As transistors are made ever tinier to fit more computing power into a smaller footprint, they bump up against a big problem: quantum mechanics. Electrons get jumpy in small devices and leak out, which wastes energy while degrading performance. Now a team of researchers is showing that it doesn’t have to be that way. With careful engineering, it’s possible to turn electrons’ quantum behavior into an advantage.
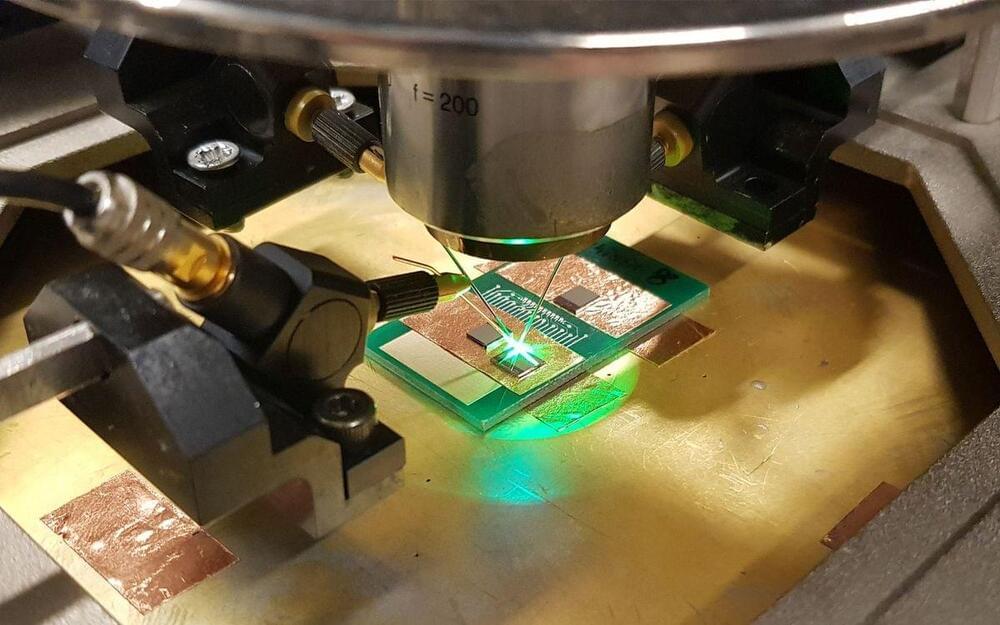
A team of English, Canadian, and Italian researchers have developed a single-molecule transistor that harnesses quantum effects. At low temperatures, the single-molecule device shows a strong change in current with only a small change in gate voltage, nearing a physical limit known as the sub-threshhold swing. Getting near or beyond this limit will allow transistors to be switched with lower voltages, making them more efficient and generating less waste heat. The research team, including physicists at Queen Mary University of London, achieved this by taking advantage of how quantum interference alters the flow of current in single molecules.
“We’ve demonstrated, in principle, that you can use destructive quantum interference for something useful.” —Jan Mol, Queen Mary University of London.