“Part of the atmosphere of this planet is moving towards us at a high velocity while another part is moving away from us at the same speed,” said Dr. Lisa Nortmann.
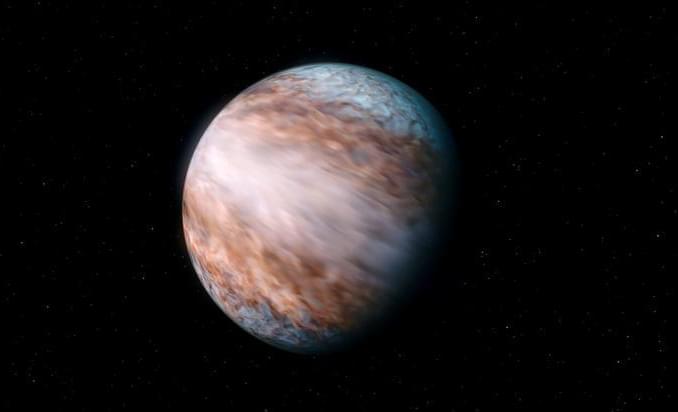
Do weather patterns on exoplanets mimic those on Earth? This is what a recent study published in Astronomy & Astrophysics hopes to address as an international team of researchers explored unique weather patterns on WASP-127b, which is a hot Jupiter exoplanet located approximately 520 light-years from Earth. This study has the potential to help scientists better understand the formation and evolution of weather patterns on exoplanets throughout the cosmos and how these patterns compare to Earth’s.
For the study, the researchers used the CRyogenic high-resolution InfraRed Echelle Spectrograph (CRIRES+) instrument installed on the European Southern Observatory’s (ESO) Very Large Telescope (VLT) to observe the atmospheric characteristics during one transit of WASP-127b passing in front of its parent star, with one orbit being completed in approximately 4.2 days.
In the end, the researchers identified signals of water (H2O) and carbon monoxide (CO) within WASP-127b’s atmosphere, along with identifying supersonic jet winds occurring at the exoplanet’s equator estimated to be traveling at approximately 7.7 kilometers per second (4.8 miles per second) or 27,720 kilometers per hour (17,280 miles per hour). These winds were identified to only exist at the equator and not at the poles. For context, the fastest winds recorded at the Earth’s equator is only a few kilometers (miles) per hour. They also found significant temperatures differences between the dayside and night side of WASP-127b, which mimics planetary atmosphere behavior of Earth and other planets in our solar system.