Radiative heat transfer is one of the most critical energy transfer mechanisms in nature. However, traditional blackbody radiation, due to its inherent characteristics, such as its non-directional, incoherent, broad-spectrum, and unpolarized nature, results in energy exchange between the radiating body and all surrounding objects, significantly limiting heat transfer efficiency and thermal flow control. These limitations hinder its practical application.
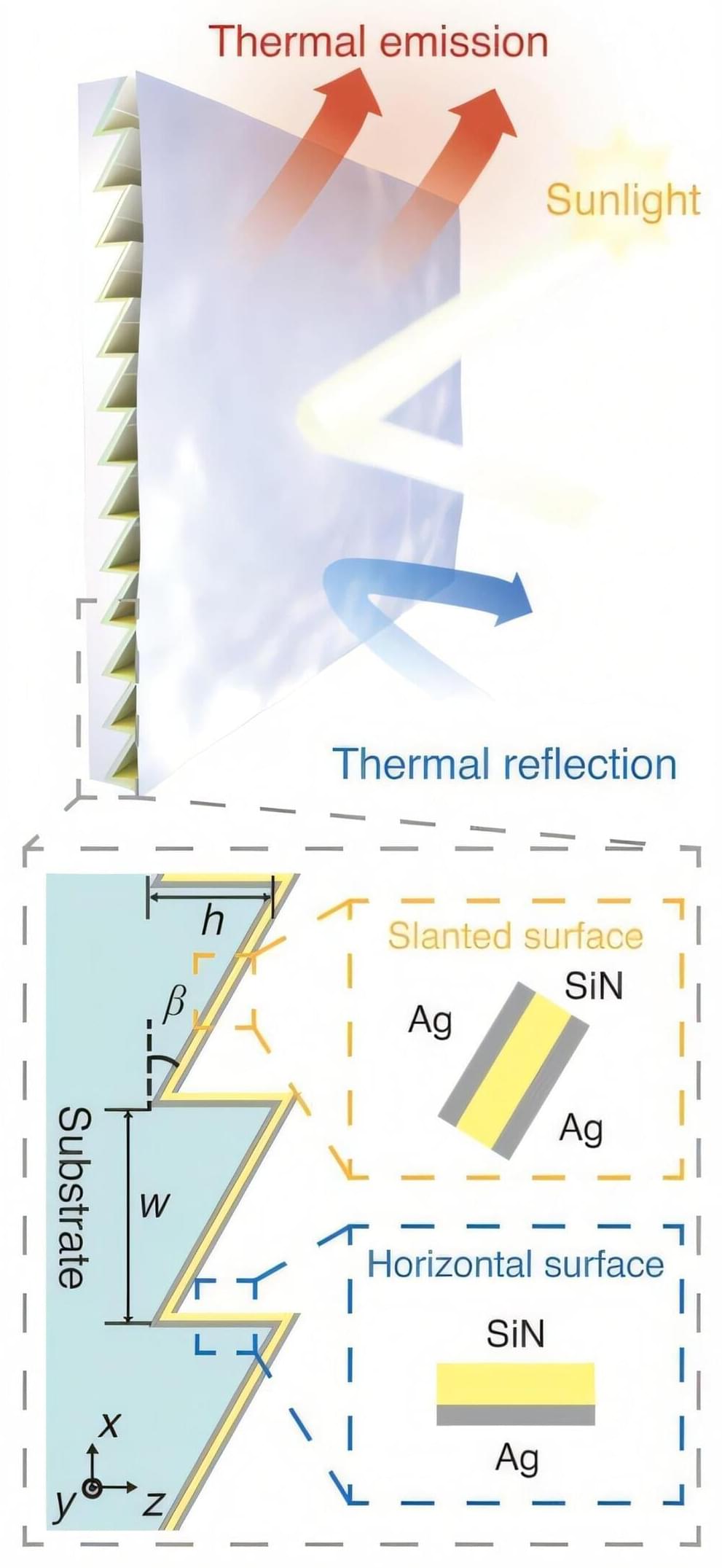
A recent study published in Science utilized thermal photonics to achieve cross-band synergistic control of thermal radiation in both angle and spectrum. The researchers then designed a directional emitter with cross-scale symmetry-breaking, angularly asymmetric and spectrally selective thermal emission, achieving daytime subambient radiative cooling on vertical surfaces.
The research team was led by Prof. Wei Li from the Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics (CIOMP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with Prof. Shanhui Fan’s team from Stanford University and Prof. Andrea Alu’s team from the City University of New York.