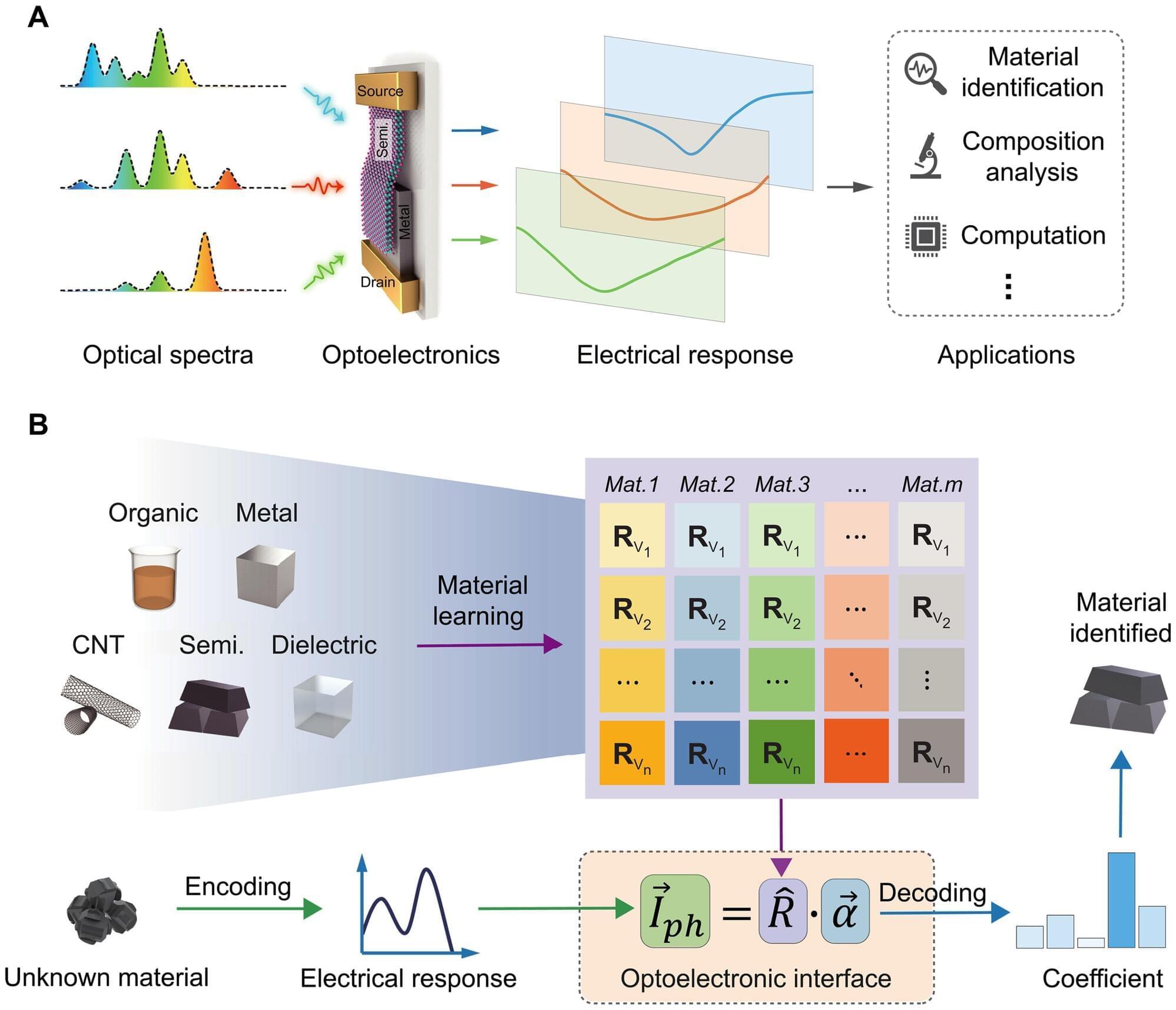
He has written five well received books on consciousness and developed the Global Neural Workspace model of Consciousness What follows bellow are some of Professor Baars’ observations, Questions (often rhetorical), Quotations, comments, reflections on career and his own theories and my comments (RS) to them as posted to LinkedIn platform. Bernard’s text is in italics. Comments to comments are indicated with ‘BB]’ and responses to those with ‘RS]’. ======== ======== ======== t aware of. ‘ +In the case of non-human animals, we have to get a little bit more creative. We have to decide what behaviors can be used similar sorts of markers as their own form of report.” — David Edelman RS] Or we could ask ~ “is the form of communication between animals sufficient for their needs?” and follow up with “is there Evolutionary Pressure for forms of communication beyond utility?” Those who follow discussion forums may appreciate that what takes an excited discussant 10 paragraphs and 1,000 flaming words can be achieved by a dog with a couple barks and the bearing of teeth ~ which is the more efficient communicative format? BB] Humans seem to have a larger repertoire of uses for consciousness — including language and longer-term planning, self-monitoring and self-reflection, inner speech, metaphor, symbolic representation of experience and deliberate use of imagery. When it comes to sensory consciousness, however, the brain shows little difference between humans and many other mammals. RS] Utility is the key ~ what are those faculties good for? Take them away, individually, and see what we end up with. As such surgical or other intervention is not a practical option we might turn to clinical conditions where patients have such deficits. We may look to Autism, where self reflection, especially in the social context, is lacking. Psychopathy, where there is no inner voice reflecting on social morals. Various other deficits leave individuals with greatly reduced capacity to strive in a community and so we may reflect on the many cognitive faculties we have that appear to have little if any use for the isolated individual. To test this we may examine those who were completely isolated for a significant period of their maturation. There have been cases of children lost in the forest (or dumped there) who survived. Without social stimulation some of heir faculties never matured ~ are these the same faculties that Bernard mentions above? BB] Perhaps half a second after you glance at a word on a page it is converted into a semantic code, to interpret its meaning, guided by the rules of grammar. Going from words to meaning requires a large, unconscious mental lexicon. The lexicon of educated speakers of English contains about 100,000 words. We can understand each one instantly, as soon as it is shown in a sentence that makes sense. Words are complicated things! The OxfordEnglish Dictionary, for example, devotes 75,000 words to clarifying the many different meanings of the word set. RS] The way words are interpreted gives us insight into the how the brain works. If approached in the follow manner we can see what is happening: For each noun there is a denotation and a connotation (the cold dictionary definition and the feeling the word evokes eg ‘Home’). There is a stand alone and contextual meaning of a word that may differ significantly eg “child” and “What are parent-child tree structures in SQL?” The ‘connotation’ is used by the brain to link words into sentences more so than the denotation. If there is a universal background language in the brain, then, it would be based on connotation, not denotation. Why? Because the connotation is innate already and words are appended to pre-existing ‘connotation’ made up of emotion, drives, feelings of all kinds. Watch a child as they acquire their first words ~ they at first use all kinds of signals to convey their intent, their intent is made up of drives, cravings, feelings etc and these become the connotations behind the words they eventually use. s BB] How does the metaphor of a theater help us think about consciousness? RS] The key to many of these approaches, and possible the downfall of at least some of them, is ‘evolvability’. We assume, from our own intuitive experience and logical deduction, that there must be a primary central control. This is a ‘top-down’ approach. But evolution must, by necessity, be ‘bottom-up’. Thus we would expect even the simplest ganglion to have at least some of the properties of consciousness in its own right. Snakes that must rely on different ‘consciousnesses’ for various functions, for instance the pursuing of prey, the killing of prey and the eating of the prey all come from processes so separate that if a mouse after a poisonous bite staggers around and ends up under the snake’s nose the snake will follow the scent trail until it ends up at the mouse, the visual and feeding systems not being able to share information. That system is evolvable, the top-down, apart from religious models, is not evolvable. Thus instead of a separate central process looking down at the senses we consider how the senses and other contributors to cognition swirl together like the funnel of a tornado to form a central consciousness that, in reality, has no independent neural underpinnings of its own due to its emergent nature. Note that ‘life’ also has this nature in that life exists when a collection of chemical reactions ‘swirl’ together, principally in a negative feedback driven homeostatic process, which is most probably also what consciousness actually is… And so we observe how the tornado’s funnel moves around the possible contributors, the audience in the analogy given, rather than a separate process that looks at individual members of the audience. Note that the separate process must consume the information on offer and process it, a ‘infinite regress’ with no end. But the swirling tornado, so to speak, is its own end and does not require any subsequent processes or processing… Note also that any collection of neurons, brain modules or even collections or communities of people can initiate this process.
This link will take you to a page that’s not on LinkedIn.