Could tiny grains from asteroid Bennu unlock the secrets of life in our solar system?
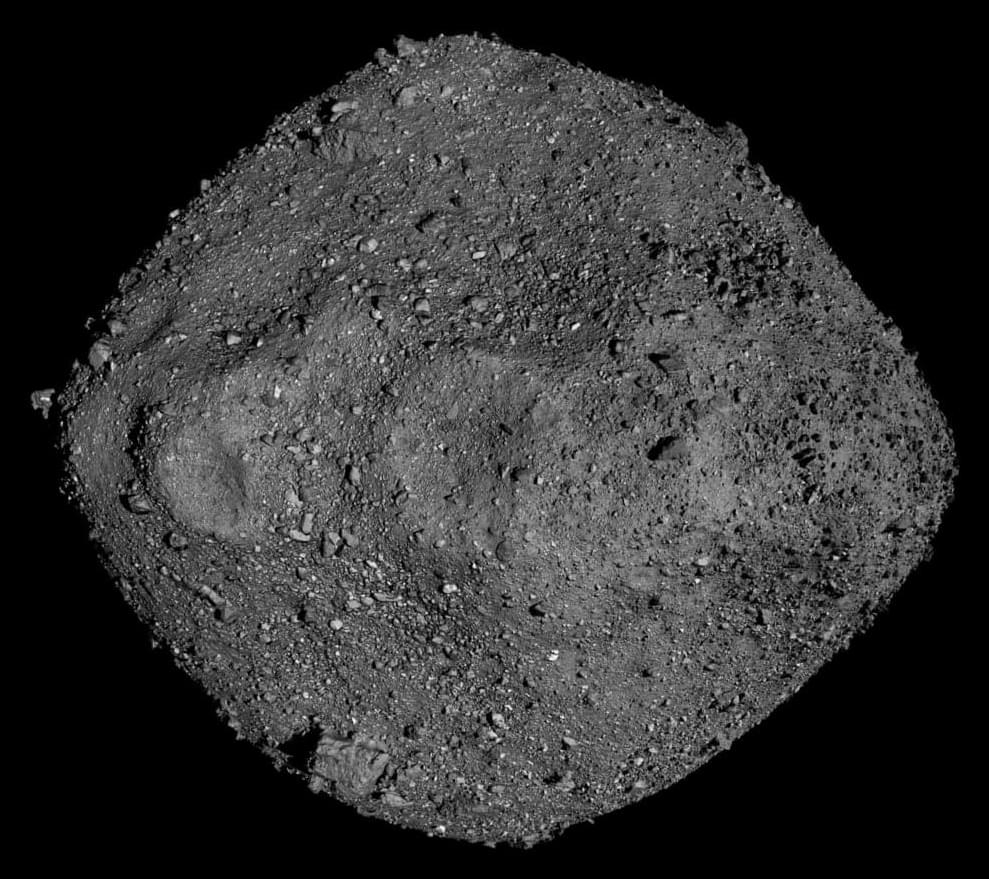
Does life exist beyond Earth and have the building blocks of life existed in our solar system for billions of years? This is what a recent study published in Nature Astronomy hopes to address as a team of international researchers analyzed dust samples obtained from the asteroid Bennu, which is hypothesized to have broken off from a larger parent body, to ascertain if it contains the building blocks of life as we know it. This study has the potential to help scientists better understand the early conditions of the solar system, along with the formation and evolution of the planets and moons that comprise it, as well.
For the study, the researchers used a transmission electron microscope at Goethe University to analyze grains that were part of the 122 grams (0.27 pounds) of dust samples returned to Earth by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission in September 2024. The goal of the study was to ascertain what components comprise Bennu, which existed since the early days of the solar system more than 4 billion years ago.
In the end, the researchers identified greater amounts of nitrogen, carbon, and ammonia than were obtained from asteroid Ryugu by Japan’s Hayabusa2 spacecraft in 2020. Additionally, this study identified 14 of the 20 amino acids that comprise Earth-based biology, along with all five nucelobases that comprise DNA and RNA. These findings indicate that the building blocks of life potentially existed in the solar system billions of years ago and could comprise some of the planetary bodies of astrobiological interest today, including Saturn’s moon Enceladus and dwarf planet Ceres.