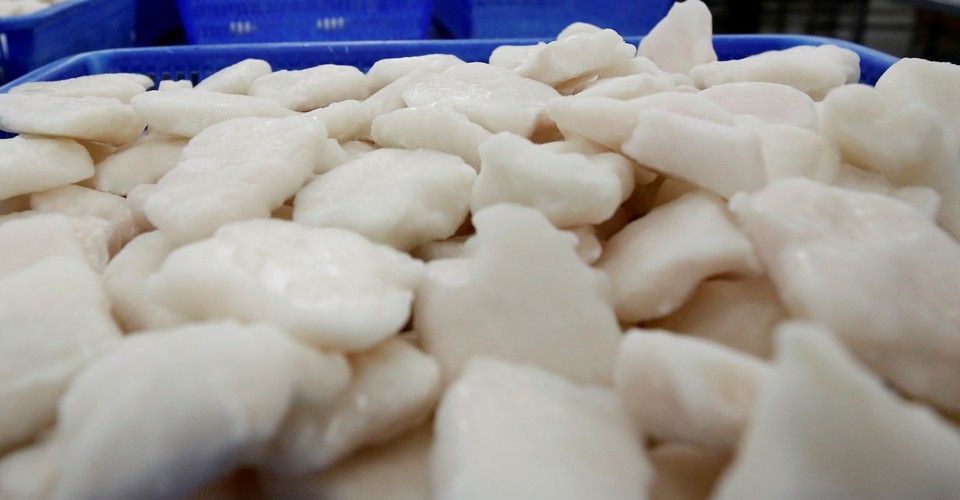
Summary: Helminthic therapy is the intentional consumption of parasites as a treatment for autoimmune disease. Out of the 7000 people who practice helminthic therapy each year, this report tells the story of a young woman who purchases black market worms and then treats herself at a high cost. Part 2 of a 2-part series. Cover photo: Eraxion / Getty Images.
Would you eat worms to boost your overall health or cure what ails you?
Over 7,000 people intentionally self-infect with parasites, and the practice is growing in popularity.