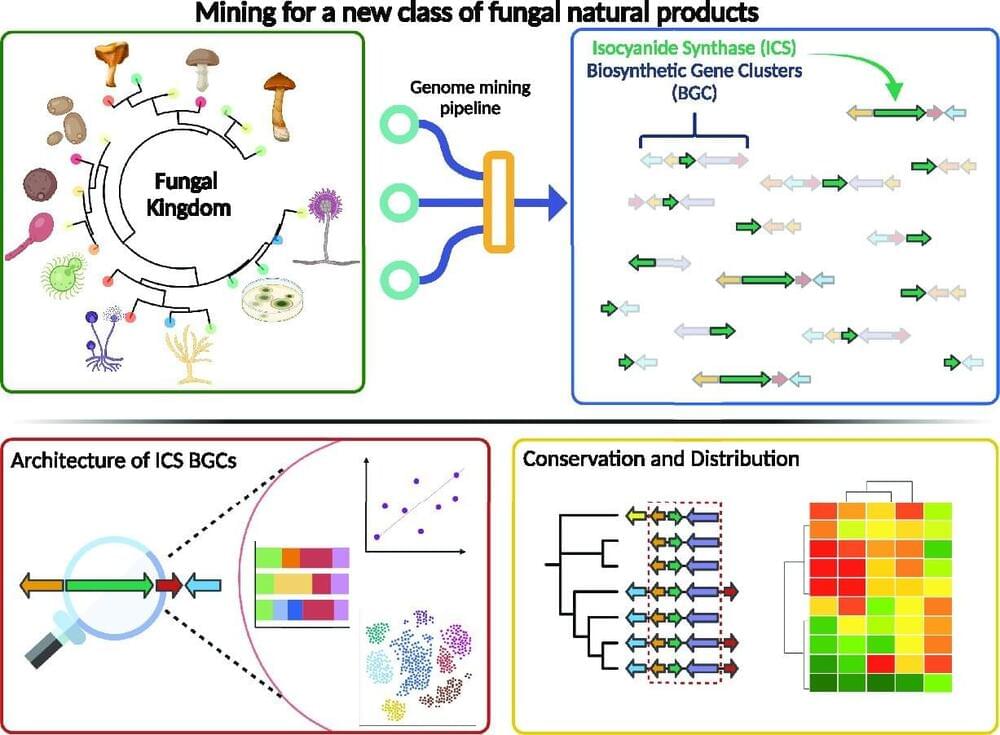
A newly described type of chemistry in fungi is both surprisingly common and likely to involve highly reactive enzymes, two traits that make the genes involved useful signposts pointing to a potential treasure trove of biological compounds with medical and chemical applications.
It was also nearly invisible to scientists until now.
In the last 15 years, the hunt for molecules from living organisms—many with promise as drugs, antimicrobial agents, chemical catalysts and even food additives—has relied on computer algorithms trained to search the DNA of bacteria, fungi and plants for genes that produce enzymes known to drive biological processes that result in interesting compounds.