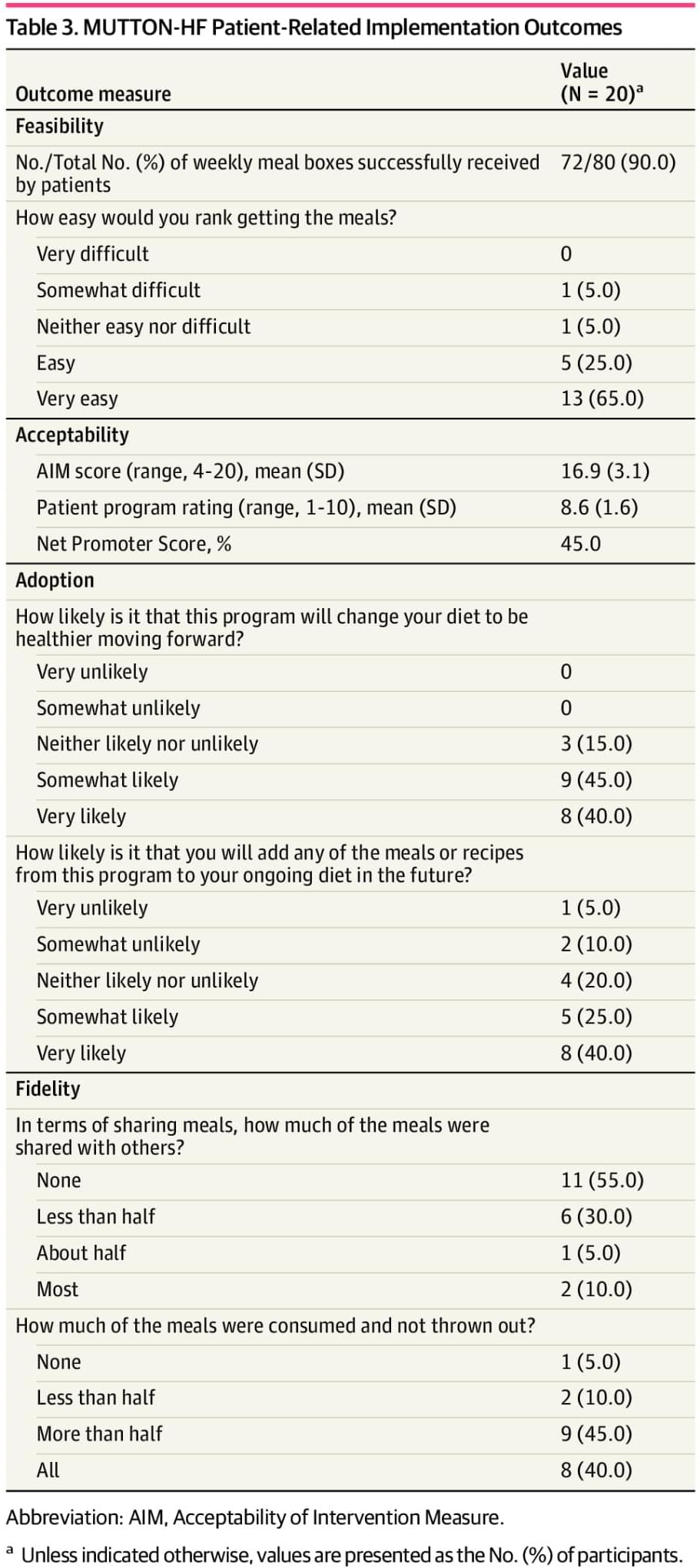
A new study by researchers at Kiel University and MPI-EvolBio describes how more efficient protein production drives the adaptation of fungi to the human body, potentially turning previously harmless species into emerging pathogens. In the wake of global change and the associated rise in temperatures, fungal infections are on the increase worldwide, threatening crops, wildlife and, also, human health. Many fungal species are completely harmless and fulfill important ecological functions, such as decomposing organic matter and releasing nutrients into the soil.
As symbionts of multicellular organisms, they perform useful functions for their host. On the other hand, some species are so-called opportunistic human pathogens: particularly in a weakened immune system, such fungi can colonize the body and cause serious and even life-threatening infections.
While fungi are often studied as pathogens of crops at institutions such as Kiel University and the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Biology in Plön (MPI-EvolBio), researchers are increasingly turning their attention to their harmful effects on humans. A research team led by Professor Eva Stukenbrock, head of the Environmental Genomics group at Kiel University and MPI-EvolBio, has conducted a new study to investigate why certain fungi might become human pathogens in the course of global change. To this end, the researchers analyzed various fungal species of the order Trichosporonales, which includes both harmless and dangerous species for humans.