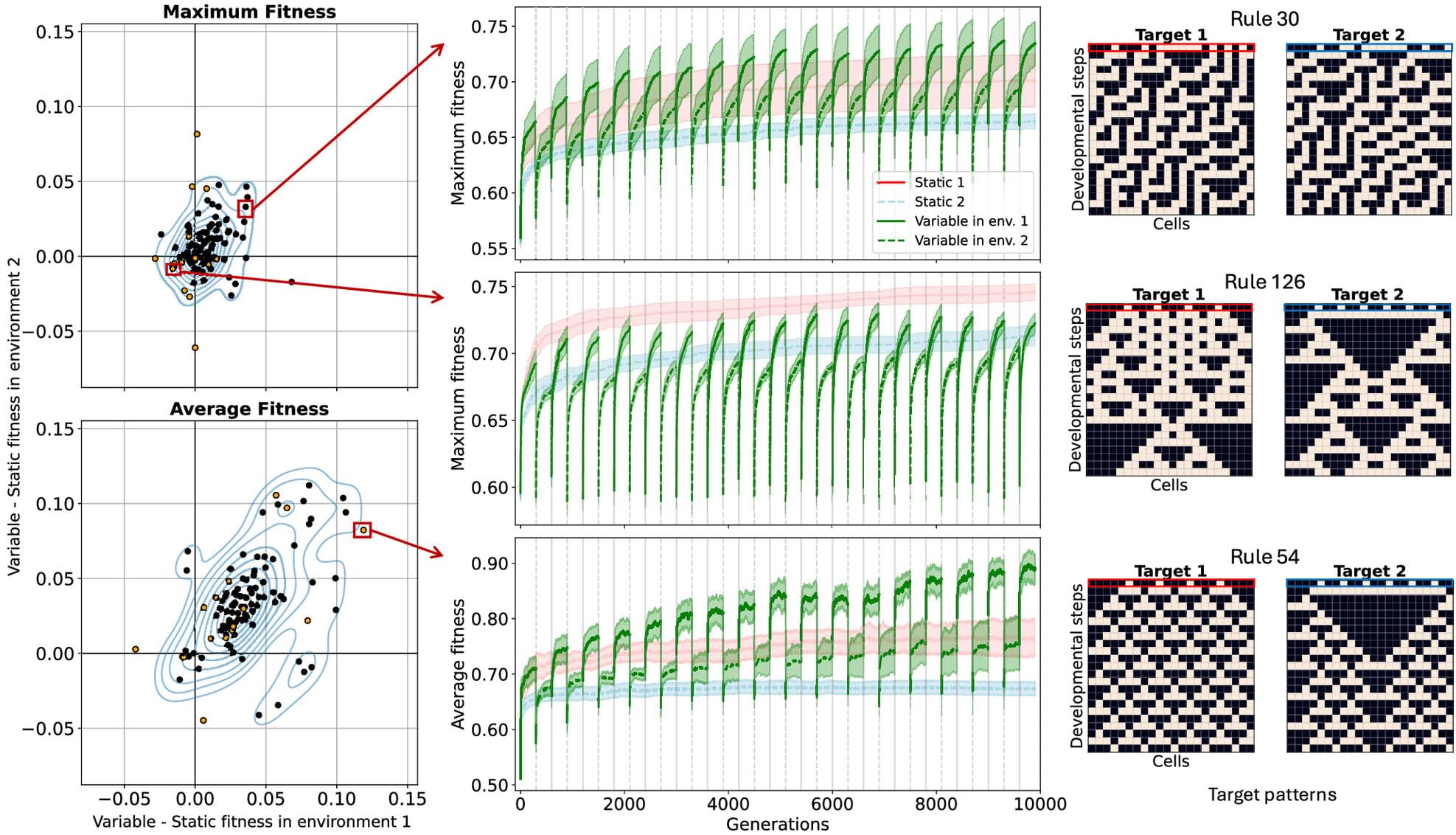
Every living being must cope with a changing world—summer gives way to winter, one year it floods and the next is a drought. It’s obvious that populations of plants and animals must constantly face new challenges, says University of Vermont scientist Csenge Petak. But what’s not obvious is how these changes in the environment affect evolution.
“Do populations benefit from lots of environmental fluctuations, making new generations more prepared to face future changes,” she wondered, “or are they impaired, forced to readapt again and again, never reaching the heights of fitness that the same populations in a stable environment could achieve?”
To explore this question, she and University of Vermont computer scientist Lapo Frati—as well as two other UVM researchers and one at the University of Cambridge—developed a first-of-its-kind study using a powerful computer model that tracks thousands of generations of digital organisms.



A new campaign dubbed ‘GhostPoster’ is hiding JavaScript code in the image logo of malicious Firefox extensions with more than 50,000 downloads, to monitor browser activity and plant a backdoor.
The malicious code grants operators persistent high-privilege access to the browser, enabling them to hijack affiliate links, inject tracking code, and commit click and ad fraud.
The hidden script is acting as a loader that fetches the main payload from a remote server. To make the process more difficult to detect, the payload is intentionally retrieved only once in ten attempts.
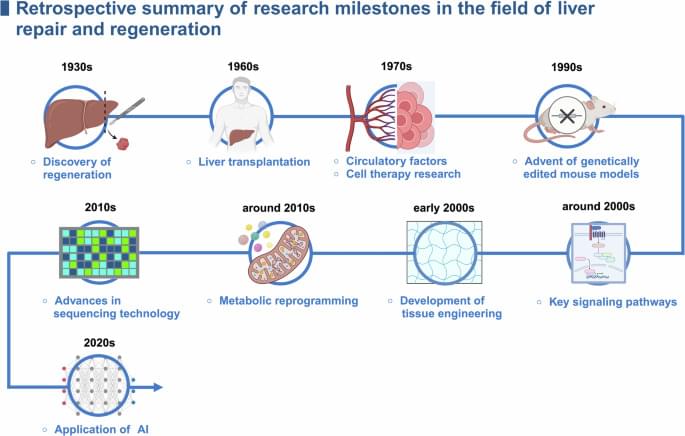
Ma, X., Huang, T., Chen, X. et al. Molecular mechanisms in liver repair and regeneration: from physiology to therapeutics. Sig Transduct Target Ther 10, 63 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-024-02104-8
