As edible, affordable lab-grown meat remains out of reach, a tiny start-up might have found a faster route to dinner tables.
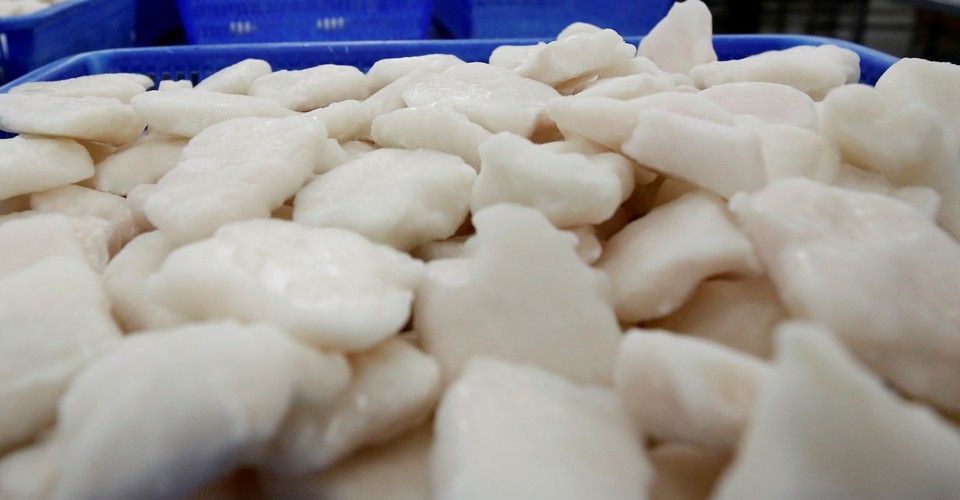


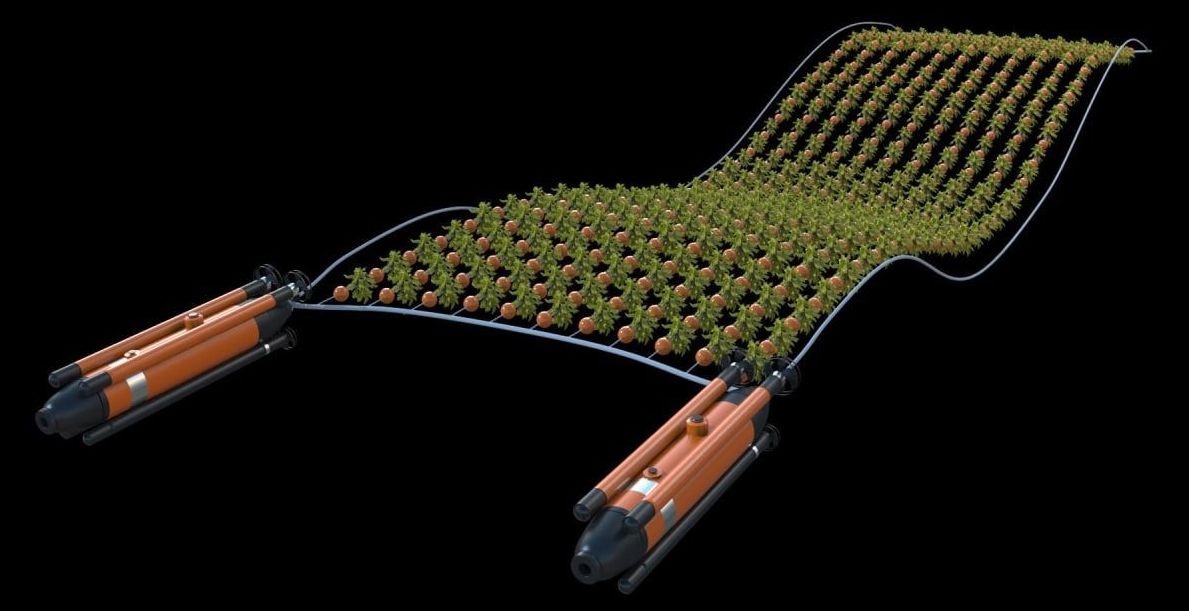
Proof that traditional farms can be 100% automated already.
This is as autonomous as farming gets, without any humans having to get themselves dirty, or even go outside.



How can we tell if a drink is beer or wine? Machine learning, of course! In this episode of Cloud AI Adventures, Yufeng walks through the 7 steps involved in applied machine learning…
The world is filled with data. Lots and lots of data. Everything from pictures, music, words, spreadsheets, videos and more. It doesn’t look like it’s going to to slow down anytime soon. Machine learning brings the promise of deriving meaning from all of that data.
From detecting skin cancer, to sorting cucumbers, to detecting escalators in need of repairs, machine learning has granted computer systems entirely new abilities.

Now a long lasting ice cream which does not melt soon is available and being sold in Japan, which is scientifically proven.
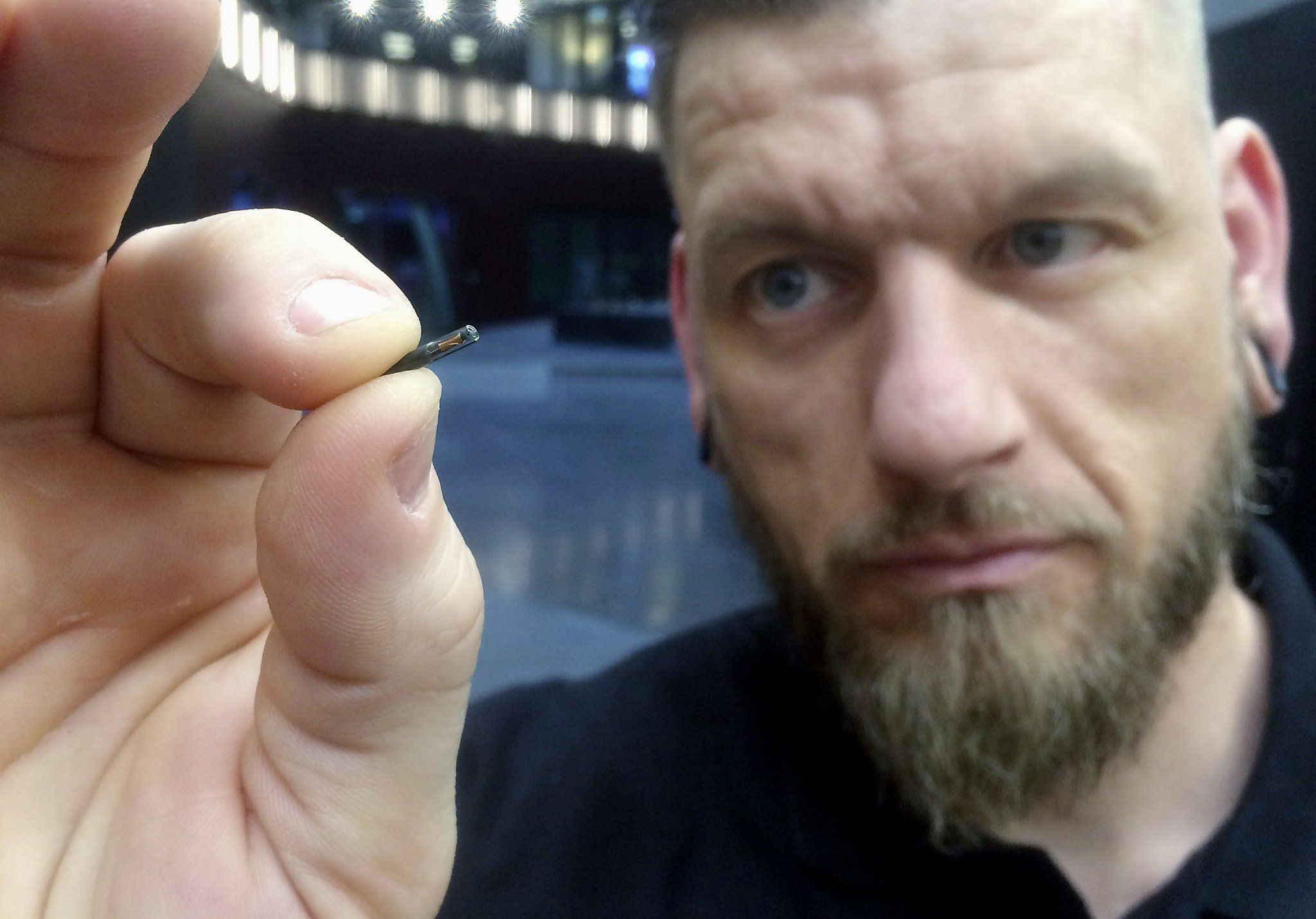

My new Op-Ed for The San Francisco Chronicle: http://www.sfchronicle.com/opinion/openforum/article/Chip-im…003194.php #transhumanism
Wisconsin company Three Square Market recently announced it will become the first U.S. company to offer its employees chip implants that can be scanned at security entrances, carry medical information and even purchase candy in some vending machines. A company in Europe already did this last year.
For many people, it sounds crazy to electively have a piece of technology embedded in their body simply for convenience’s sake. But a growing number of Americans are doing it, including me.
I got my RFID implant two years ago, and now I use it to send text messages, bypass security codes on my computer, and open my front door. Soon I’ll get the software to start my car, and then my life will be totally keyless.
The type of chip implants in humans varies depending on the manufacturer or purpose of the device. A few hundred thousand people around the world have cochlear implants, which allow deaf people to hear. Others have implants to help with Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s or even depression. A growing number of transhumanists — people who want to use radical technology in their bodies — have the $60 implant I have. It’s tiny, about the size of a grain of rice, and is injected into the body by a syringe. The injection process — usually in the hand near the thumb — is often bloodless and takes seconds to complete.