Scientists from CiQUS, ICN2, University of Cantabria, DIPC and DTU join forces to develop a versatile method for building brick-by-brick carbon nanocircuits with tunable properties.
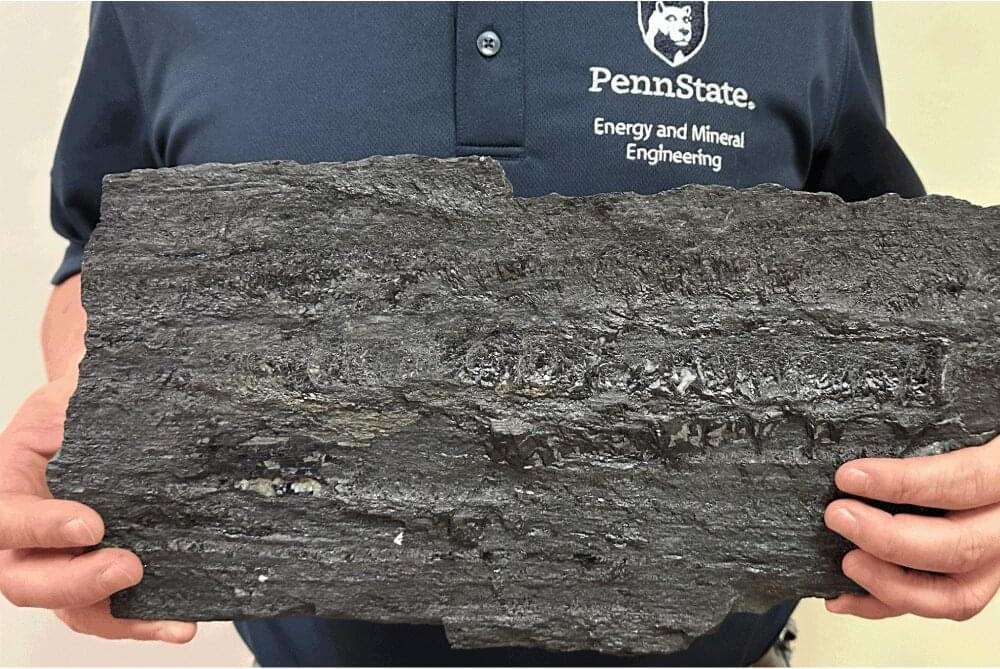



The quest to develop hydrogen as a clean energy source that could curb our dependence on fossil fuels may lead to an unexpected place—coal. A team of Penn State scientists found that coal may represent a potential way to store hydrogen gas, much like batteries store energy for future use, addressing a major hurdle in developing a clean energy supply chain.
“We found that coal can be this geological hydrogen battery,” said Shimin Liu, associate professor of energy and mineral engineering at Penn State. “You could inject and store the hydrogen energy and have it there when you need to use it.”
Hydrogen is a clean burning fuel and shows promise for use in the most energy intensive sectors of our economy—transportation, electricity generation and manufacturing. But much work remains to build a hydrogen infrastructure and make it an affordable and reliable energy source, the scientists said.
The psychedelic substances 5-MeO-DMT causes a long-lasting increase in the number of tiny protrusions called dendritic spines in the brain, according to new research published in Neuropsychopharmacology. The study, which was conducted on mice, sheds light on the behavioral and neural mechanisms of 5-MeO-DMT.
Serotonergic psychedelics (such as psilocybin and LSD) have shown promise as potential therapeutics for mental illnesses like depression and anxiety. Short-acting compounds are particularly interesting because they require less dosing time, which could improve patient access to treatment. In humans, 5-MeO-DMT produces a short-lasting experience due to its rapid breakdown in the body.
“My lab started research on psychiatric drugs like ketamine and psychedelics about 10 years ago. We were motivated by how basic science and clinical research can together powerfully move a drug forward to become medicine. Specifically I believe there is a lot of potential for psychedelics as therapeutics, and that drives our interest in this topic,” said study author Alex Kwan (@kwanalexc), an associate professor in the Meinig School of Biomedical Engineering at Cornell University.
A team of engineers at the University of Massachusetts Amherst has recently shown that nearly any material can be turned into a device that continuously harvests electricity from humidity in the air. The secret lies in being able to pepper the material with nanopores less than 100 nanometers in diameter. The research appeared in the journal Advanced Materials.
“This is very exciting,” says Xiaomeng Liu, a graduate student in electrical and computer engineering in UMass Amherst’s College of Engineering and the paper’s lead author. “We are opening up a wide door for harvesting clean electricity from thin air.”
“The air contains an enormous amount of electricity,” says Jun Yao, assistant professor of electrical and computer engineering in the College of Engineering at UMass Amherst, and the paper’s senior author. “Think of a cloud, which is nothing more than a mass of water droplets. Each of those droplets contains a charge, and when conditions are right, the cloud can produce a lightning bolt—but we don’t know how to reliably capture electricity from lightning. What we’ve done is to create a human-built, small-scale cloud that produces electricity for us predictably and continuously so that we can harvest it.”
After three years of upgrading and waiting, due in part to the coronavirus pandemic, the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-wave Observatory has officially resumed its hunt for the signatures of crashing black holes and neutron stars.
“Our LIGO teams have worked through hardship during the past two-plus years to be ready for this moment, and we are indeed ready,” Caltech physicist Albert Lazzarini, the deputy director of the LIGO Laboratory, said in a news release.
Lazzarini said the engineering tests leading up to today’s official start of Observing Run 4, or O4, have already revealed a number of candidate events that have been shared with the astronomical community.
With the new method, scientists can explore many cancer mutations whose roles are unknown, helping them develop new drugs that target those mutations.
MIT
MIT is an acronym for the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. It is a prestigious private research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts that was founded in 1861. It is organized into five Schools: architecture and planning; engineering; humanities, arts, and social sciences; management; and science. MIT’s impact includes many scientific breakthroughs and technological advances. Their stated goal is to make a better world through education, research, and innovation.
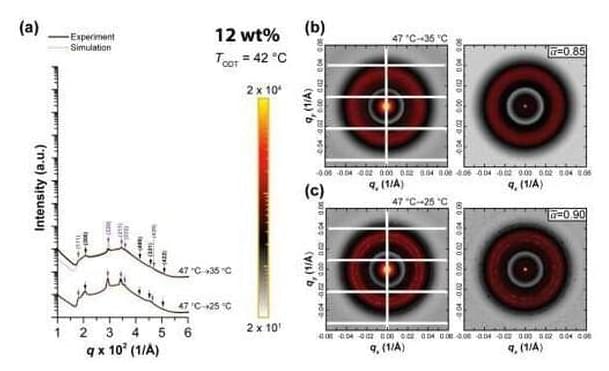
When most people think of crystals, they picture suncatchers that act as rainbow prisms or the semi-transparent stones that some believe hold healing powers. However, to scientists and engineers, crystals are a form of materials in which their constituents—atoms, molecules, or nanoparticles—are arranged regularly in space. In other words, crystals are defined by the regular arrangement of their constituents. Common examples are diamonds, table salt, or sugar cubes.
However, in research just published in Soft Matter, a team led by Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute’s Sangwoo Lee, associate professor in the Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering, discovered that crystal structures are not necessarily always regularly arranged. The discovery advances the field of materials science and has unrealized implications for the materials used for semiconductors, solar panels, and electric vehicle technologies.
One of the most common and important classes of crystal structures is the close-packed structures of regular spheres constructed by stacking layers of spheres in a honeycomb arrangement. There are many ways to stack the layers to construct close-packed structures, and how nature selects specific stacking is an important question in materials and physics research. In the close-packing construction, there is a very unusual structure with irregularly spaced constituents known as the random stacking of two-dimensional hexagonal layers (RHCP). This structure was first observed from cobalt metal in 1942, but it has been regarded as a transitional and energetically unpreferred state.
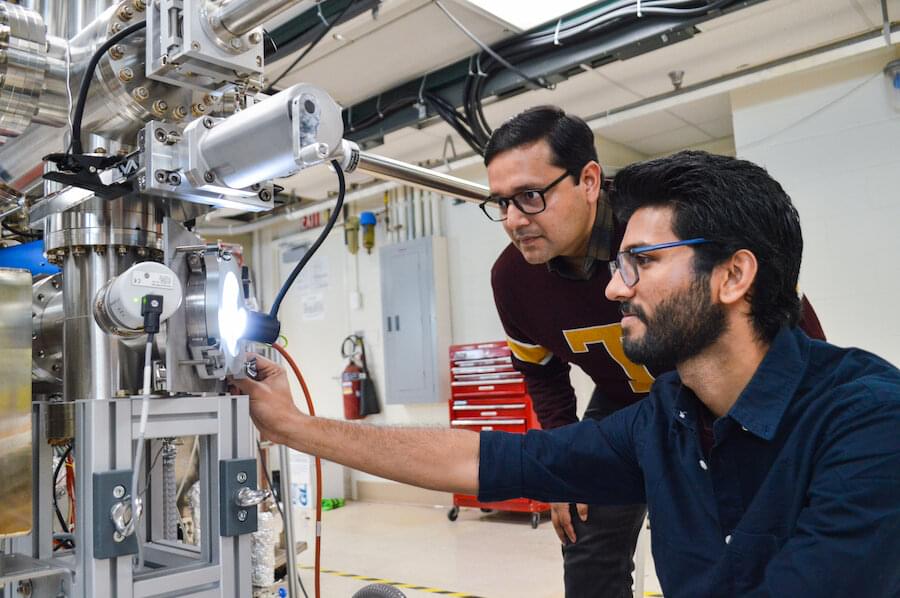

A University of Minnesota Twin Cities-led team has developed a first-of-its-kind, breakthrough method that makes it easier to create high-quality metal oxide thin films out of “stubborn” metals that have historically been difficult to synthesize in an atomically precise manner. This research paves the way for scientists to develop better materials for various next-generation applications including quantum computing, microelectronics, sensors, and energy catalysis.
The researchers’ paper is published in Nature Nanotechnology.
“This is truly remarkable discovery, as it unveils an unparalleled and simple way for navigating material synthesis at the atomic scale by harnessing the power of epitaxial strain,” said Bharat Jalan, senior author on the paper and a professor and Shell Chair in the University of Minnesota Department of Chemical Engineering and Materials Science.
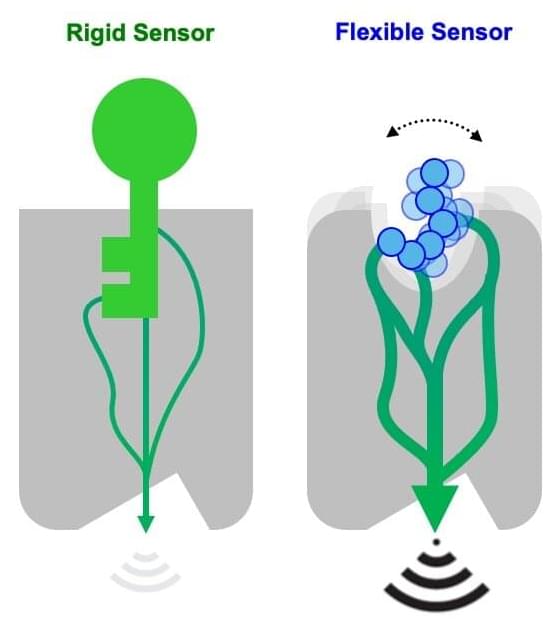
Biosensors are artificial molecular complexes designed to detect the presence of target chemicals or even biomolecules. Consequently, biosensors have become important in diagnostics and synthetic cell biology. However, typical methods for engineering biosensors focus on optimizing the interactions between static binding surfaces, and current biosensor designs can only recognize structurally well-defined molecules, which can be too rigid for “real-life” biology.
“We developed a novel computational approach for designing protein-peptide ligand binding and applied it to engineer cell-surface chemotactic receptors that reprogrammed cell migration,” says EPFL professor Patrick Barth. “We think that our work could broadly impact the design of protein binding and cell engineering applications.”
The new biosensors developed by Barth’s group can sense flexible compounds and trigger complex cellular responses, which open up new possibilities for biosensor applications. The researchers created a computational framework, which is a computer-based system, for designing protein complexes that can change their shape and function dynamically—as opposed to the conventional static approaches. The framework can look at previously unexplored protein sequences to come up with new ways for the protein’s groups to be activated, even in ways that are different to their natural function.
Researchers at the university of chicago.
Founded in 1,890, the University of Chicago (UChicago, U of C, or Chicago) is a private research university in Chicago, Illinois. Located on a 217-acre campus in Chicago’s Hyde Park neighborhood, near Lake Michigan, the school holds top-ten positions in various national and international rankings. UChicago is also well known for its professional schools: Pritzker School of Medicine, Booth School of Business, Law School, School of Social Service Administration, Harris School of Public Policy Studies, Divinity School and the Graham School of Continuing Liberal and Professional Studies, and Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering.