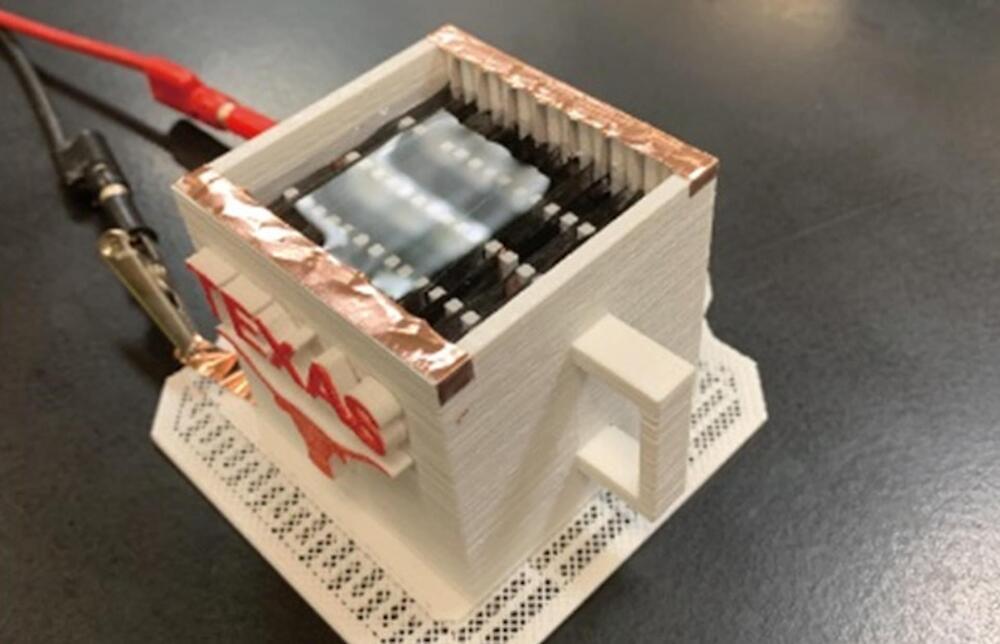
A researcher at The University of Texas at Austin has developed a mug-sized device that can clean water using only a small jolt of electricity. The device could be used to help get drinking water to people left stranded by extreme weather events.
Dr. Donglei “Emma” Fan — an associate professor in the Walker Department of Mechanical Engineering at the Cockrell School of Engineering — along with her research team, was able to create the device using a specially designed “branched” electrode, now patented.
The electrode, when electrified, created a field that E. coli and other bacterial cells are attracted to, causing them to “swim” into the electrode branches. In lab experiments, the device successfully removed 99.997% of E. coli bacteria from water samples in just 20 minutes.