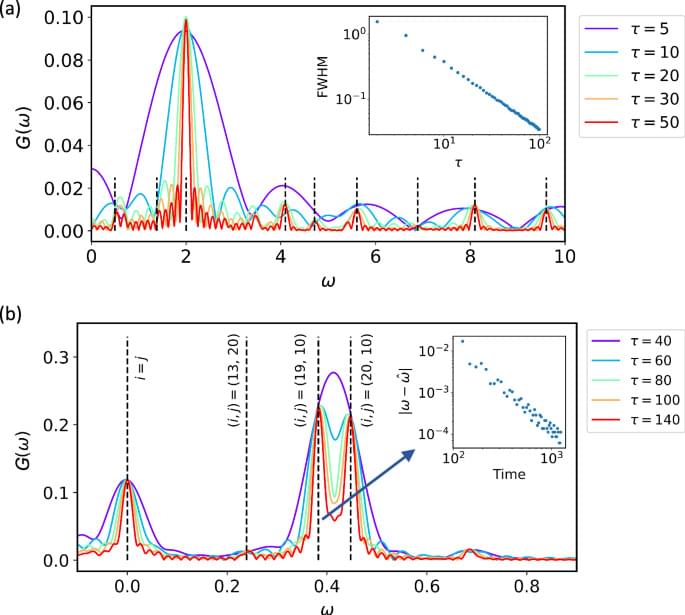
To test this new system, the team executed what is known as Grover’s search algorithm—first described by Indian-American computer scientist Lov Grover in 1996. This search looks for a particular item in a large, unstructured dataset using superposition and entanglement in parallel. The search algorithm also exhibits a quadratic speedup, meaning a quantum computer can solve a problem with the square root of the input rather than just a linear increase. The authors report that the system achieved a 71 percent success rate.
While operating a successful distributed system is a big step forward for quantum computing, the team reiterates that the engineering challenges remain daunting. However, networking together quantum processors into a distributed network using quantum teleportation provides a small glimmer of light at the end of a long, dark quantum computing development tunnel.
“Scaling up quantum computers remains a formidable technical challenge that will likely require new physics insights as well as intensive engineering effort over the coming years,” David Lucas, principal investigator of the study from Oxford University, said in a press statement. “Our experiment demonstrates that network-distributed quantum information processing is feasible with current technology.”