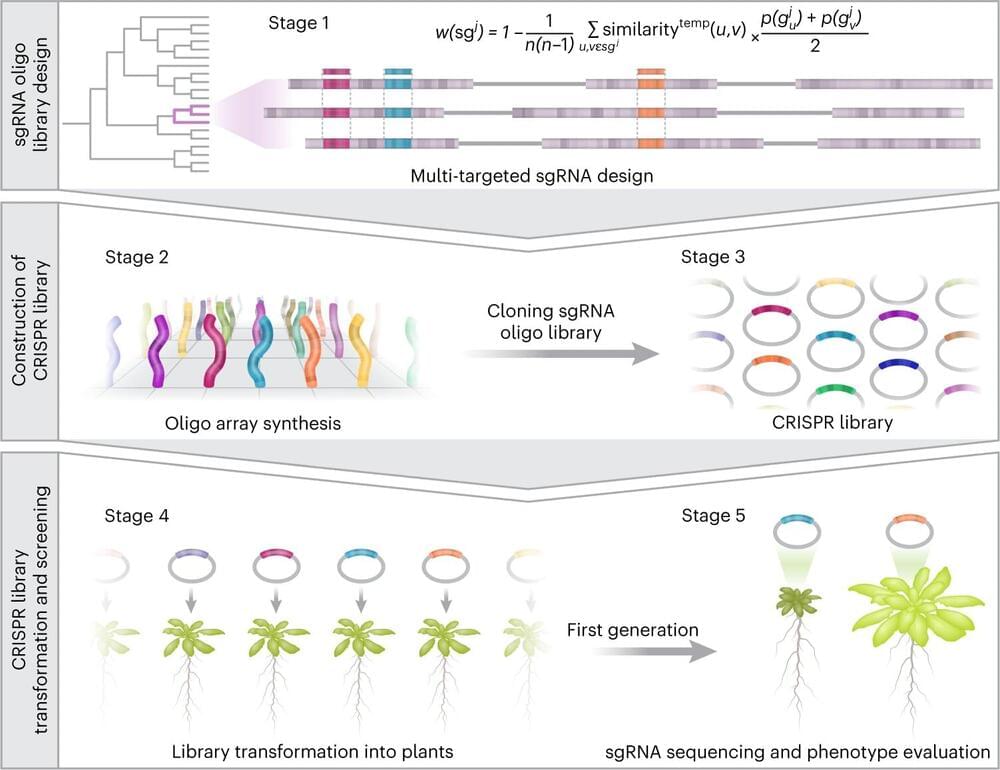
For the first time, researchers from Tel Aviv University have developed a genome-scale technology that makes it possible to reveal the role of genes and traits in plants previously hidden by functional redundancy.
The researchers point out that since the agricultural revolution, man has improved plant varieties for agricultural purposes by creating genetic diversity. But until this recent development, it was only possible to examine the functions of single genes, which make up only 20% of the genome. For the remaining 80% of the genome, made up of genes grouped in families, there was no effective way, on the large scale of the whole genome, to determine their role in the plant.
As a result of this unique development, the team of researchers managed to isolate and identify dozens of new features that had been overlooked until now. The development is expected to revolutionize the way agricultural crops are improved as it can be applied to most crops and agricultural traits, such as increased yield and resistance to drought or pests.