Research shows a high-magnesium diet could slow brain aging and lower dementia risk.
A study from the Australian National University shows that increased magnesium intake may help protect against age-related brain decline, particularly benefiting women.
Researchers analyzed data from over 6,000 participants aged 40–73, tracking their dietary magnesium consumption and its effects on brain volume and white matter lesions. Those consuming more than 550 mg of magnesium daily had brains appearing nearly a year younger by age 55 compared to those with lower intake.
The study also found that postmenopausal women experienced the greatest neuroprotective benefits, possibly due to magnesium’s anti-inflammatory properties.
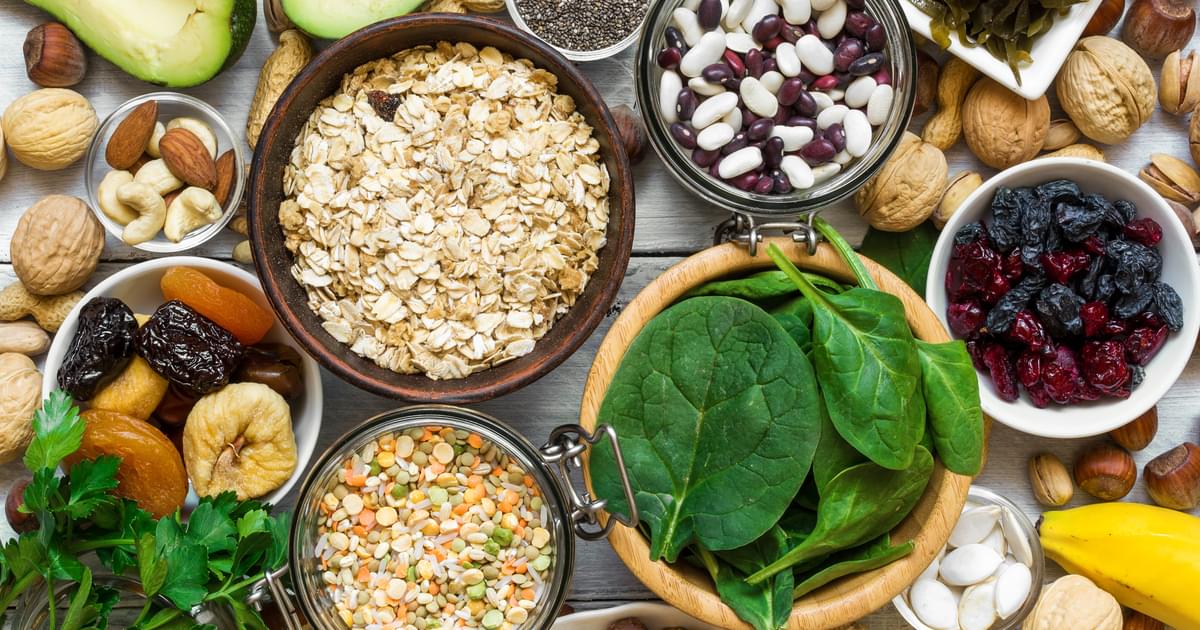
Magnesium, found in foods like leafy greens, nuts, seeds, legumes, and whole grains, has long been known for its health benefits, but this research highlights its potential role in dementia prevention. With no cure for dementia, experts stress the importance of dietary strategies for brain health.
Study co-author Dr. Erin Walsh emphasizes the need for further research to confirm these findings and inform public health recommendations. Given the rising global prevalence of dementia, this study underscores the importance of modifiable lifestyle factors in reducing cognitive decline and promoting long-term brain health.