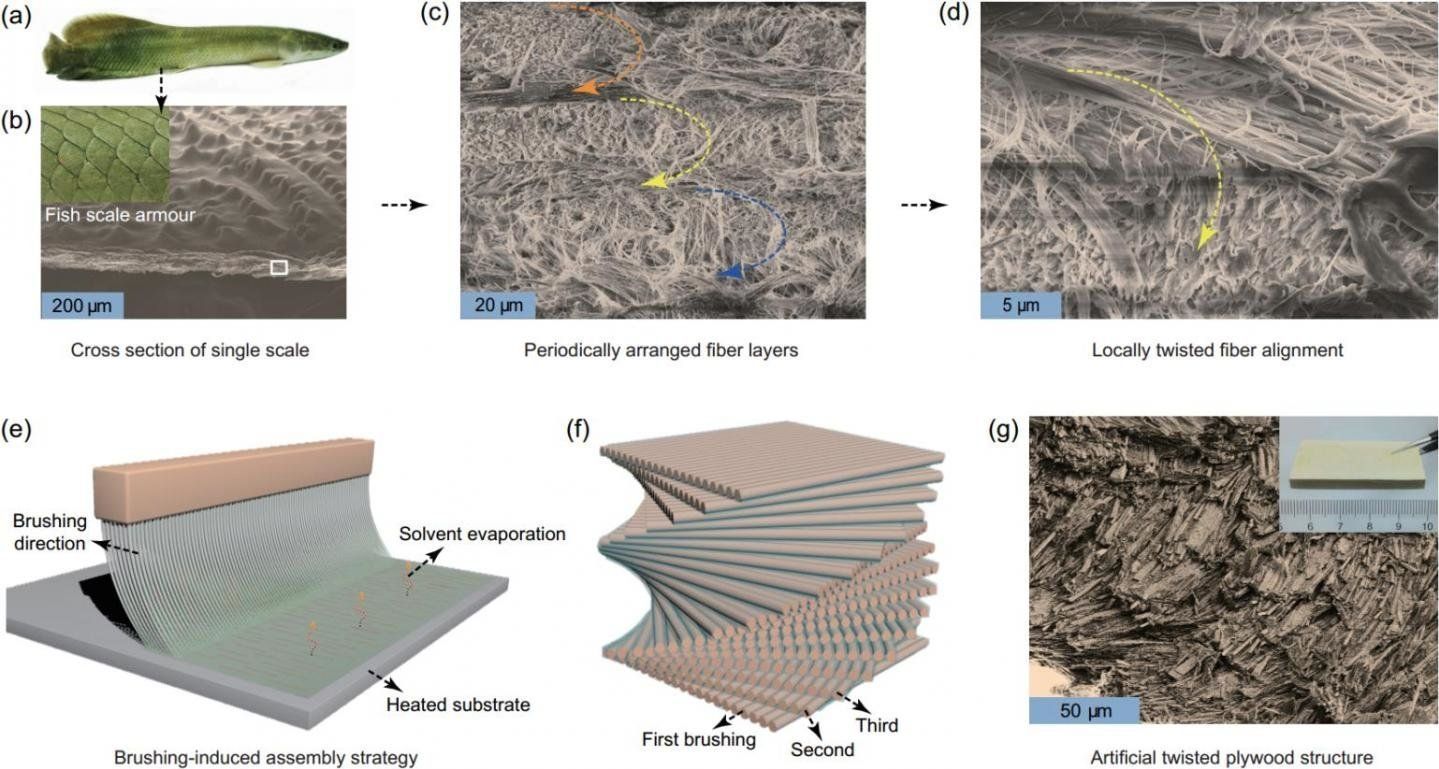
Over hundreds of millions of years of evolution, nature has produced a myriad of biological materials that serve either as skeletons or as defensive or offensive weapons. Although these natural structural materials are derived from relatively sterile natural components, such as fragile minerals and ductile biopolymers, they often exhibit extraordinary mechanical properties due to their highly ordered hierarchical structures and sophisticated interfacial design. Therefore, they are always a research subject for scientists aiming to create advanced artificial structural materials.
Through microstructural observation, researchers have determined that many biological materials, including fish scales, crab claws and bone, all have a characteristic “twisted plywood” structure that consists of a highly ordered arrangement of micro/nanoscale fiber lamellas. They are structurally sophisticated natural fiber-reinforced composites and often exhibit excellent damage tolerance that is desirable for engineering structural materials, but difficult to obtain. Therefore, researchers are seeking to mimic this kind of natural hierarchical structure and interfacial design by using artificial synthetic and abundant one-dimensional micro/nanoscale fibers as building blocks. In this way, they hope to produce high-performance artificial structural materials superior to existing materials.